Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
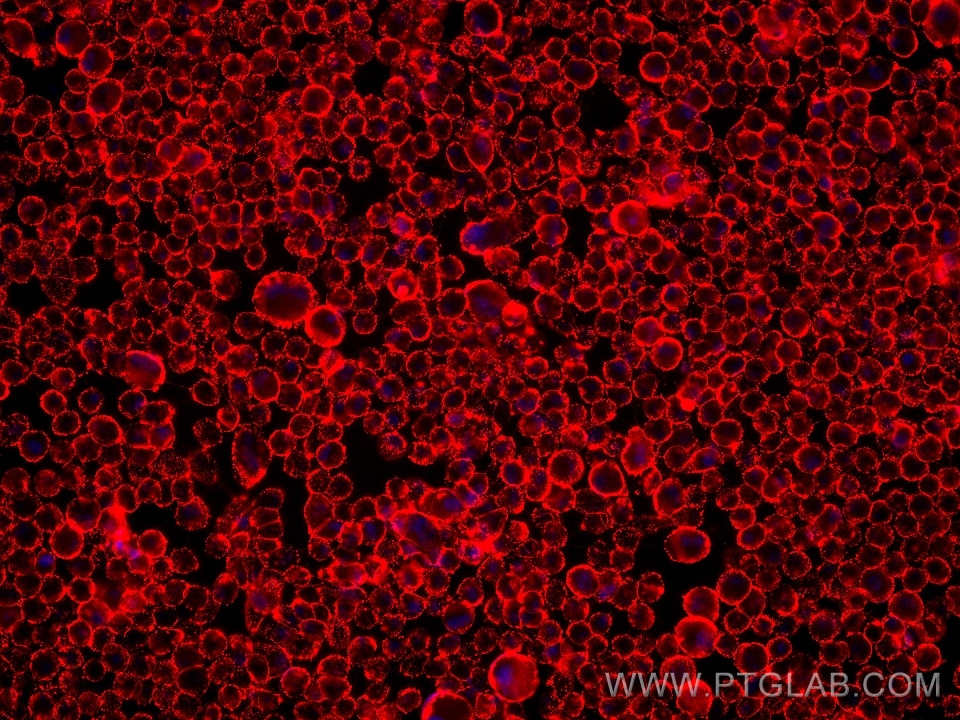
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | hTERT-RPE1 cells |
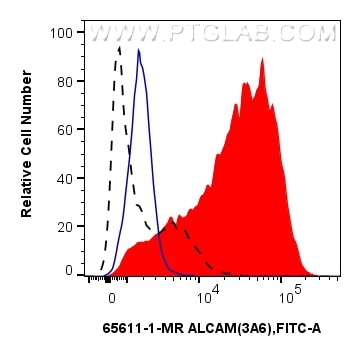
| Positive FC detected in | PHA treated human PBMCs |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
65611-1-MR targets ALCAM in IF/ICC, FC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Cultured human thymic epithelial cells 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule |
| Calculated molecular weight | 105 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC057809 |
| Gene Symbol | ALCAM |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 214 |
| RRID | AB_3670358 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM, also known as CD166) is a cell adhesion molecule that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is involved in cell-cell adhesion through homophilic and heterophilic (to CD6) interactions. ALCAM is widely expressed in a variety of normal tissues and cell types, including activated T cells and monocytes, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, neuronal cells, hepatocytes, and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (PMID: 7760007; 25221999). Altered ALCAM expression has been associated with the differentiation state and progression in some neoplasms including melanoma, prostate, colorectal, and breast cancers (PMID: 20461761; 18172759).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for ALCAM antibody 65611-1-MR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |