mTOR Substrates Antibody Kit
Host
Rabbit
Reactivity
Target Dependent
Applications
Target Dependent
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Cat no : PK30025
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
The mTOR Substrates Antibody Kit provides a cost-effective tool for studying mTOR activation as well as key proteins that are phosphorylated downstream. Perfect for signal transduction researchers starting a new project, screening multiple prospective targets, or those who simply require less volume.
The mTOR Substrates Antibody Kit contains antibodies against 5 key phospho-protein targets of the mTOR pathway.
| Antigen | Catalog No. | Host, clonality | Tested Reactivity | Applications | Volume |
|
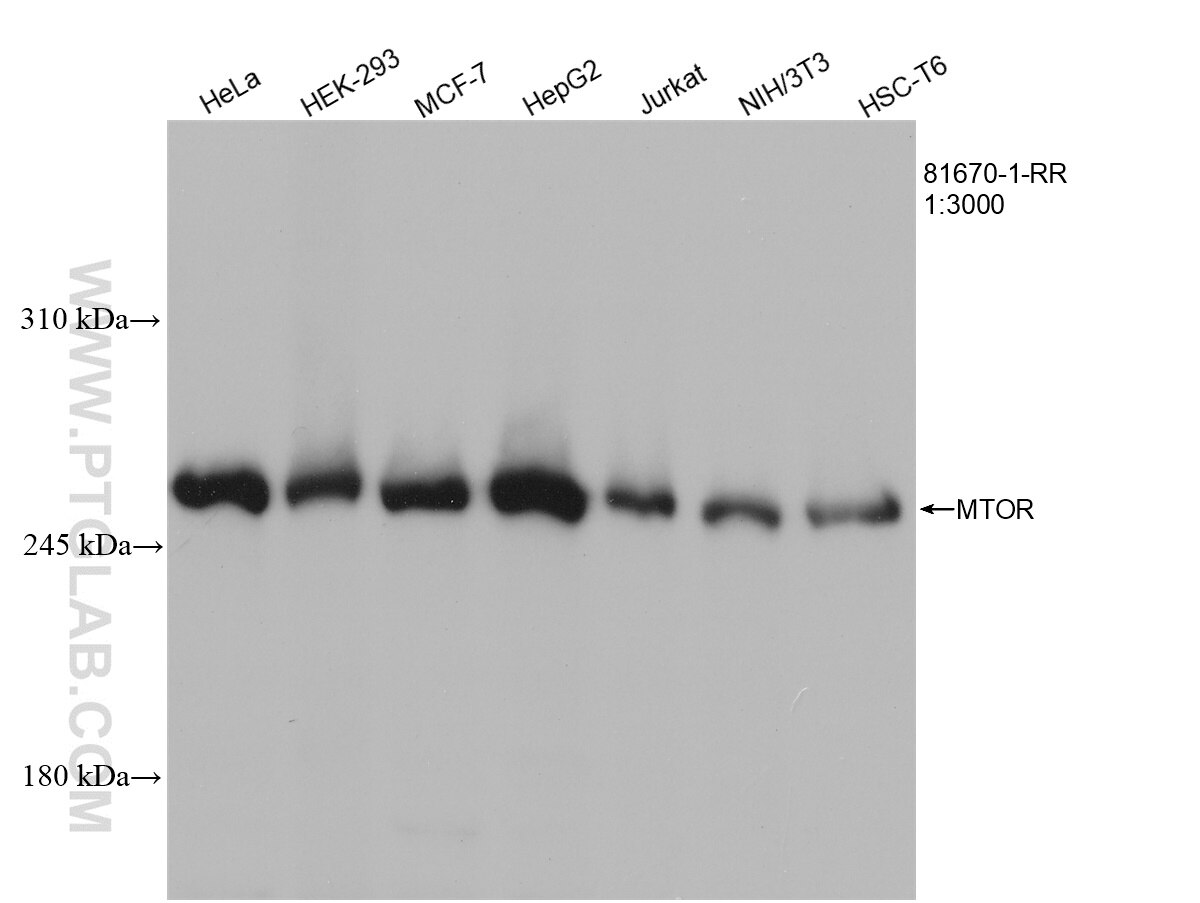
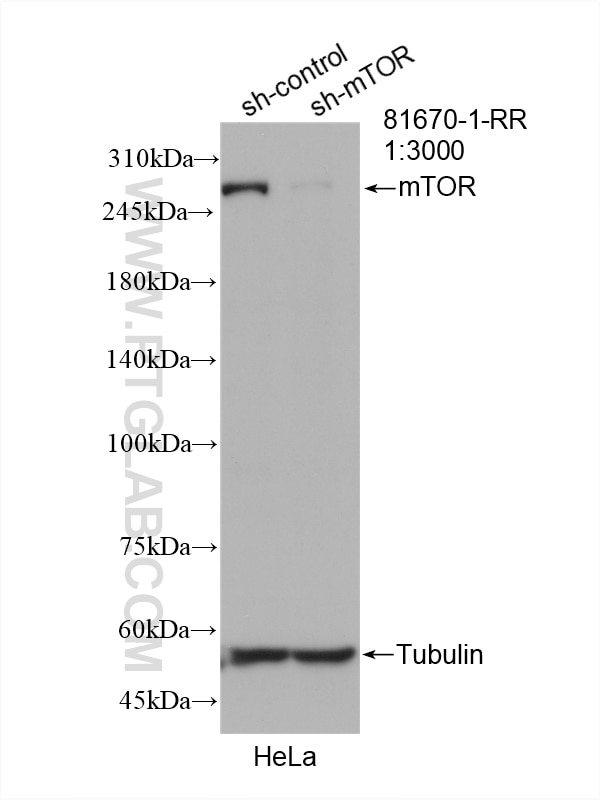
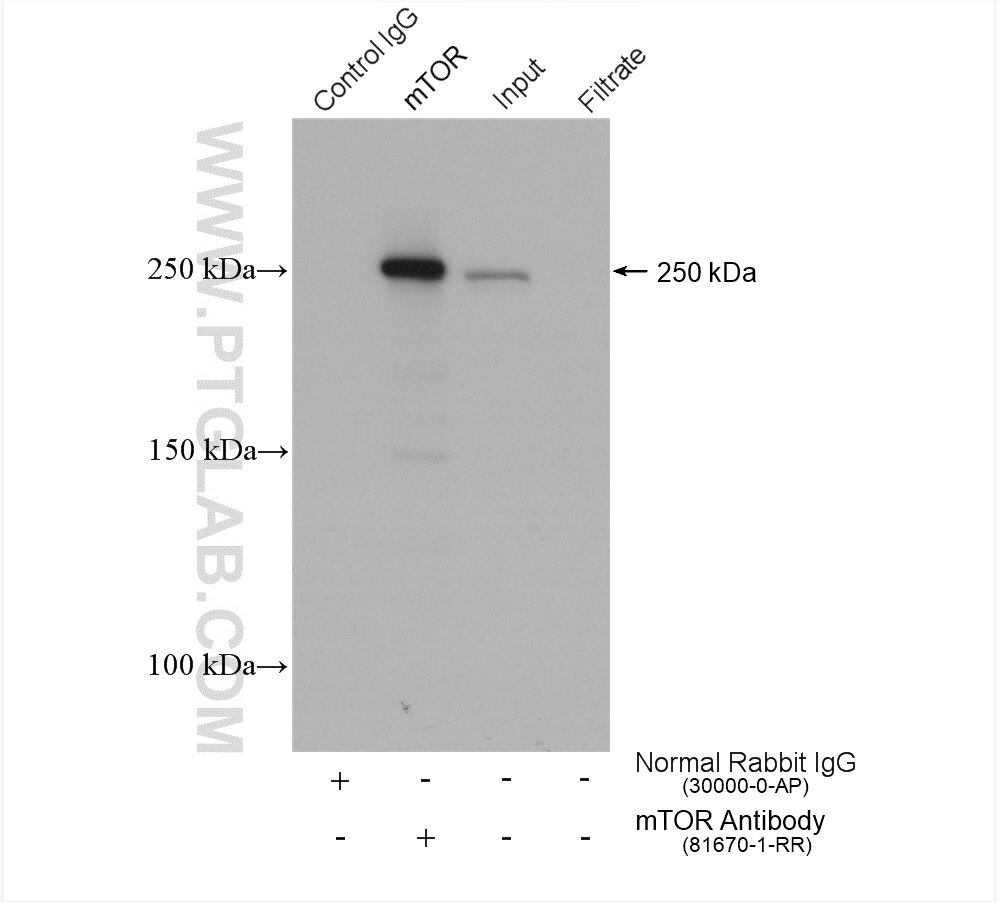
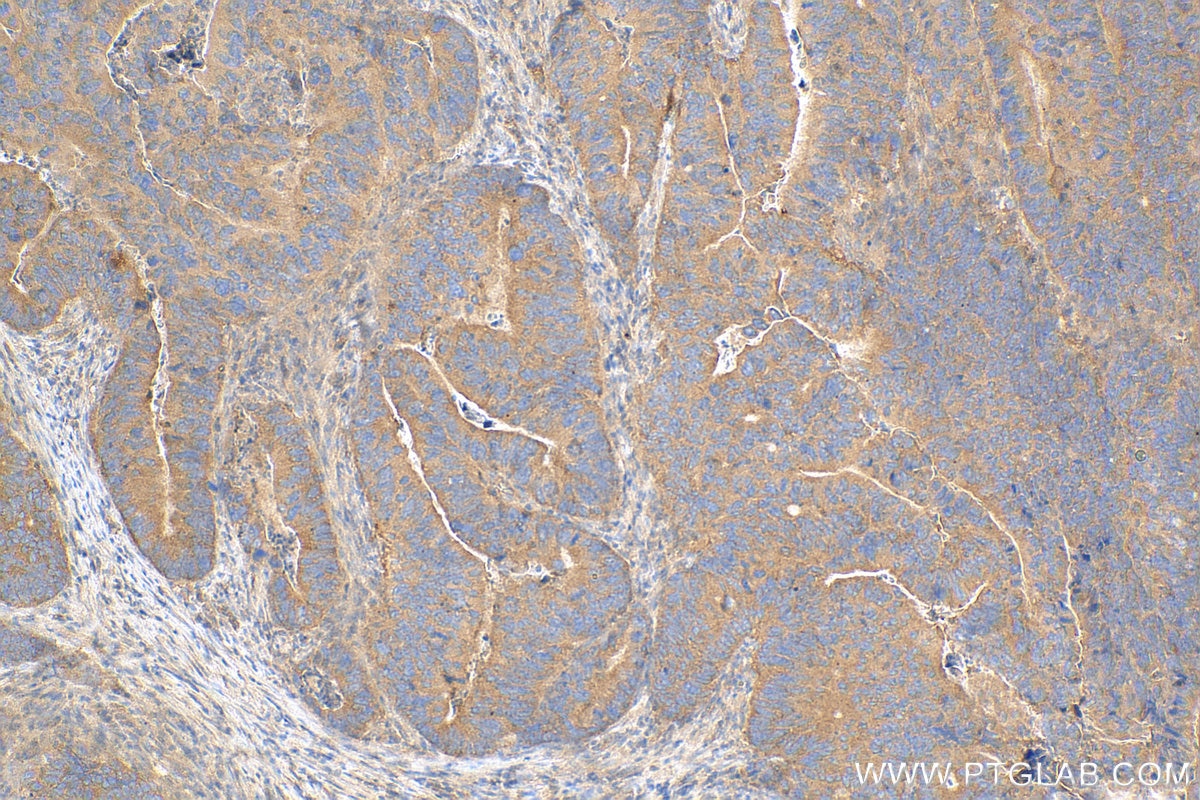
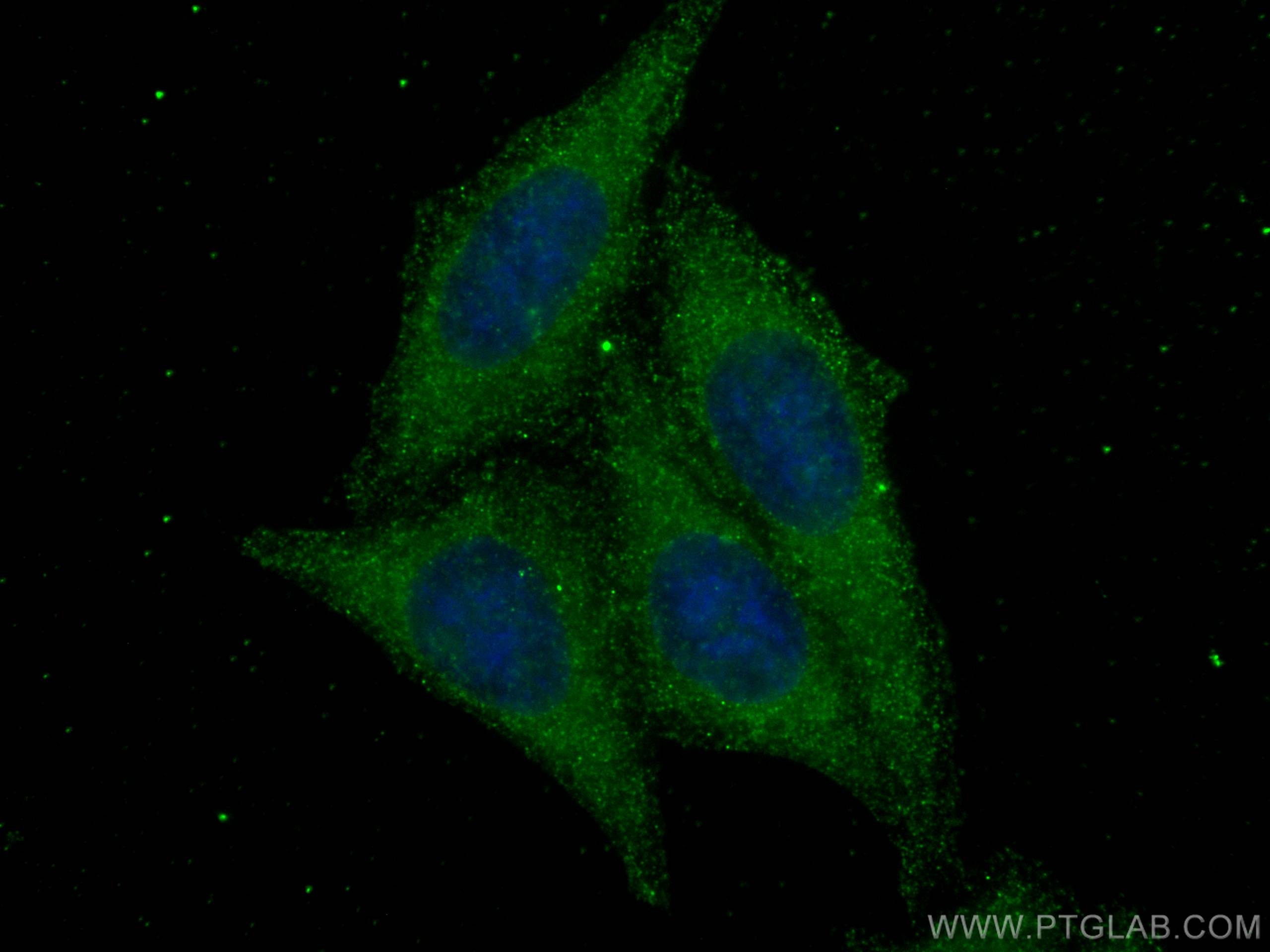
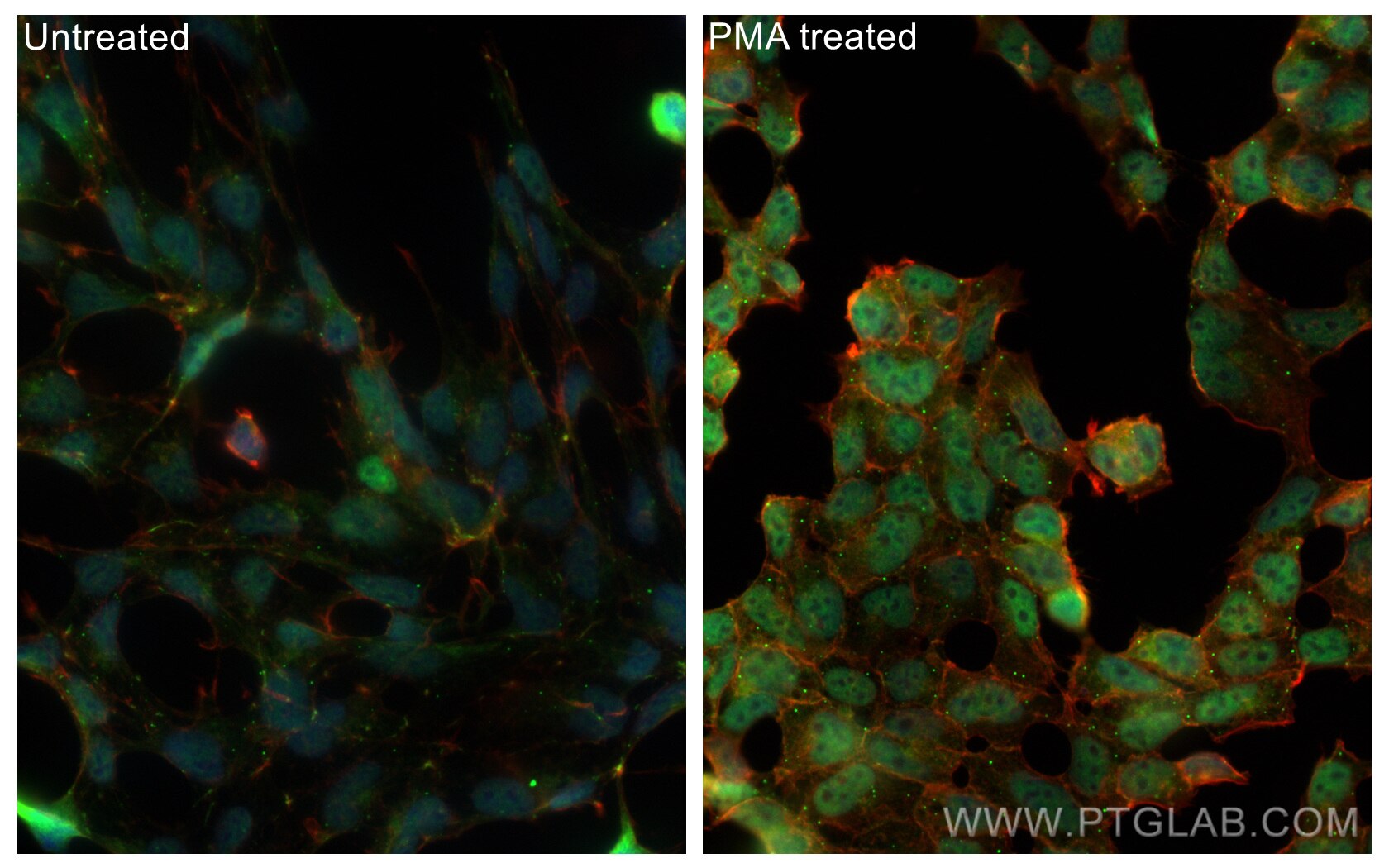
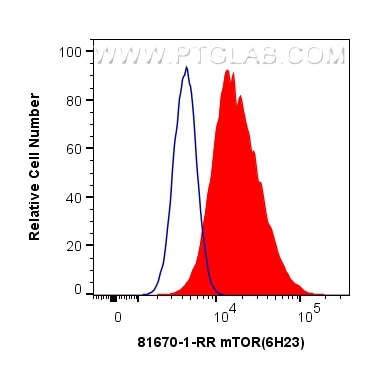
mTOR |
81670-1-RR | Rabbit Monoclonal | H, M, R | WB, IP, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra) | 20 uL |
|
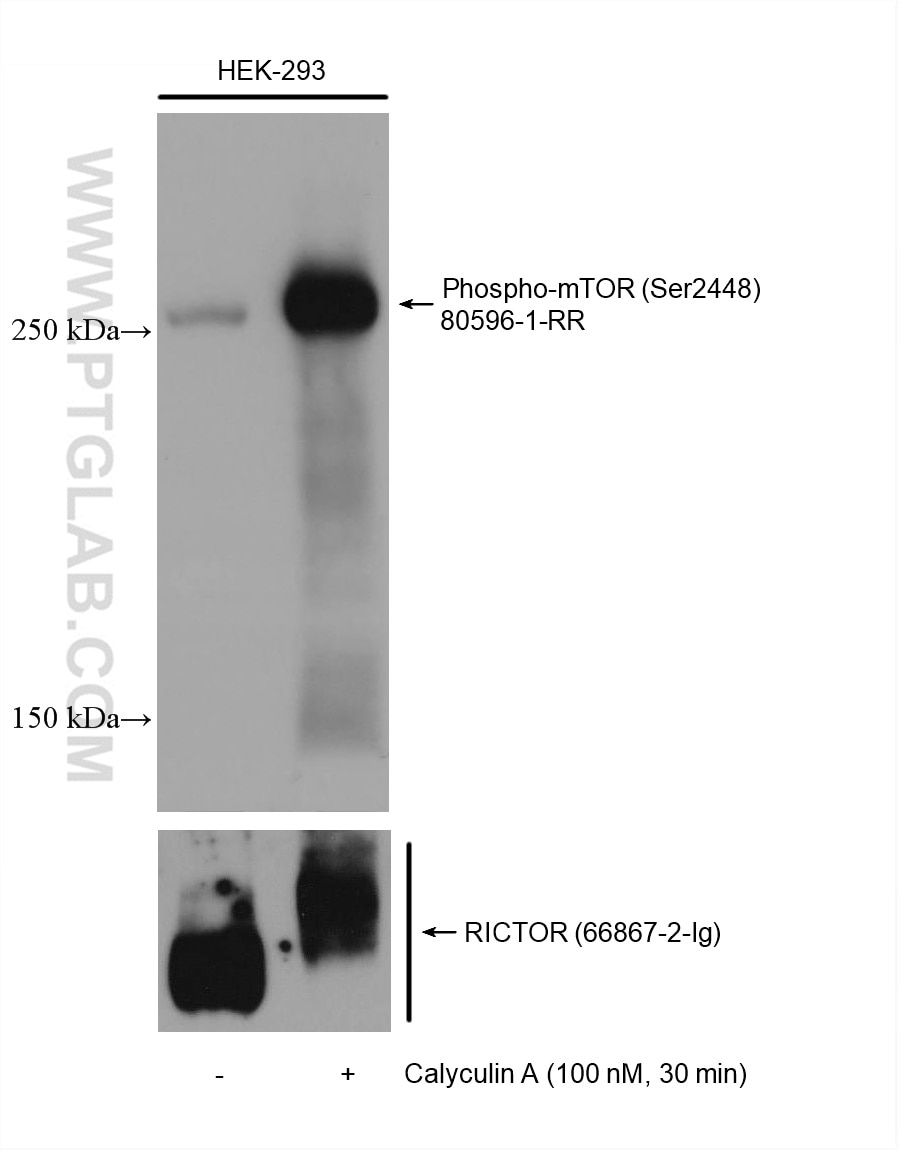
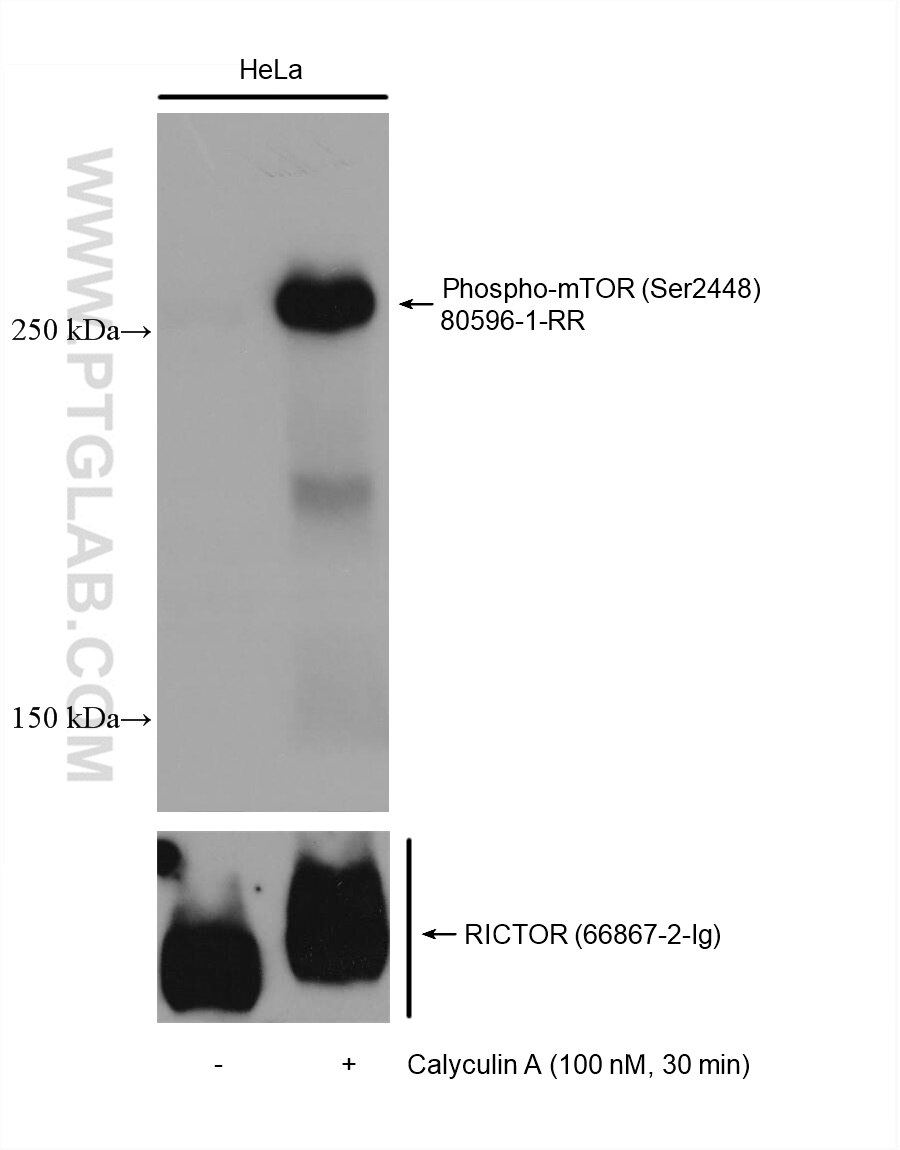
Phospho-mTOR (Ser2448) |
80596-1-RR | Rabbit Monoclonal | H, R | WB, IF/ICC | 20 uL |
|
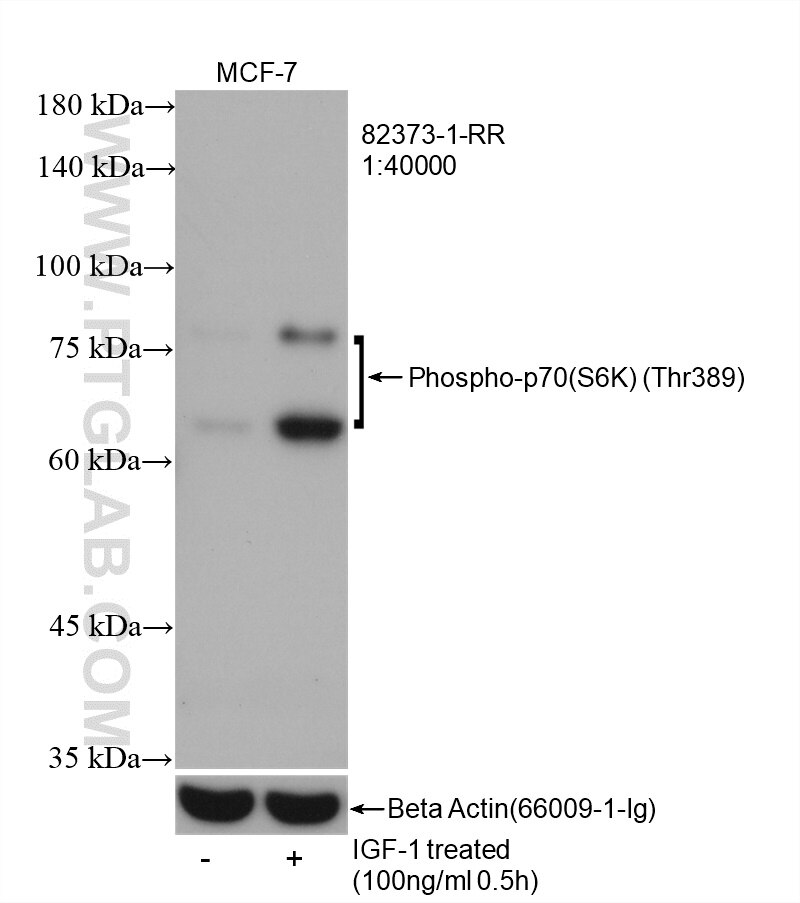
Phospho-p70(S6K) (Thr389) |
82373-1-RR | Rabbit Monoclonal | H | WB | 20 uL |
|
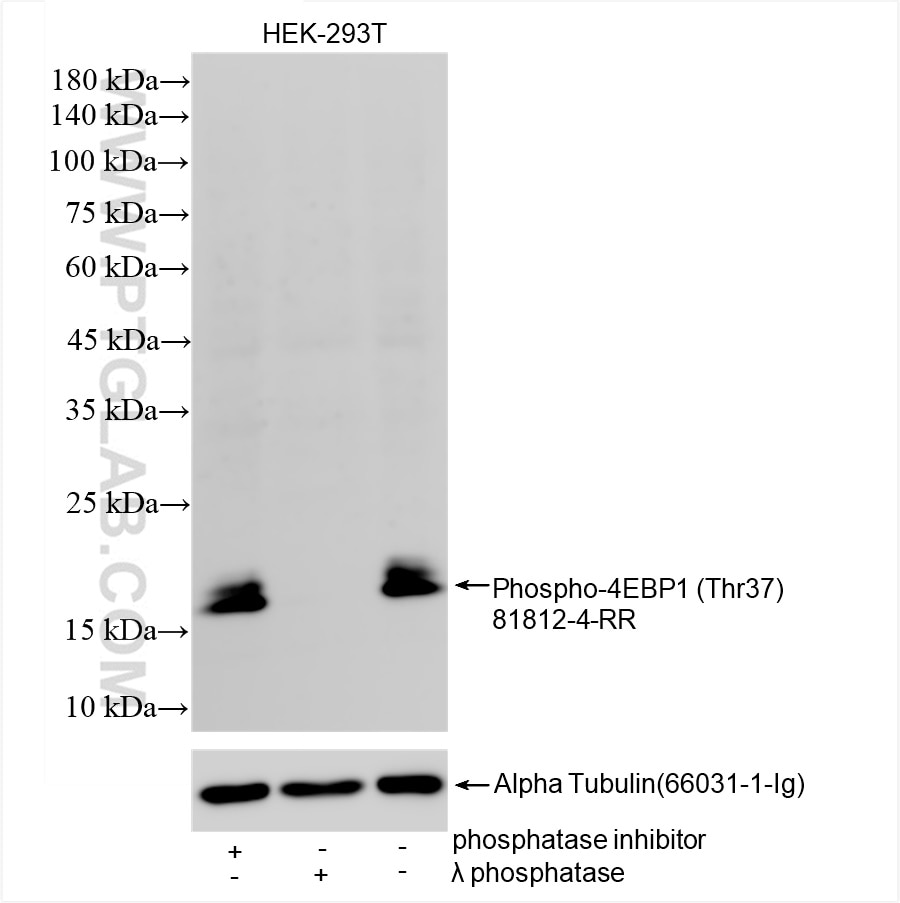
Phospho-4EBP1 (Thr37) |
81812-4-RR | Rabbit Monoclonal | H | WB | 20 uL |
|
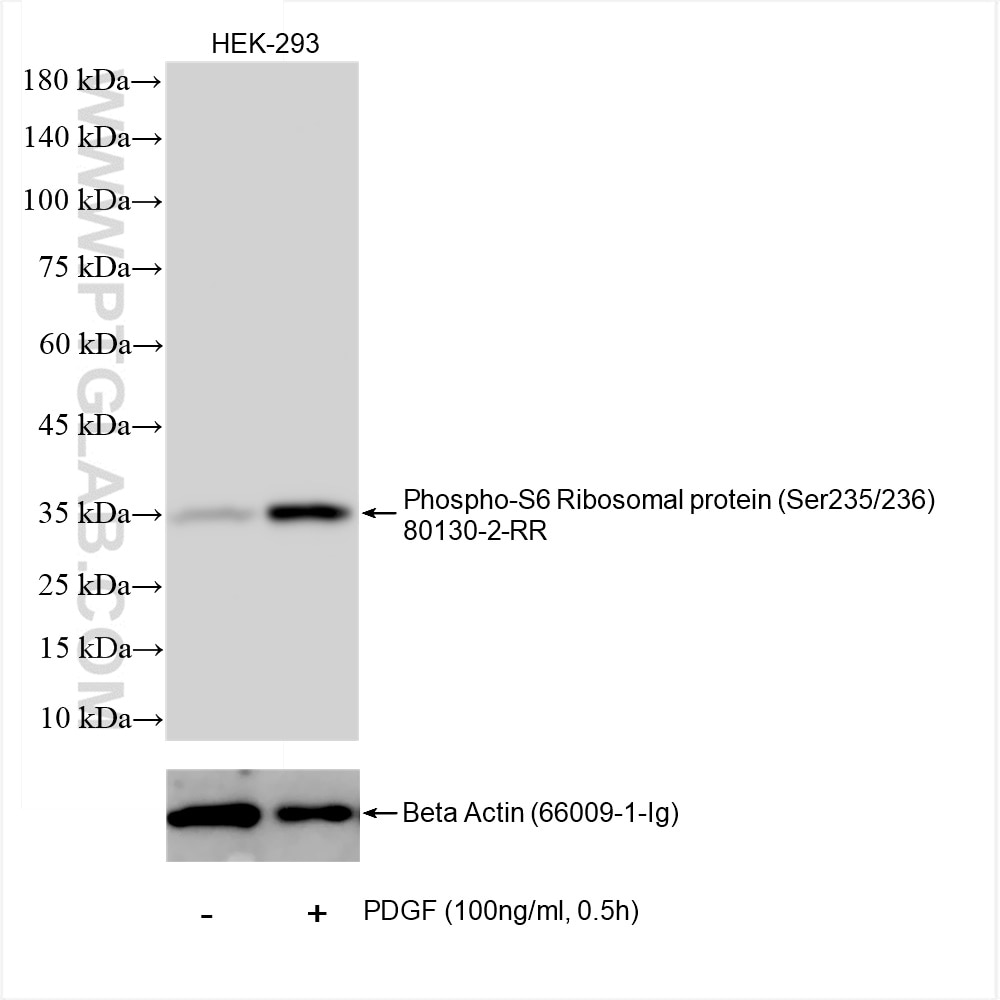
Phospho-RPS6 (Ser235/236) |
80130-2-RR | Rabbit Monoclonal | H | WB | 20 uL |
Storage
Store at -20°C. Stable for one year from the date of receipt.
Background Information
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) forms the center of a powerful signaling pathway that regulates cell metabolism, proliferation, and survival. Its activation is contingent upon phosphorylation at the Ser2448 residue, which is typically mediated upstream by AKT. The activated mTOR can then phosphorylate multiple substrates downstream to control the various effector functions of the mTOR pathway. Phosphorylation of p70(S6K) at the Thr389 residue results in its full activation and promotion of cell proliferation and mRNA translation via subsequent phosphorylation of RPS6 at the Ser 235 and 236 residues. mTOR can also promote translation through phosphorylation of 4EBP1 at the Thr 37 and 46 residues. These phosphorylation events reduce the ability of 4EBP1 to bind to eIF4E, which in turn reduces the inhibition of cap-dependent translation.
Standard Protocols
Click here to view our standard protocols for various applications including WB, IP, IHC, IF, FC, and ELISA.