Validation Data Gallery
Filter:
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
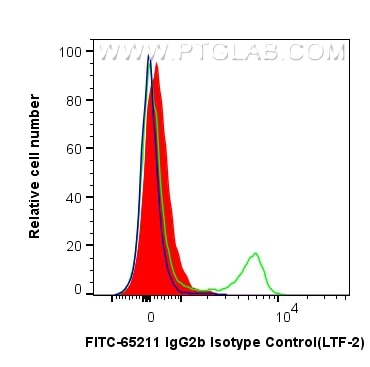
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.25 ug per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| FC | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
FITC-65211 targets IgG2b Isotype Control in FC applications and shows reactivity with samples.
| Tested Reactivity | |
| Host / Isotype | Rat / IgG2b, kappa |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
N/A 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | IgG2b Isotype Control |
| Gene Symbol | |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | |
| RRID | AB_2883825 |
| Conjugate | FITC Plus Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 495 nm / 524 nm |
| 激发激光 | Blue laser (488 nm) |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
The LTF-2 immunoglobulin is useful as an isotype-matched control. The LTF-2 immunolglobulin has an unknown binding specificity and is used as an isotype control for rat IgG2b antibodies. This antibody has been quality-tested for flow cytometry as negative control.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for FITC Plus IgG2b Isotype Control antibody FITC-65211 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |