Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
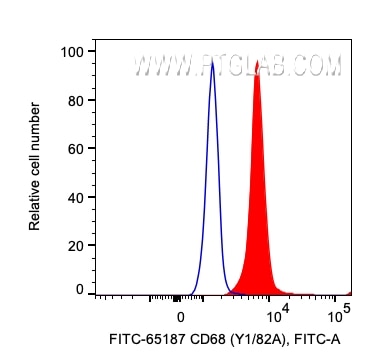
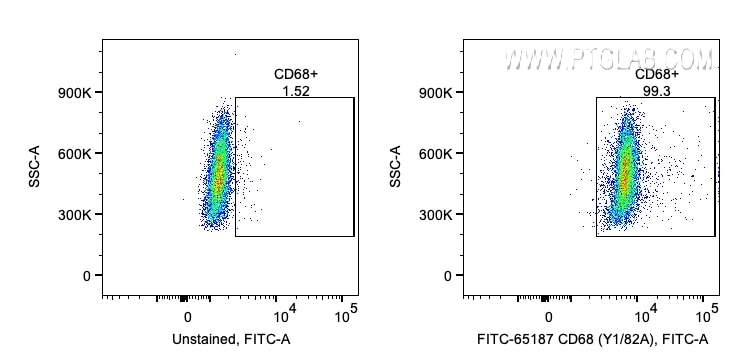
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | human PBMCs |
| Positive FC detected in | human PBMCs |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 5 ul per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : |
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is 5 μl per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or 5 μl per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
FITC-65187 targets CD68 in IF, FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b, kappa |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Lysosomal contents of lung macrophages 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | CD68 molecule |
| Calculated molecular weight | 37 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC015557 |
| Gene Symbol | CD68 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 968 |
| RRID | AB_2924123 |
| Conjugate | FITC Plus Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 495 nm / 524 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Purified by protein-A affinity chromatography |
| UNIPROT ID | P34810 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide and 0.5% BSA{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
CD68 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is highly expressed by human monocytes and tissue macrophages. It belongs to the lysosomal/endosomal-associated membrane glycoprotein (LAMP) family and primarily localizes to lysosomes and endosomes with a smaller fraction circulating to the cell surface. CD68 is also a member of the scavenger receptor family. It may play a role in phagocytic activities of tissue macrophages.
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Rep Methods Modeling alcohol-associated liver disease in humans using adipose stromal or stem cell-derived organoids |