Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
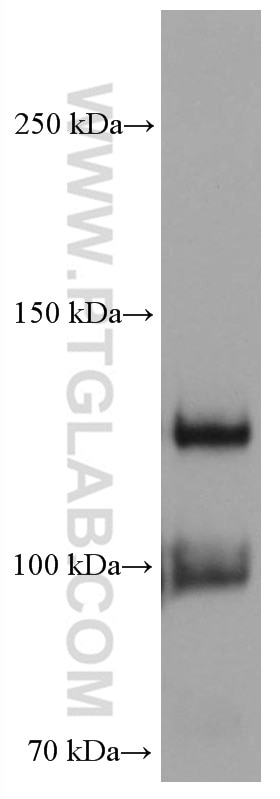
| Positive WB detected in | human placenta tissue |
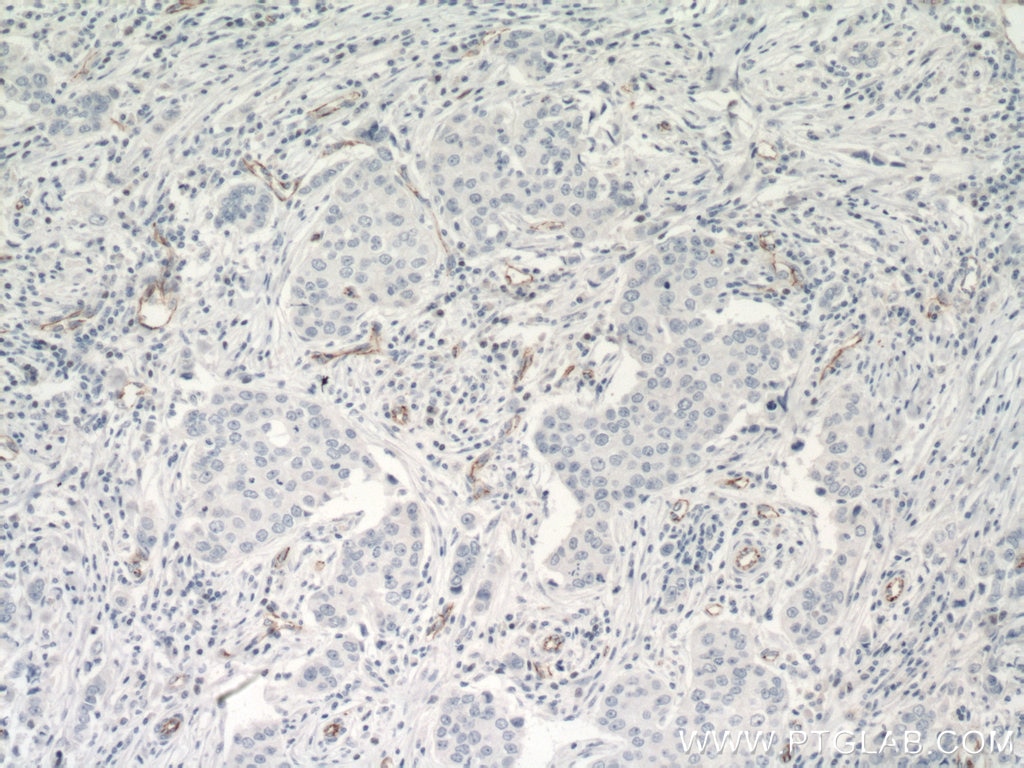
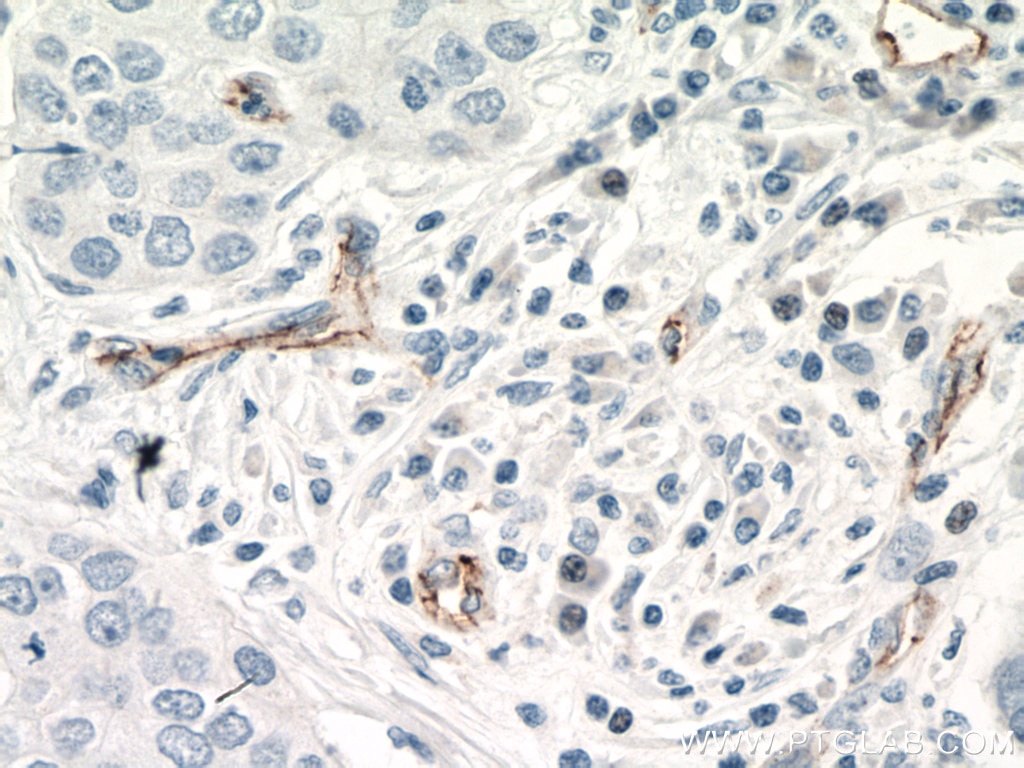
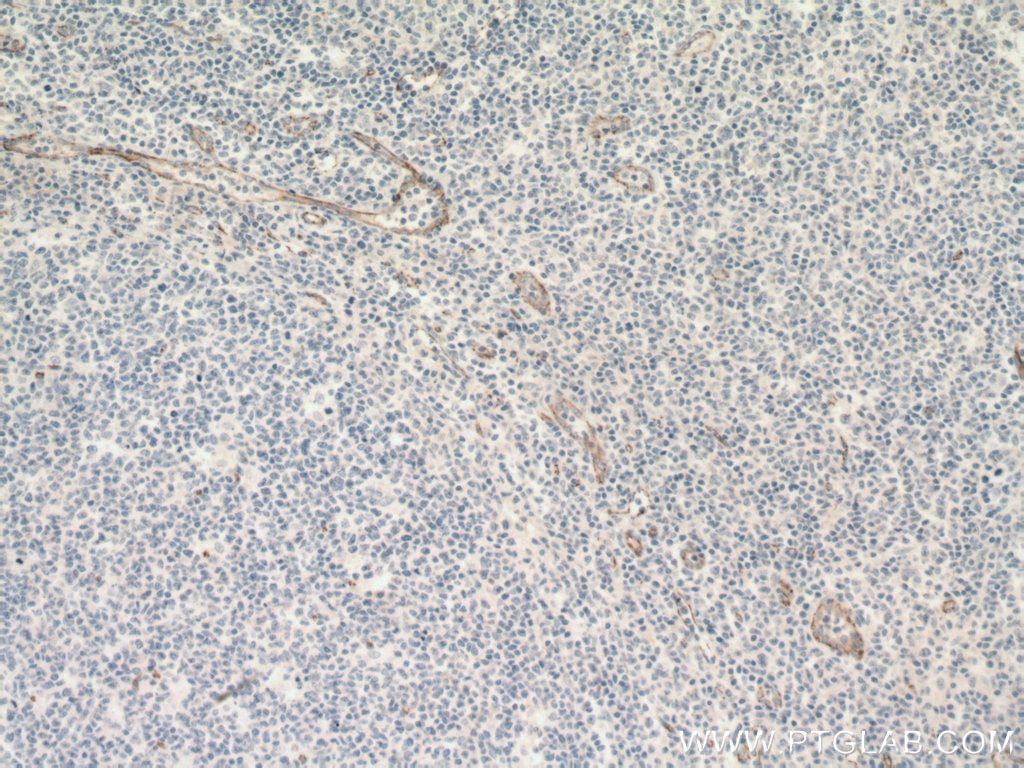
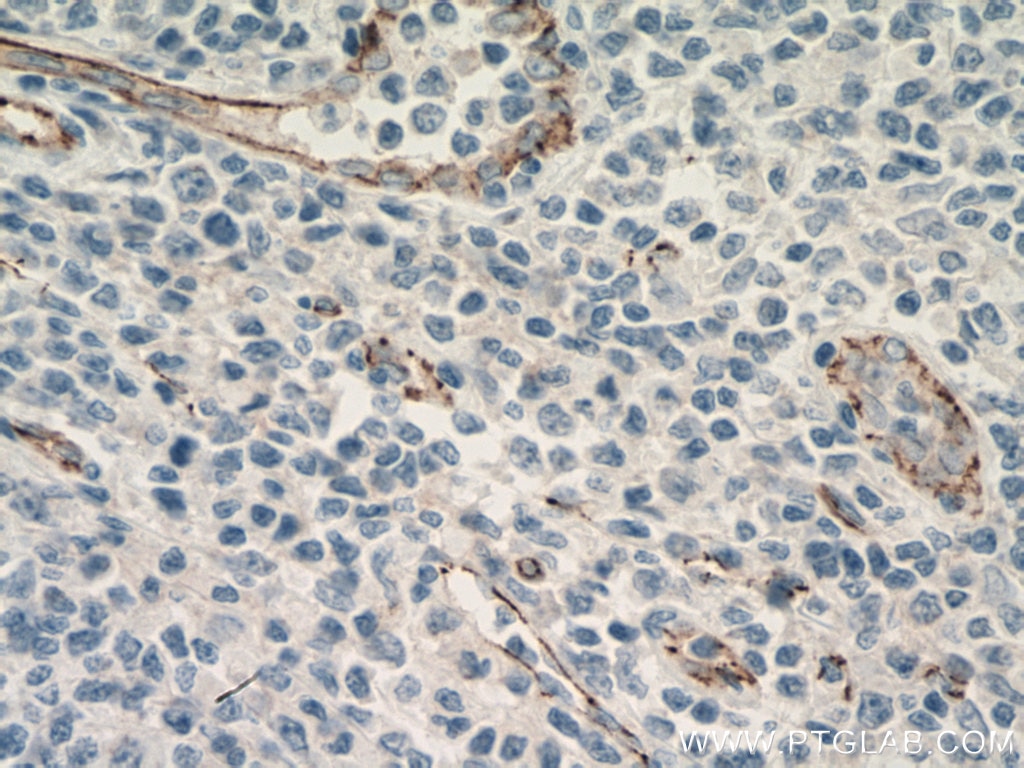
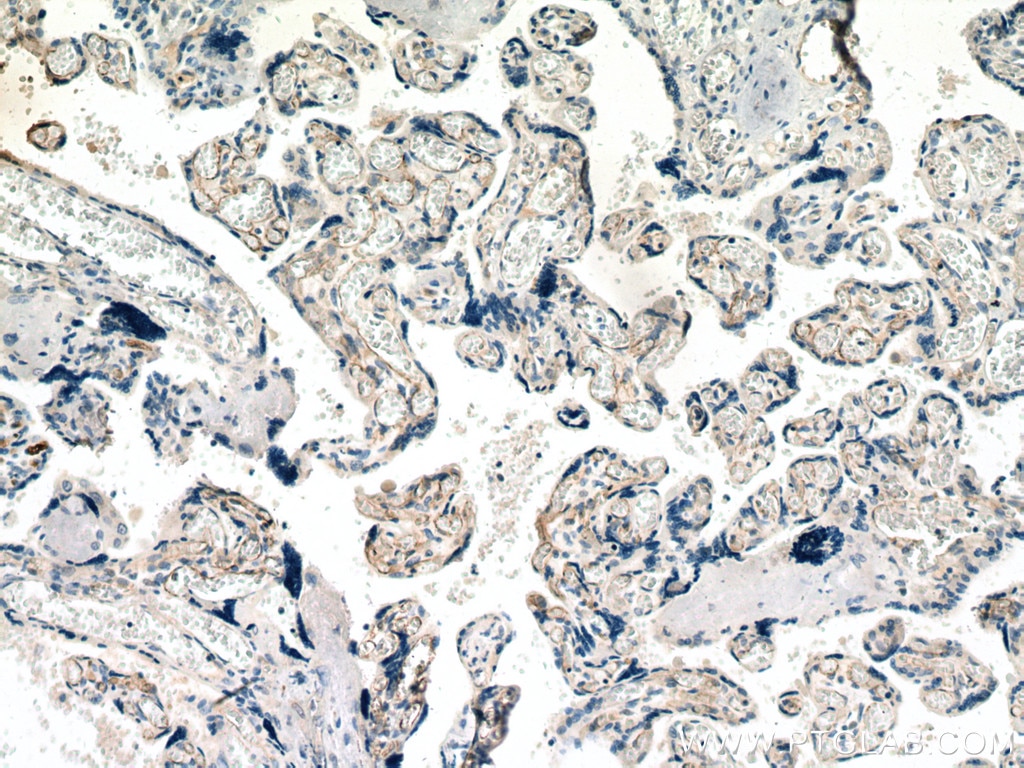
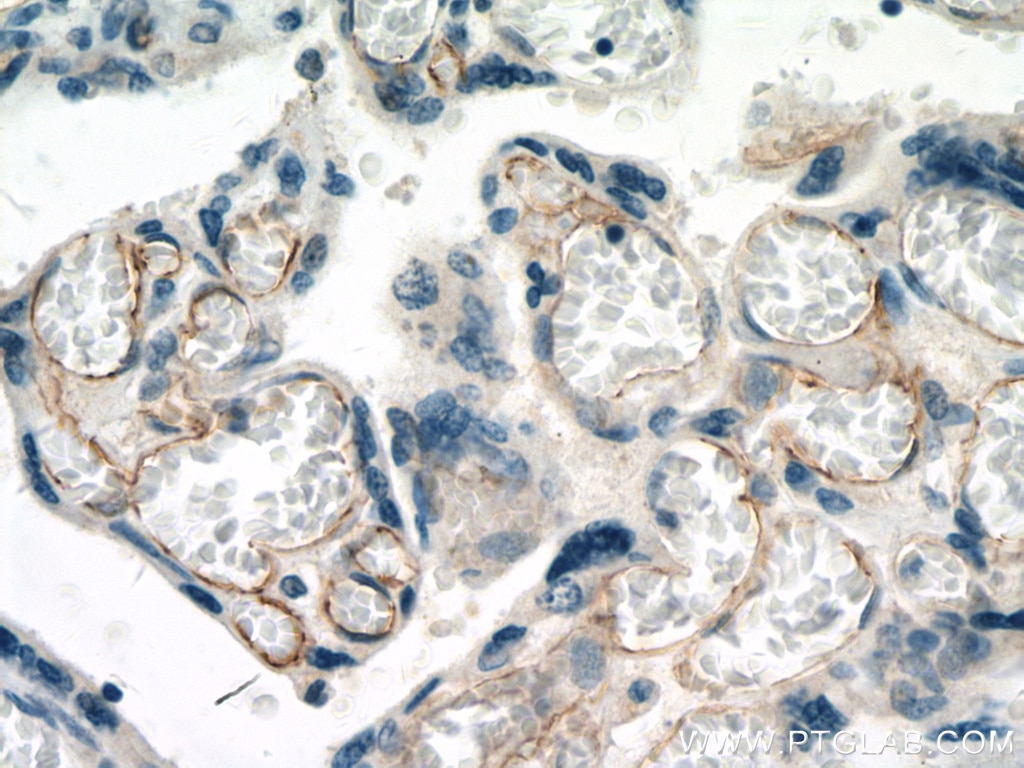
| Positive IHC detected in | human breast cancer tissue, human tonsillitis tissue, human placenta tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
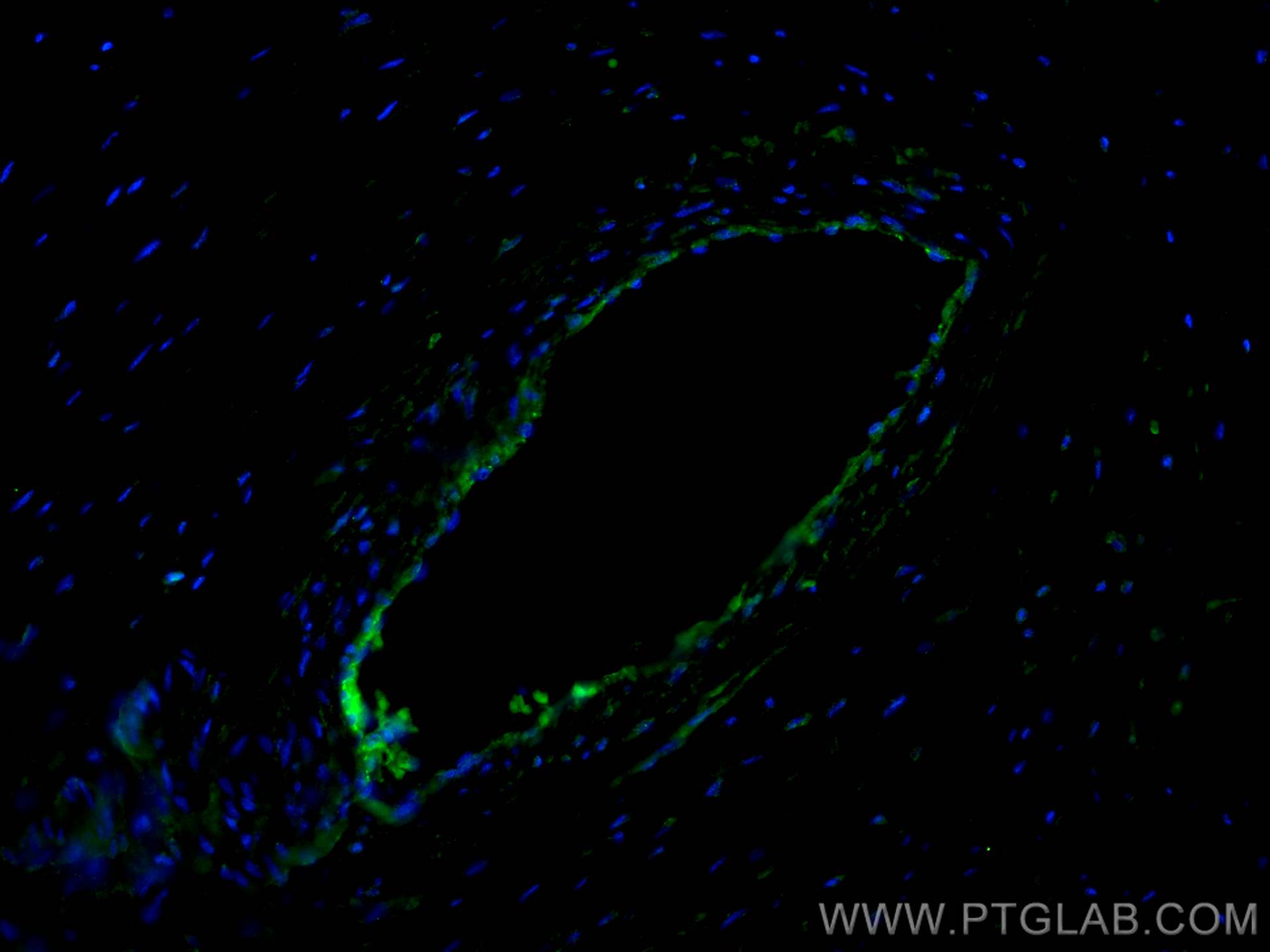
| Positive IF-P detected in | human placenta tissue |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HUVEC cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:100-1:400 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:200-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:750-1:3000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 27 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
| IF | See 12 publications below |
Product Information
66804-1-Ig targets VE-cadherin/CD144 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag27501 Product name: Recombinant human CDH5 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 54-241 aa of NM_001795 Sequence: MHIDEEKNTSLPHHVGKIKSSVSRKNAKYLLKGEYVGKVFRVDAETGDVFAIERLDRENISEYHLTAVIVDKDTGENLETPSSFTIKVHDVNDNWPVFTHRLFNASVPESSAVGTSVISVTAVDADDPTVGDHASVMYQILKGKEYFAIDNSGRIITITKSLDREKQARYEIVVEARDAQGLRGDSGT 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | cadherin 5, type 2 (vascular endothelium) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 88 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 125 kDa, 100 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_001795 |
| Gene Symbol | VE-cadherin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1003 |
| RRID | AB_2882147 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P33151 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Cadherins are a family of transmembrane glycoproteins that mediate calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion and play an important role in the maintenance of normal tissue architecture. Vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin), also known as Cadherin-5 (CDH5) or CD144, is a member of the type II classical cadherin family of cell adhesion proteins (PMID: 21269602). VE-cadherin is expressed specifically in endothelial cells and mediates homophilic adhesion in the vascular endothelium (PMID: 1522121; 8555485; 21269602). VE-cadherin plays a role in the organization of lateral endothelial junctions and in the control of permeability properties of vascular endothelium (PMID: 1522121). VE-cadherin has also been shown to be required for angiogenesis (PMID: 16473763; 18162609).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for VE-cadherin/CD144 antibody 66804-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for VE-cadherin/CD144 antibody 66804-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for VE-cadherin/CD144 antibody 66804-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Adv Mater Glycated ECM Derived Carbon Dots Inhibit Tumor Vasculogenic Mimicry by Disrupting RAGE Nuclear Translocation and Its Interaction With HMGB1 | ||
Acta Pharmacol Sin Endothelial deubiquinatase YOD1 mediates Ang II-induced vascular endothelial-mesenchymal transition and remodeling by regulating β-catenin | ||
EMBO Rep Mouse endothelial OTUD1 promotes angiotensin II-induced vascular remodeling by deubiquitinating SMAD3 | ||
Biomed Pharmacother Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inflammation by regulating CCN1 | ||
Regen Biomater Microvascular network based on the Hilbert curve for nutrient transport in thick tissue | ||
J Invest Dermatol Endothelial Piezo1 mediates barrier dysfunction and NLRP3 inflammasomes activation in psoriasis |