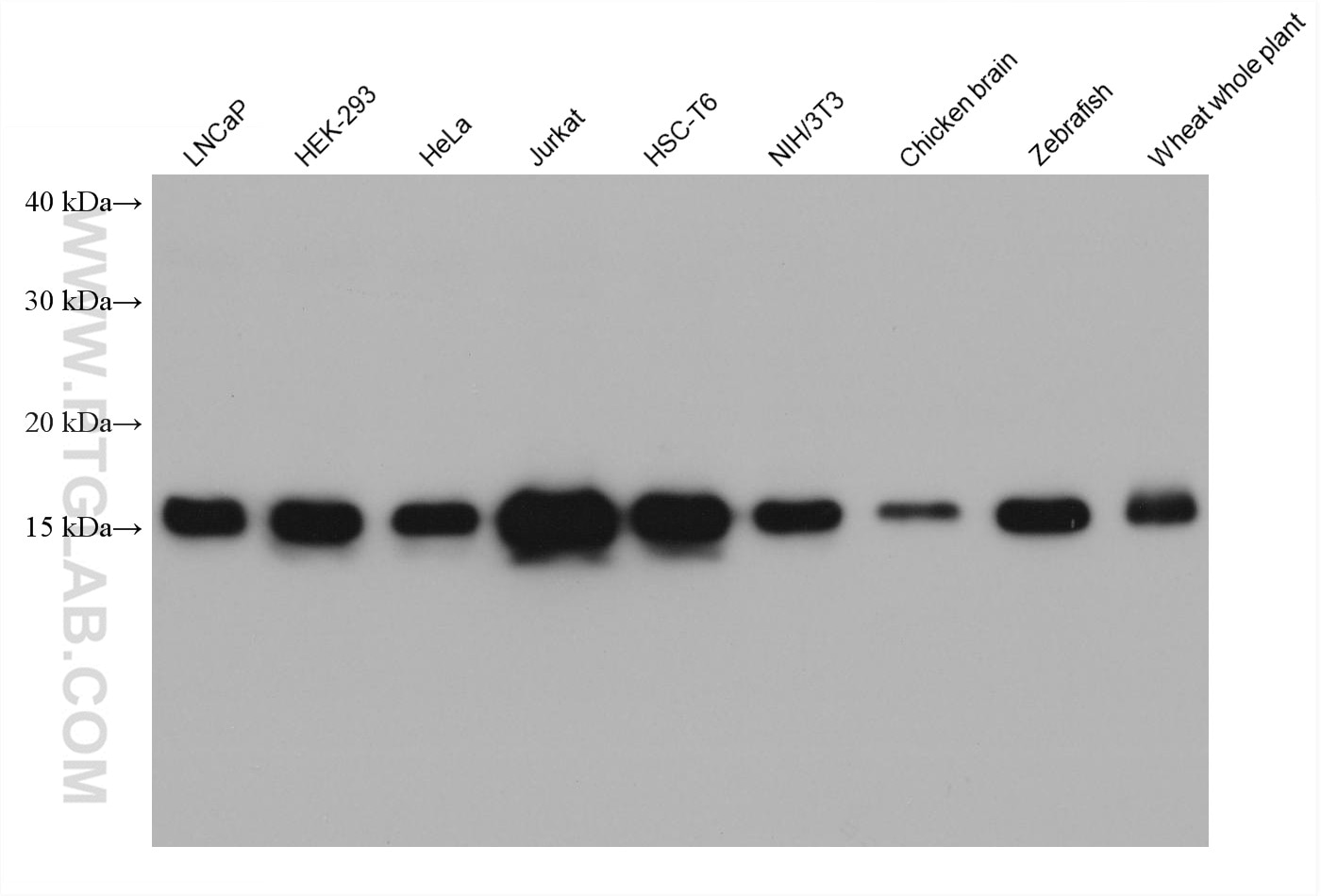
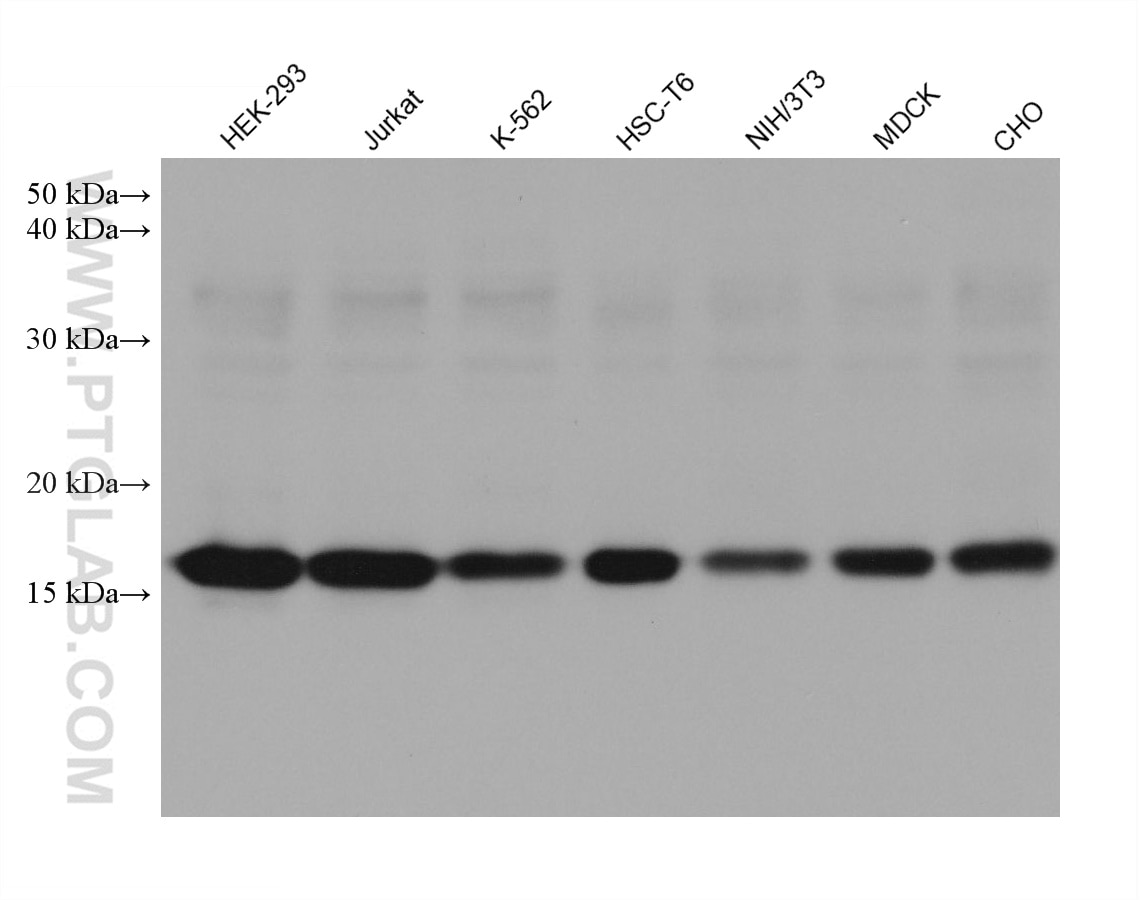
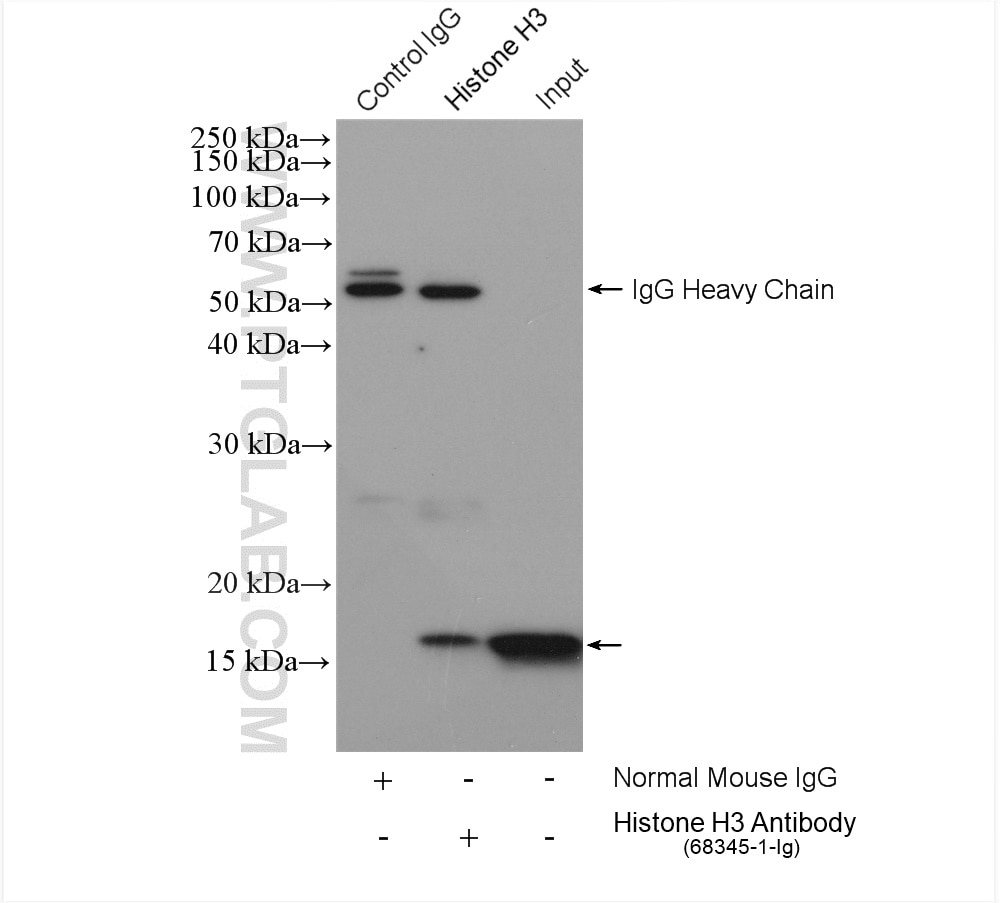
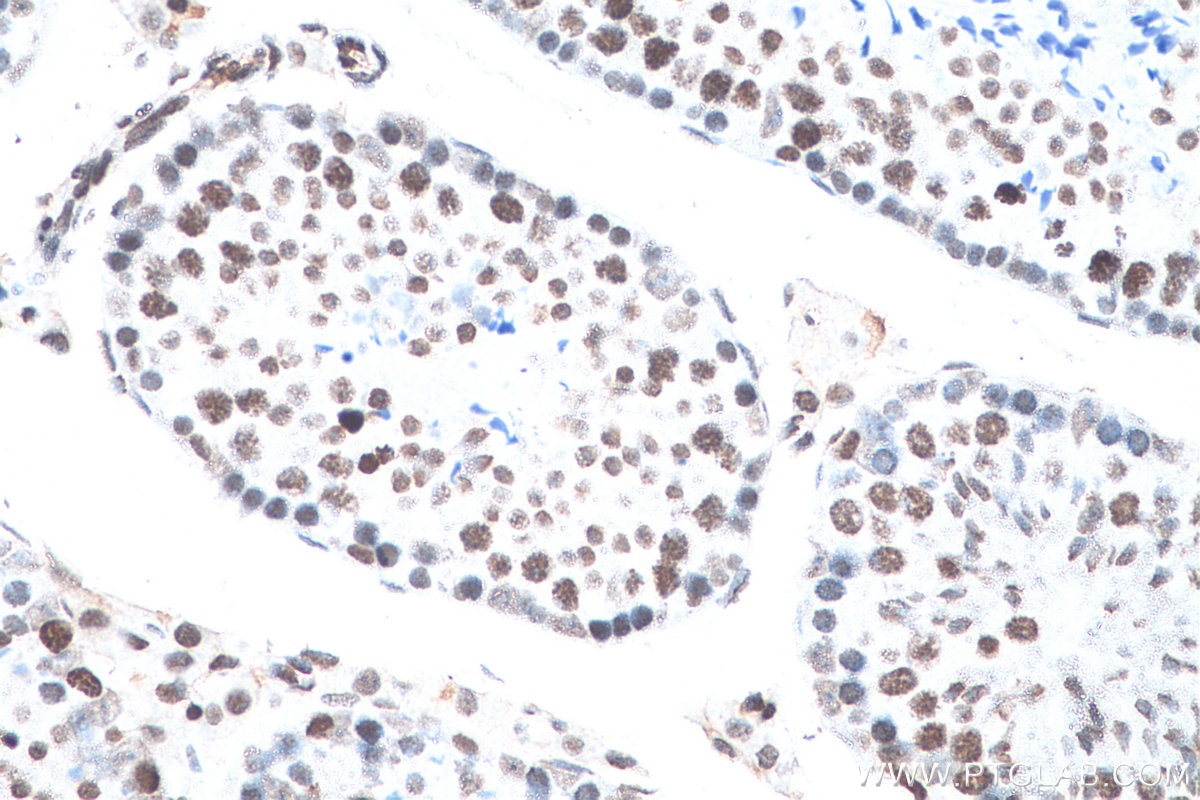
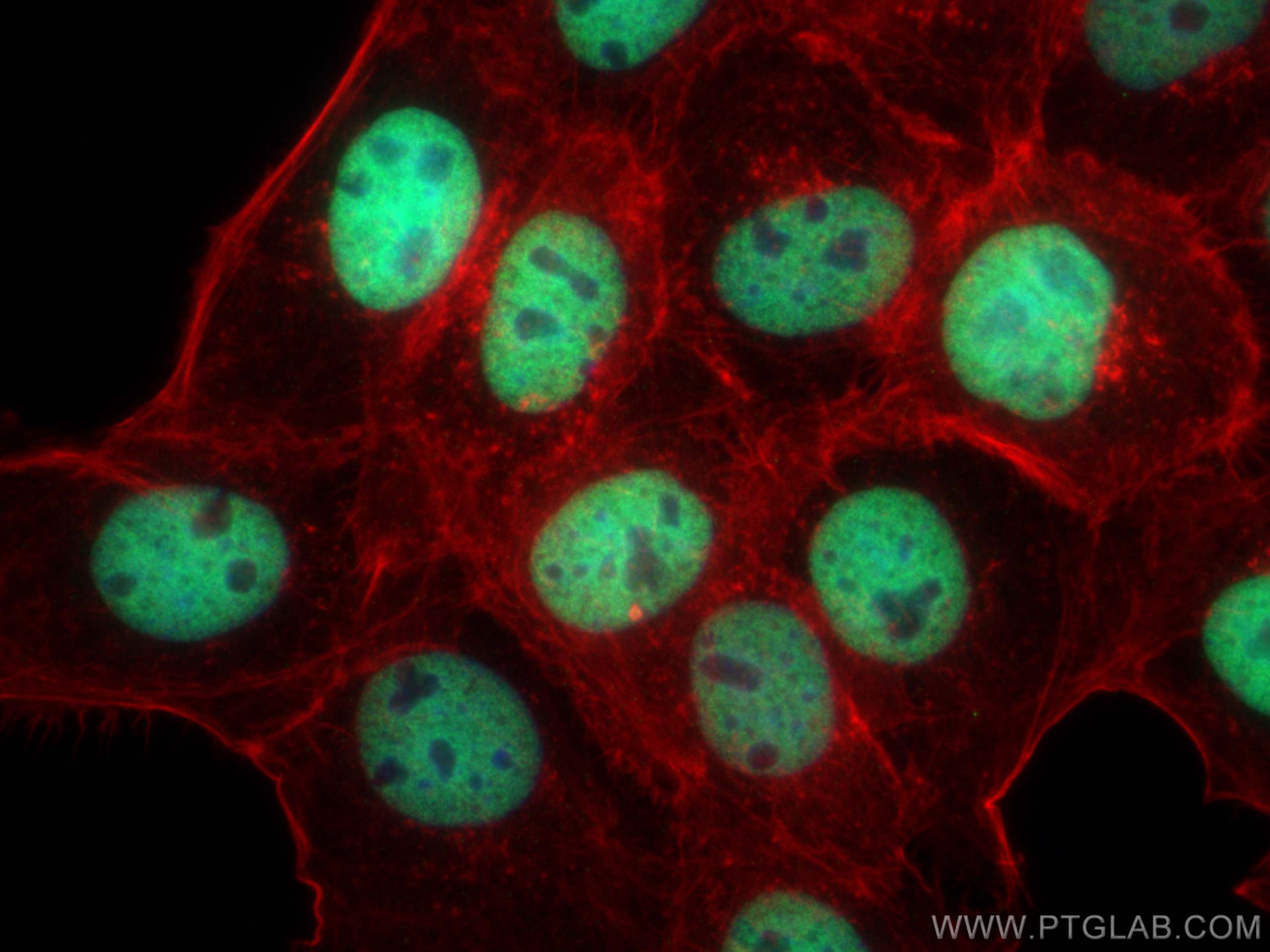
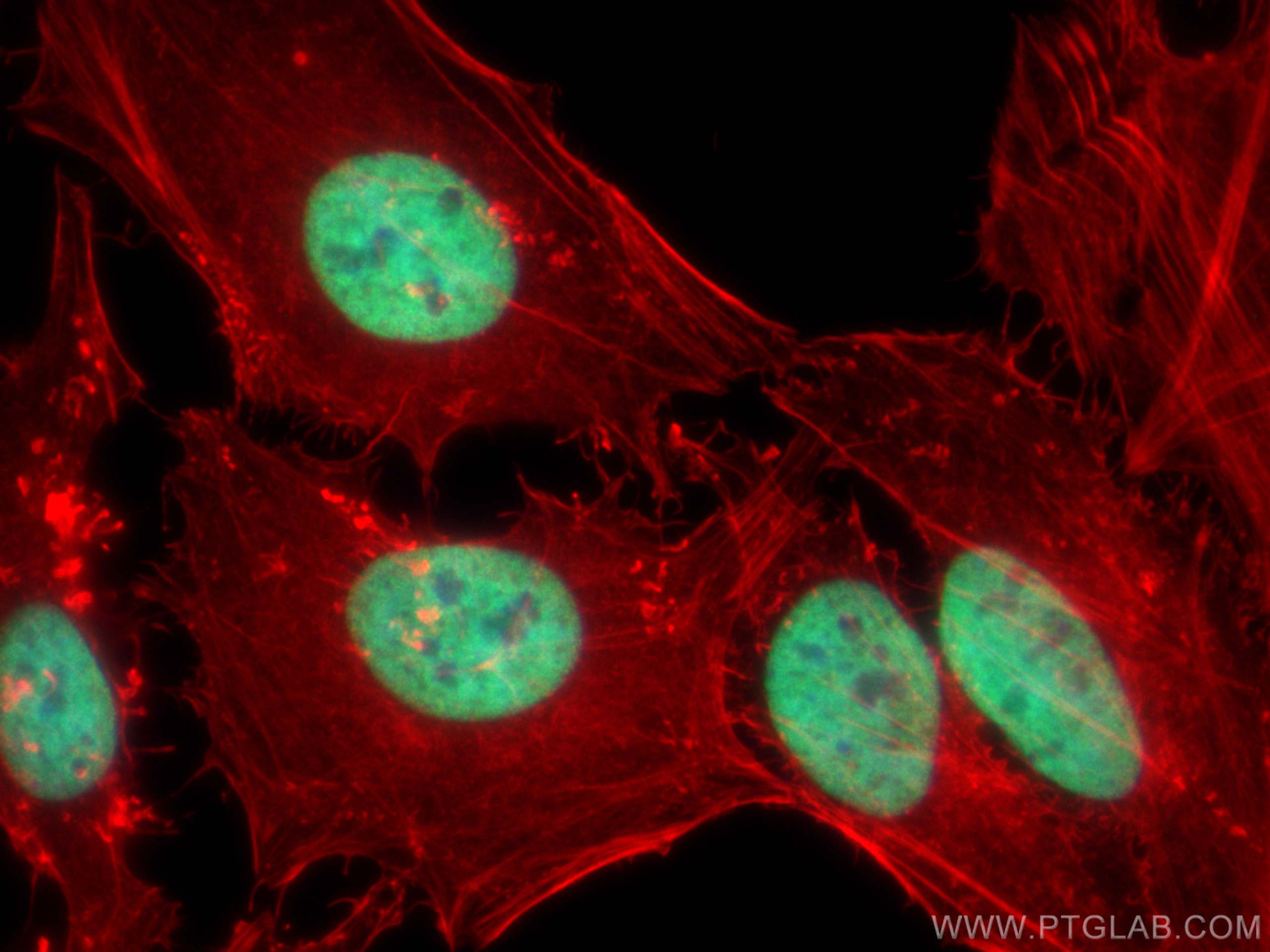
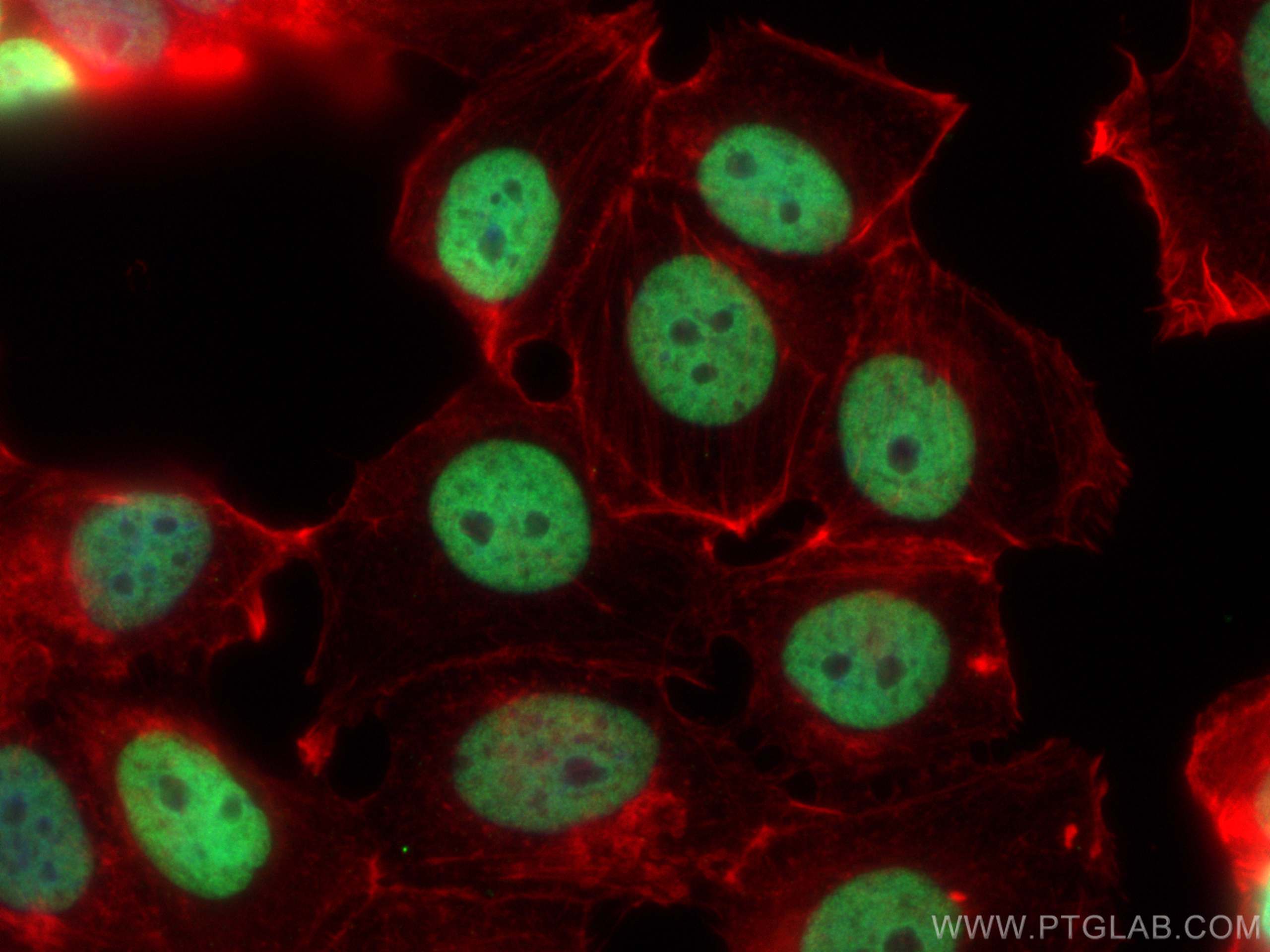
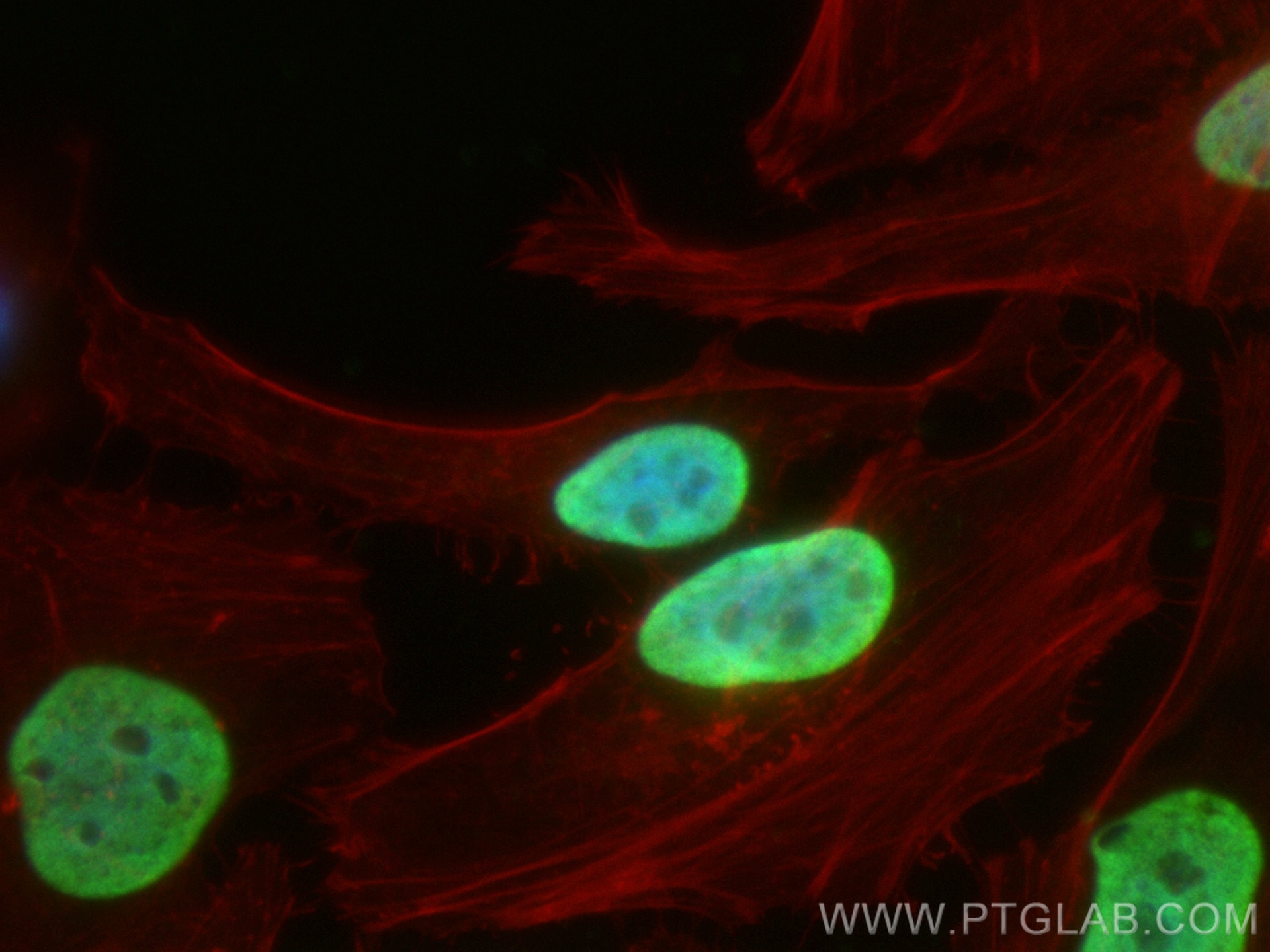
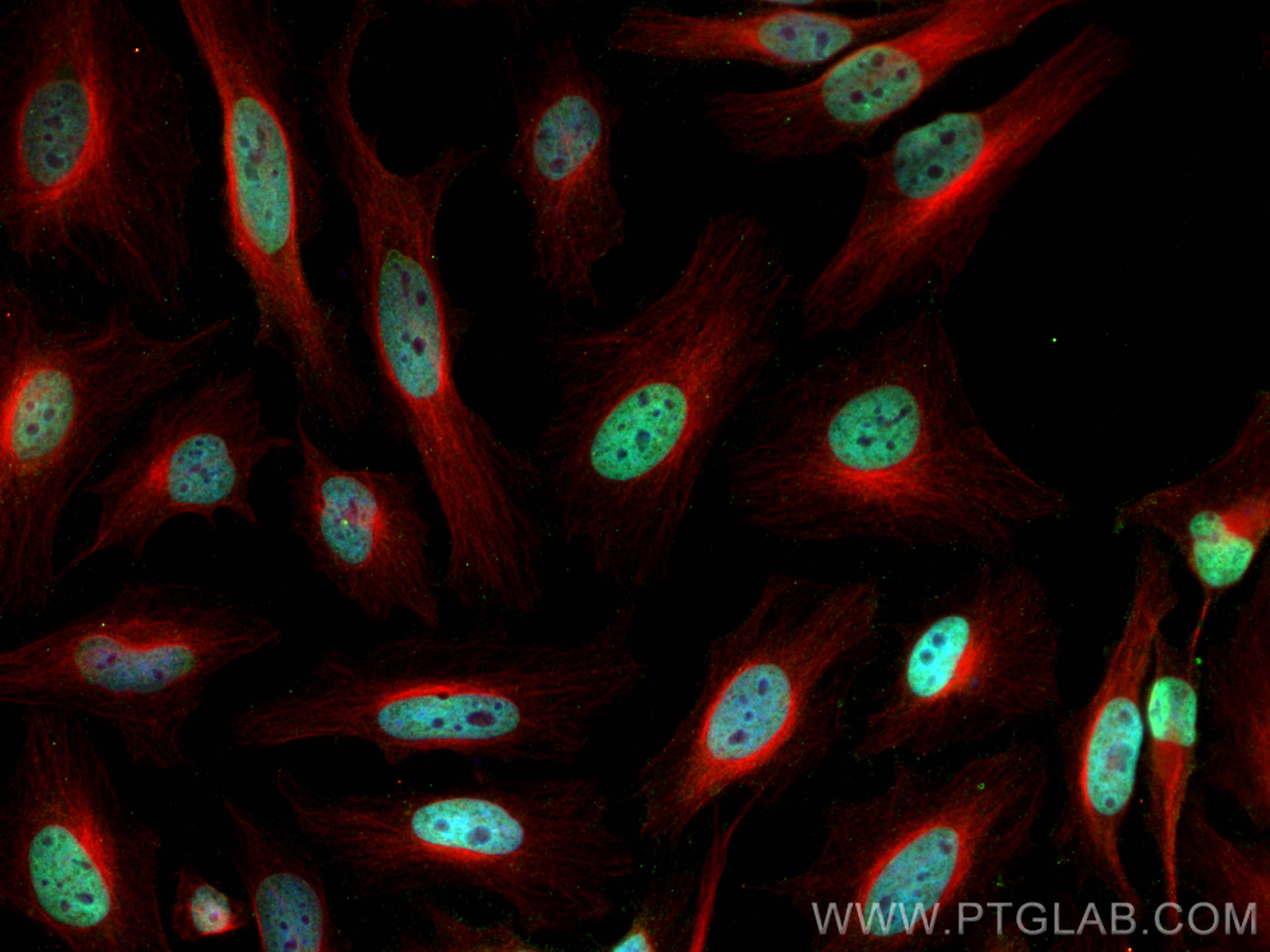
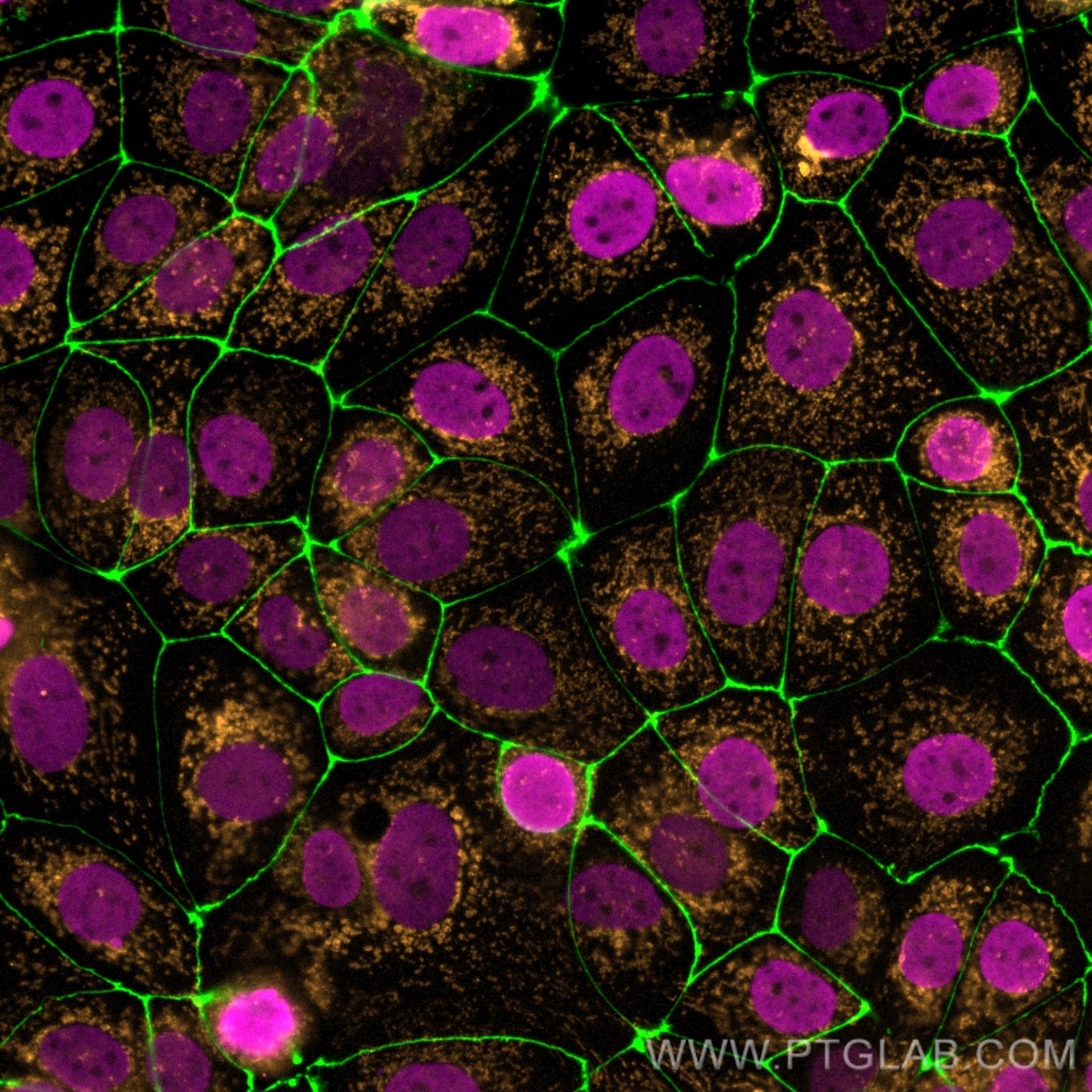
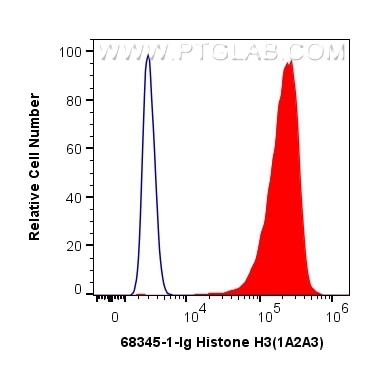
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
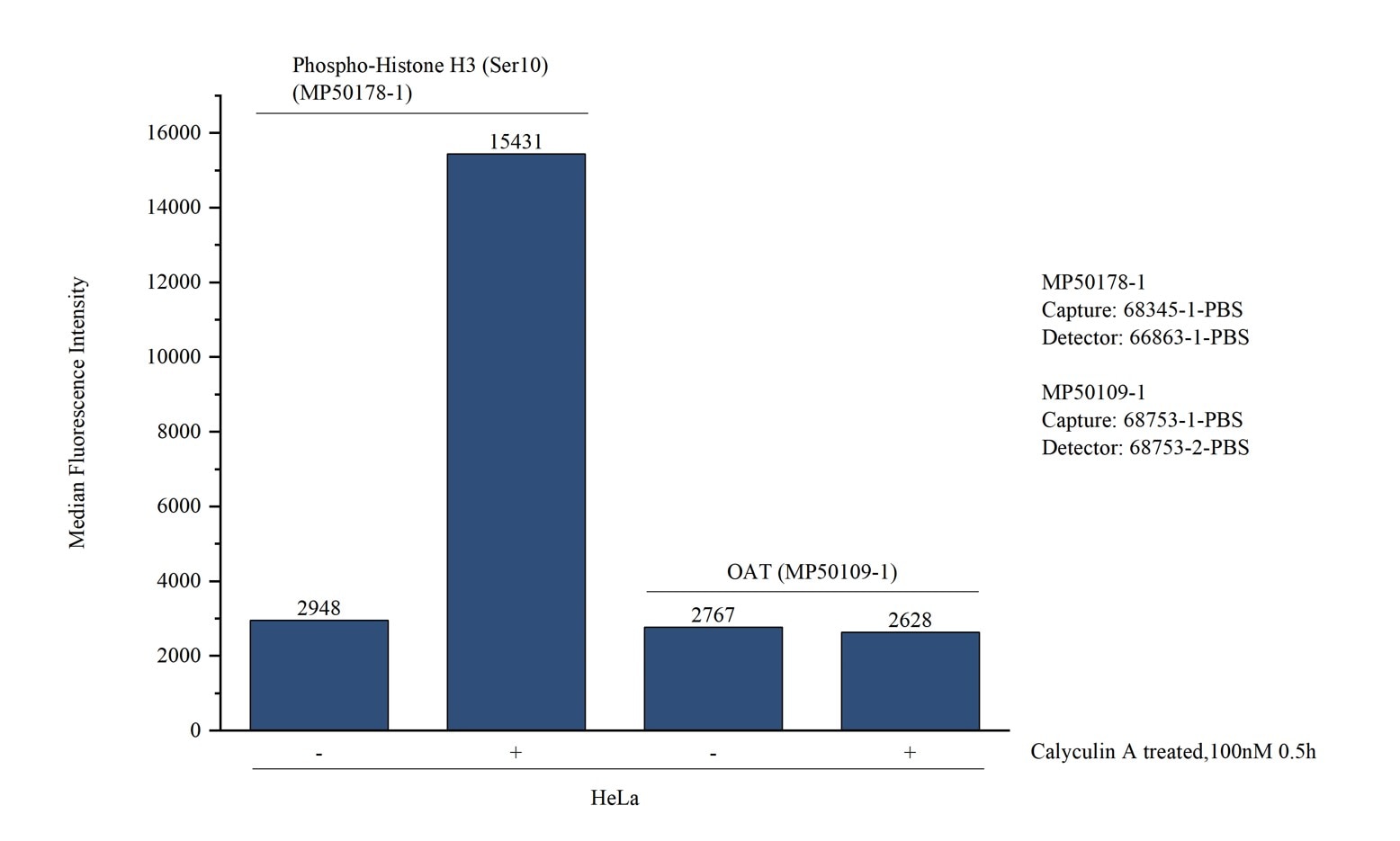
68345-1-PBS targets Histone H3 as part of a matched antibody pair:
MP50178-1: 68345-1-PBS capture and 66863-1-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit, canine, chicken, zebrafish, hamster, dog, wheat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | histone cluster 1, H3a |
| Observed molecular weight | 15-17 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC066245 |
| Gene Symbol | HIST1H3A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8350 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P68431 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Histones are small, highly basic proteins that consist of a globular domain with unstructured N- and C-terminal tails protruding from the main structure. Histone H3 is one of the five main histones that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form an octamer, around which approximately 146 bp of DNA is wrapped in repeating units, called nucleosomes. In addition to their role in DNA compartmentalization, histones also play crucial roles in various biologic processes, including gene expression and regulation, DNA repair, chromatin condensation, cell cycle progression, chromosome segregation, and apoptosis. The ability of histones to regulate chromatin dynamics primarily originates from various posttranslational modifications carried out by histone-modifying enzymes.