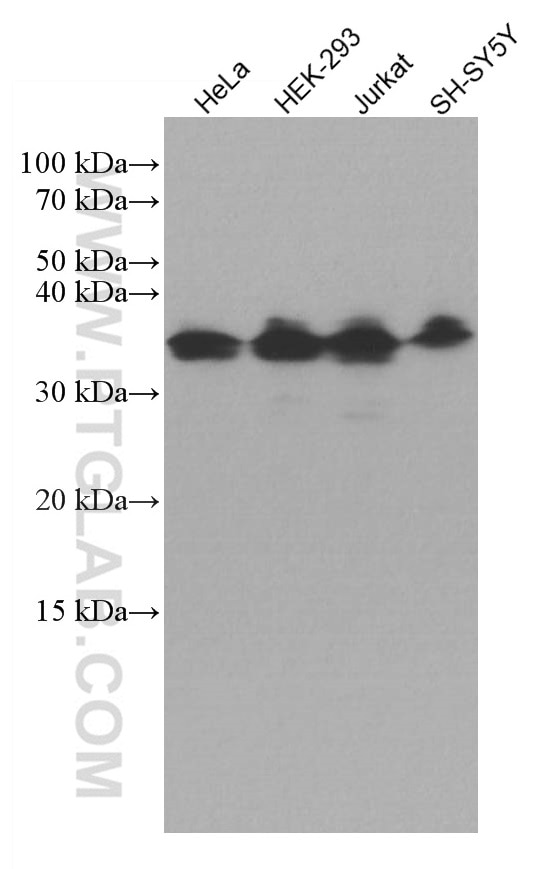
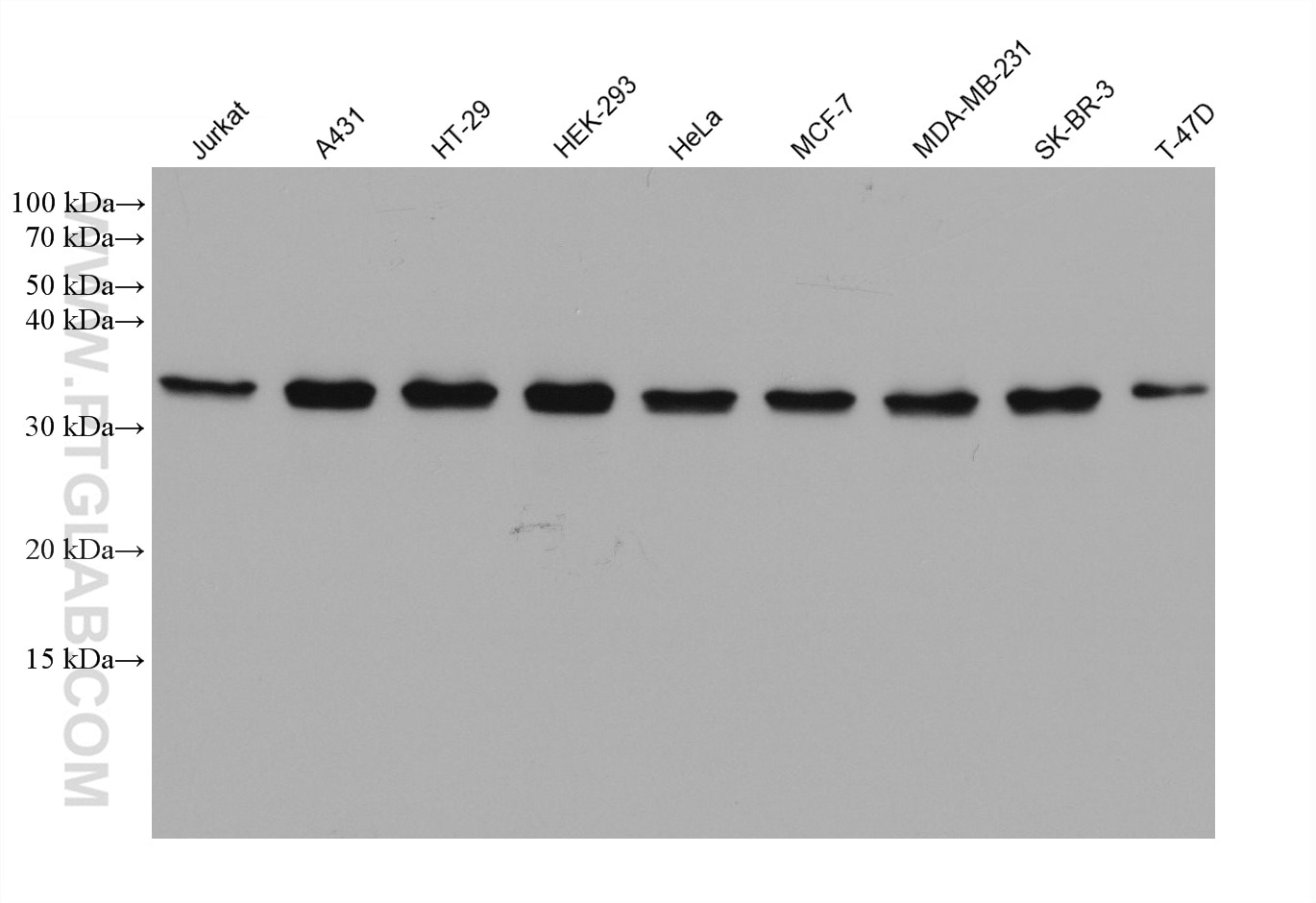
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
67066-1-PBS targets ATF5 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | ATF5 fusion protein Ag7214 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | activating transcription factor 5 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 31 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 30-35 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC005174 |
| Gene Symbol | ATF5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 22809 |
| RRID | AB_2882376 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9Y2D1 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
ATF5, also named as Activating transcription factor 5, is a 282 amino acid protein, which belongs to the bZIP family. ATF5 is Widely expressed with higher expression levels in liver. ATF5 is actively transported to the centrosome and accumulated in the pericentriolar material (PCM) during G1 to M phase via a microtubule-dependent mechanism. During late telophase and cytokinesis, it translocates from the centrosome to the midbody (PMID: 26213385) . ATF5 as a transcription factor that either stimulates or represses gene transcription through binding of different DNA regulatory elements such as cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AC][AG]-3'), ATF5-specific response element (ARE) (consensus: 5'-C[CT]TCT[CT]CCTT[AT]-3') but also the amino acid response element (AARE), present in many viral and cellular promoters. Critically ATF5 is involved, often in a cell type-dependent manner, in cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation (PubMed:10373550, PubMed:15358120, PubMed:21212266, PubMed:20654631).