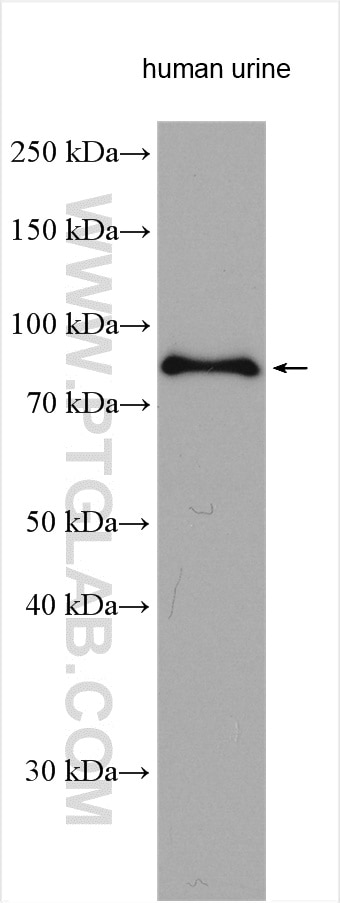
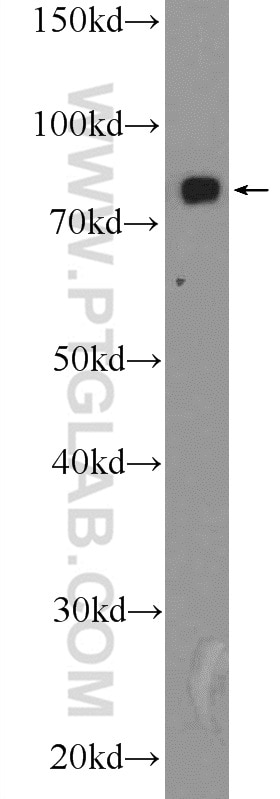
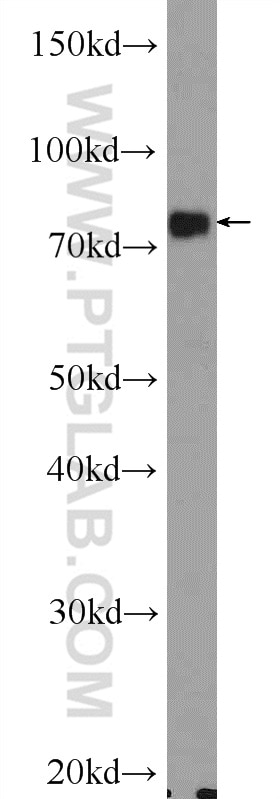
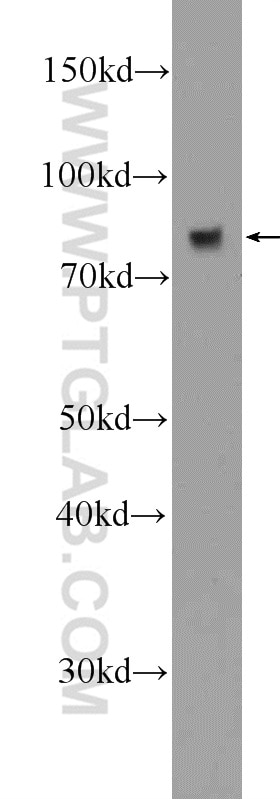
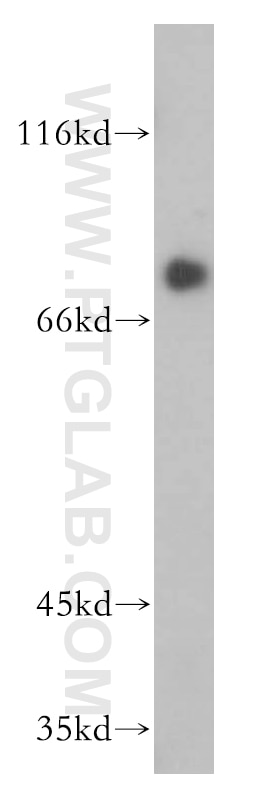
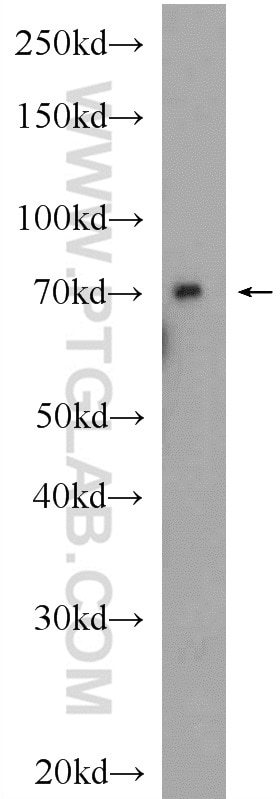
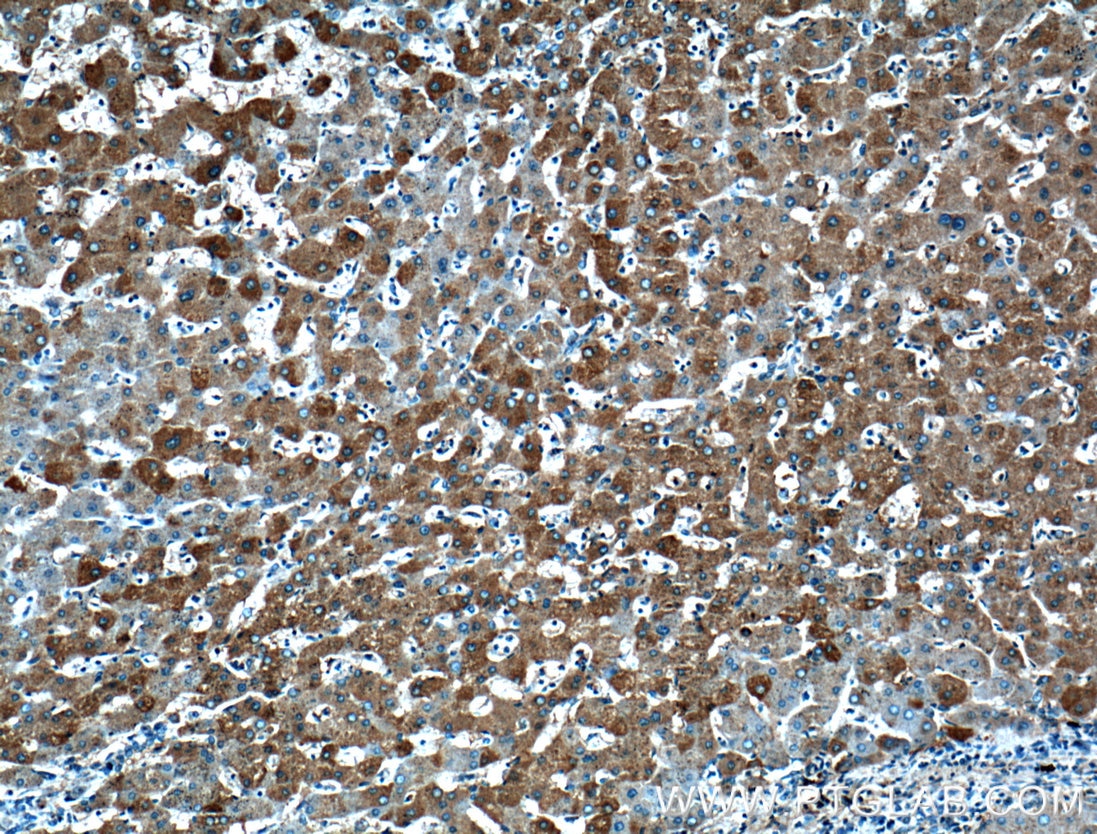
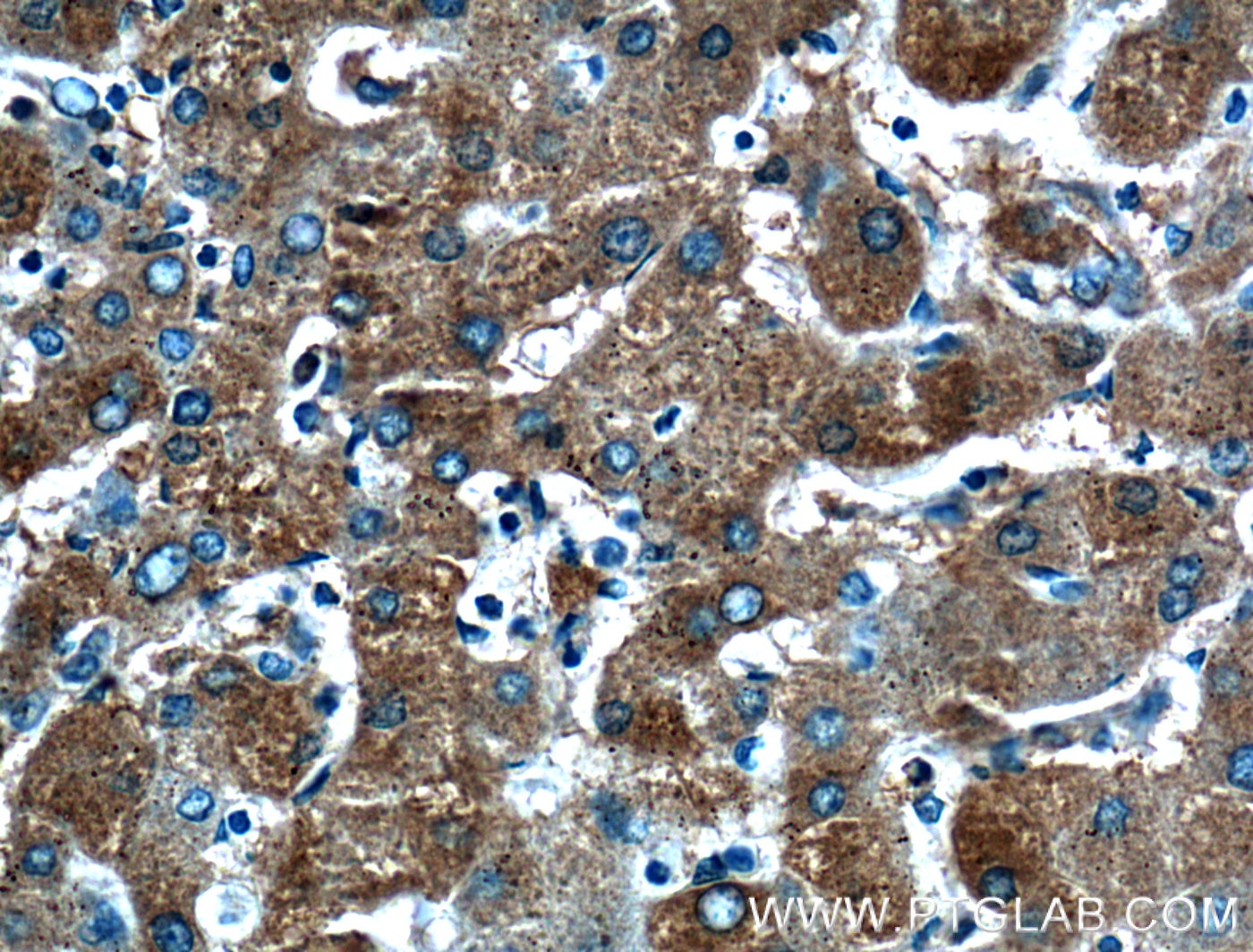
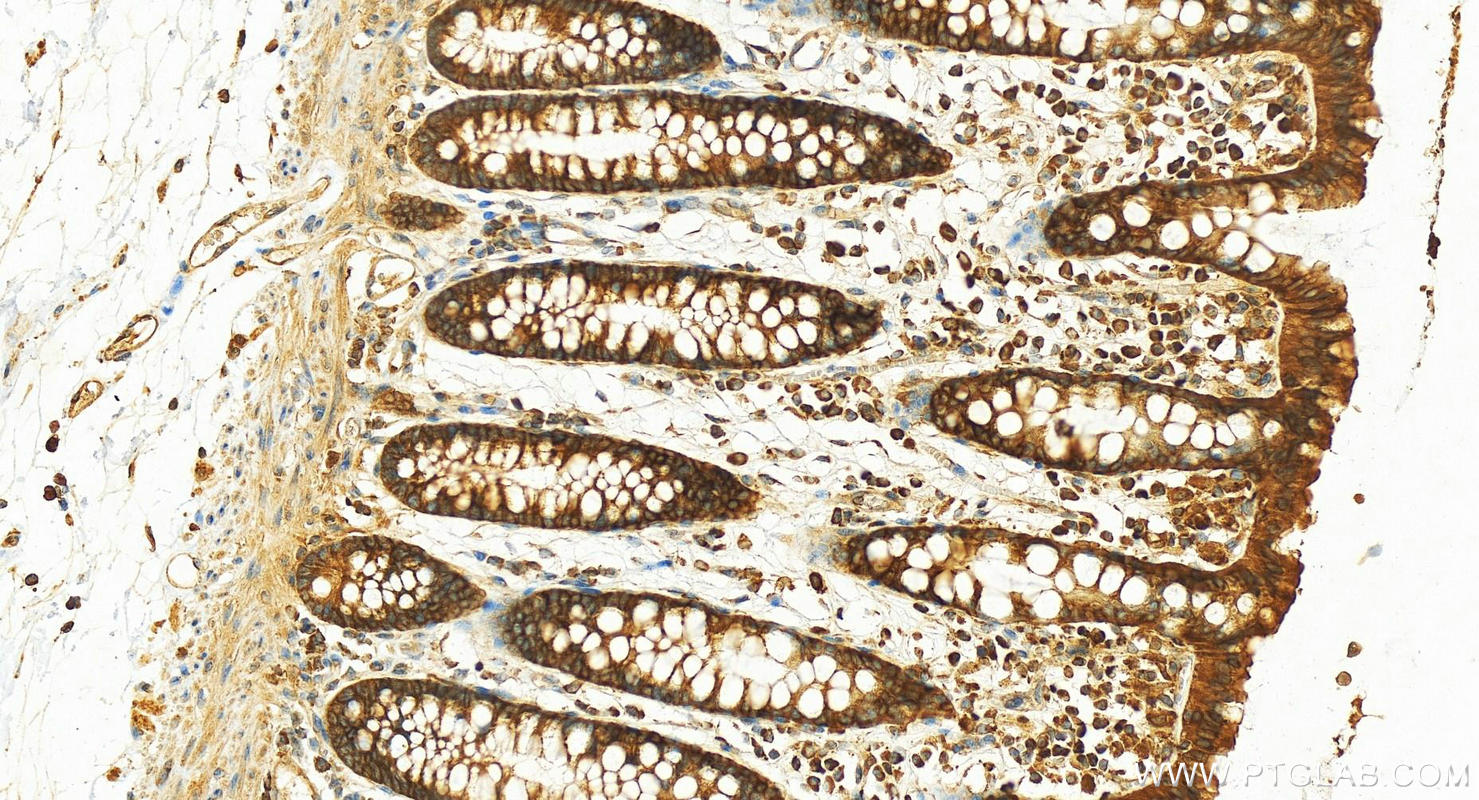
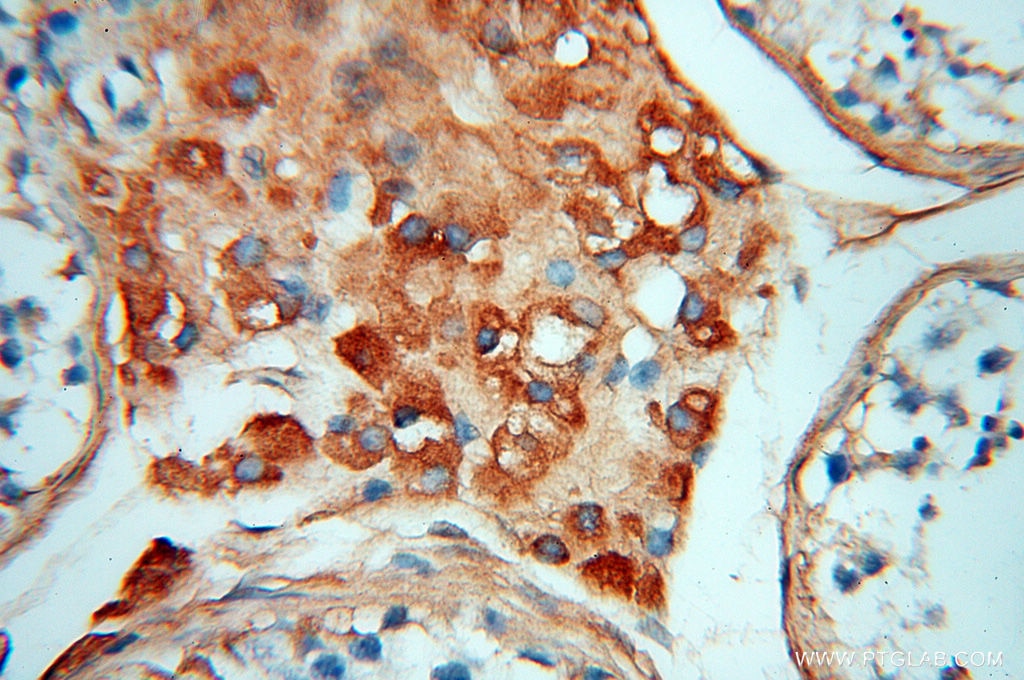
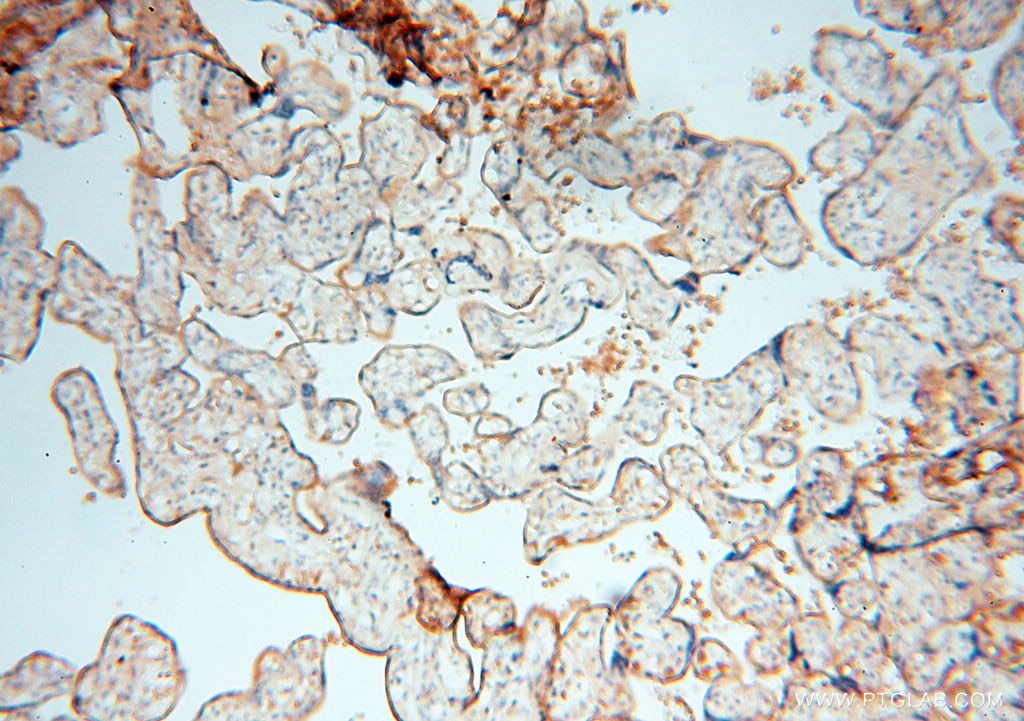
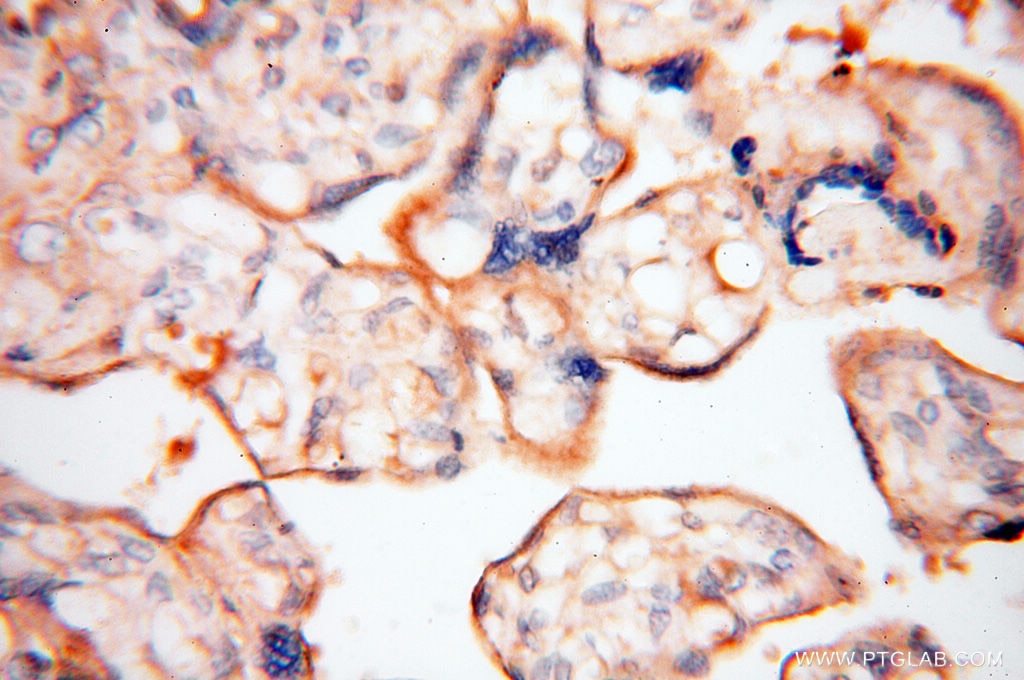
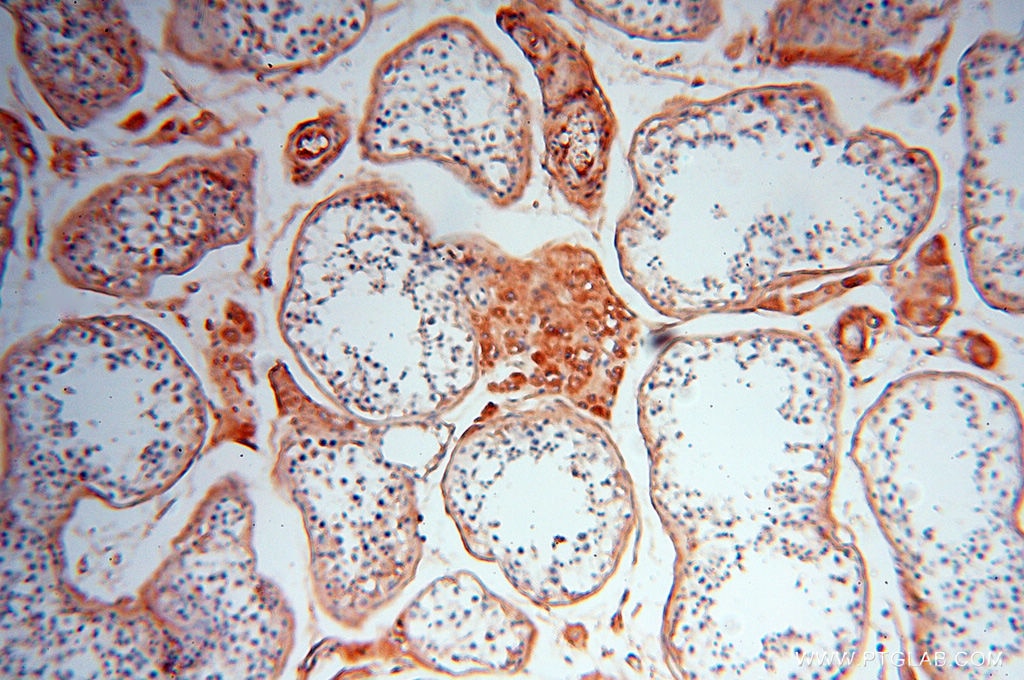
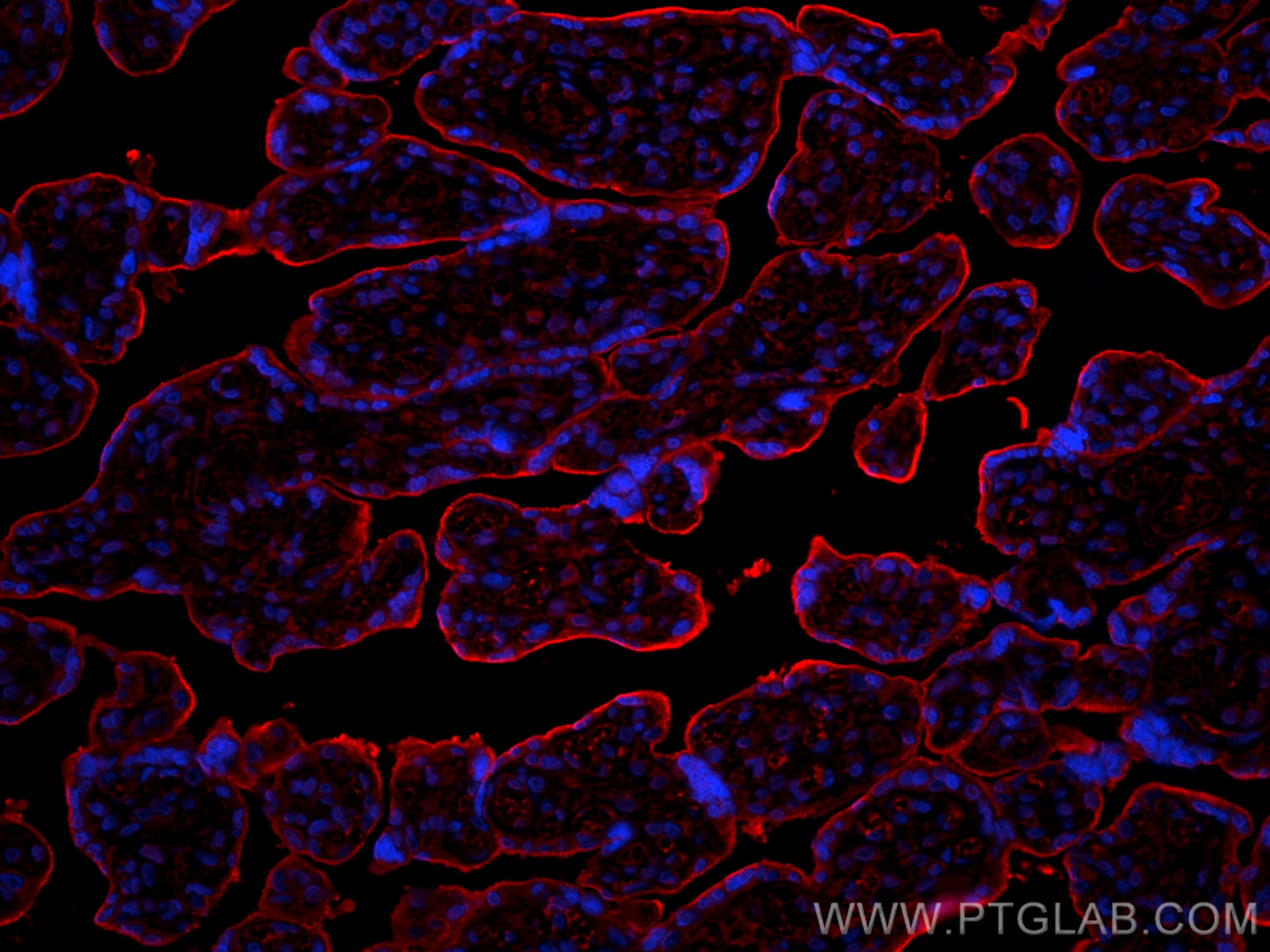
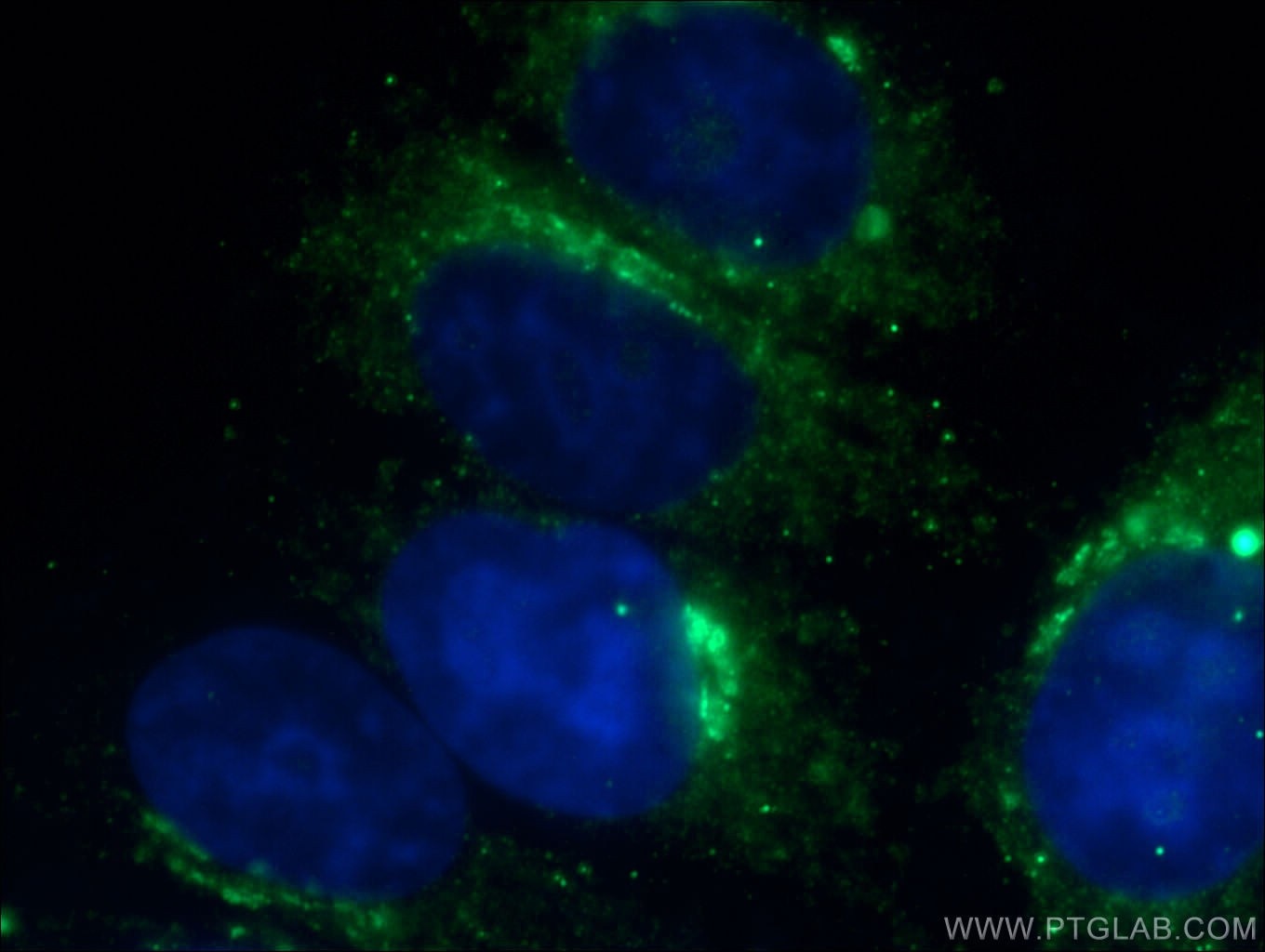
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
17435-1-PBS targets Transferrin/TF in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Transferrin/TF fusion protein Ag11504 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | transferrin |
| Calculated molecular weight | 698 aa, 77 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 77 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC059367 |
| Gene Symbol | TF |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7018 |
| RRID | AB_2035023 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P02787 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
What is the tissue specificity of TF?
Transferrin is synthesized mainly in the liver.
What is the calculated molecular weight of TF?
77 kDa
How many iron atoms can bind to TF?
Each of the two lobes of TF has one high-affinity Fe(III) binding site. Since binding of iron and bicarbonate
releases free H+ ions, affinity decreases in acidic conditions, in which TF also remains bound to its receptor.
What is the primary role of TF?
TF serves as a serum metal-binding protein, playing a key role in iron metabolism and delivery for erythropoiesis.
What is the role of TF in human diseases?
TF deficiency results in an exhibition of congenital atransferrinemia (hypotransferrinemia) in which there is a
decrease in hepcidin expression, causing increased iron levels.
Is TF essential for iron delivery?
Congenital atransferrinemia results in an iron overload in some tissues, such as the liver, suggesting that while TF is not essential for iron delivery to all organs, it is needed for iron level regulation.
In what circumstances do TF levels decrease?
Inflammation and iron overload both can cause a decline in TF levels.
How does TF affect hormonal balance?
TF positively regulates expression of hepcidin, a peptide hormone synthesized by the liver.
How does TF deficiency cause increased iron levels?
TF regulates hepcidin, which in turn is a negative regulator of intestinal iron absorption, resulting in TF
deficiency causing both anemia, and, paradoxically, increased iron levels in some tissues.
PMIDs: 23046645, 9635730, 22294463, 24589273