Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
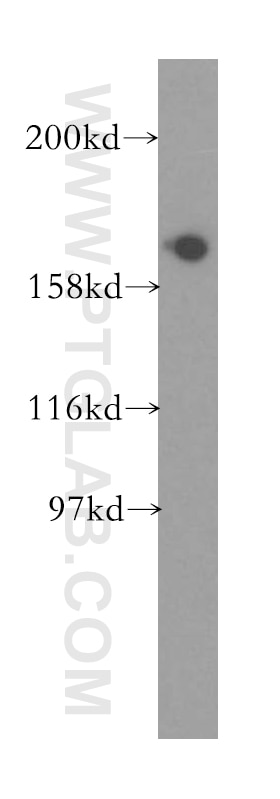
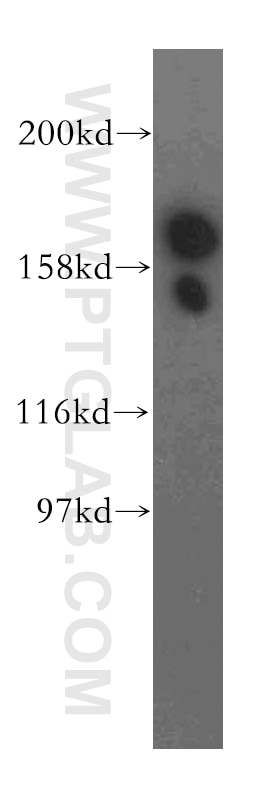
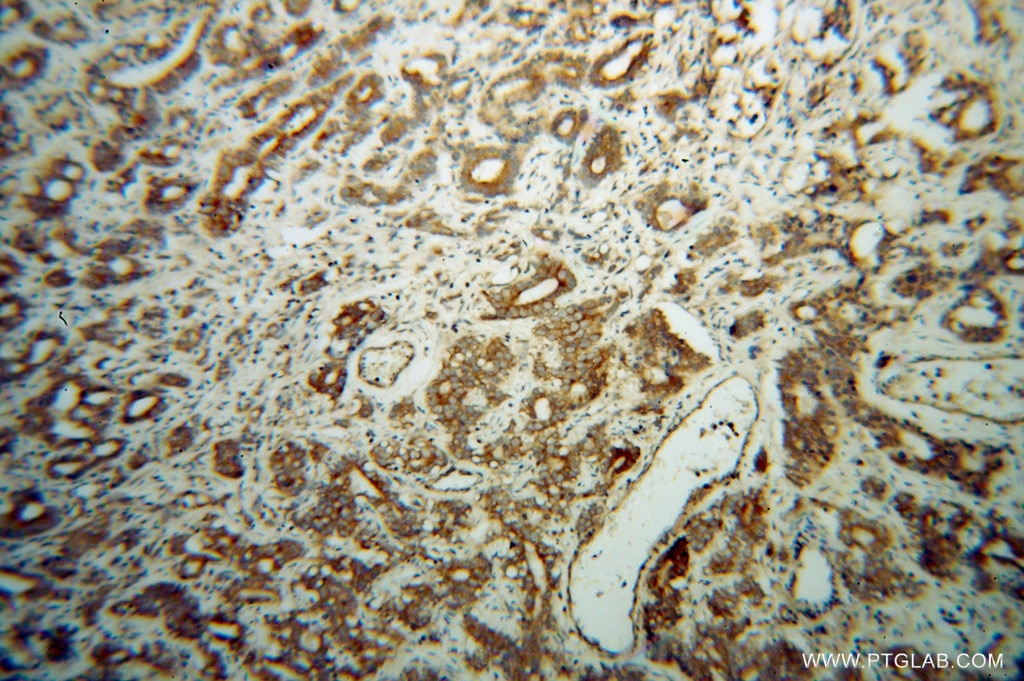
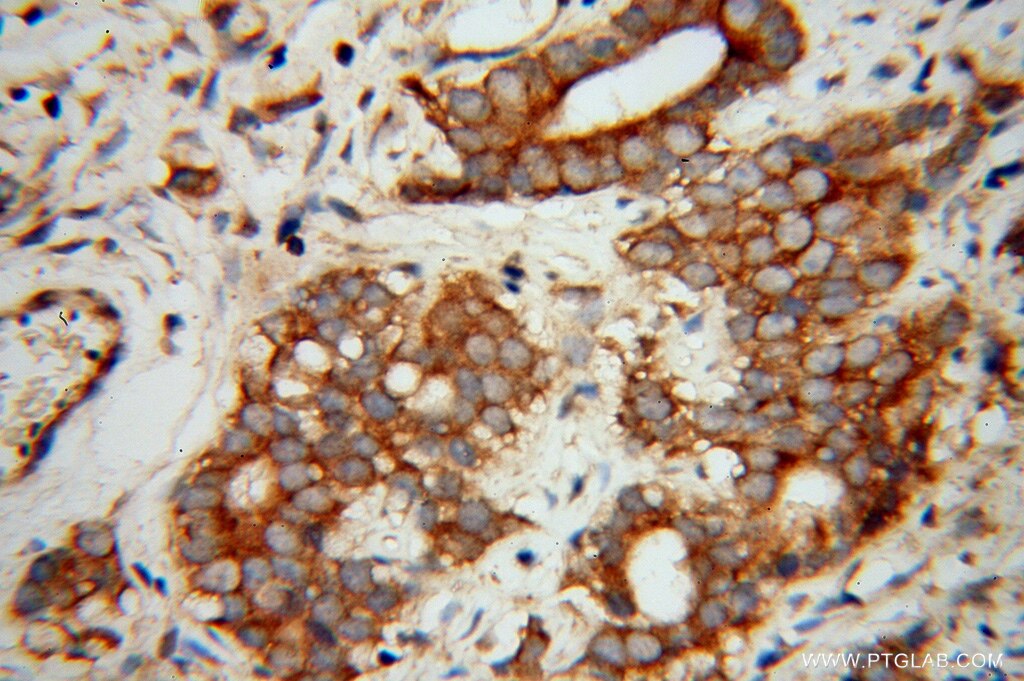
13527-1-PBS targets EIF5B in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | EIF5B fusion protein Ag4404 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B |
| Calculated molecular weight | 1220 aa, 139 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 175 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC032639 |
| Gene Symbol | EIF5B |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9669 |
| RRID | AB_2096200 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O60841 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Translation initiation requires the delivery of the initiator methionine tRNA to the 40S ribosomal subunit. The initiator methionine tRNA is delivered by the heterotrimeric complex EIF2 in a ternary complex with GTP that interacts with the 40S subunit. The resulting complex then binds to an mRNA and scans for the AUG start codon. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B (EIF5B) plays a role in recognition of the AUG codon in conjunction with translation factor eIF2, which functions to general translation initiation by promoting the binding of the formylmethionine-tRNA to ribosomes, and promotes joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit. A single crossreactive polypeptide of 175 kDa was detected, whereas the predicted size of the protein was 139 kDa. This size discrepancy may be the result of posttranslational modifications of EIF5B or, perhaps more likely, of unusual behavior in SDS-PAGE caused by the highly charged N-terminal region of EIF5B (PMID: 10200264 ).