Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
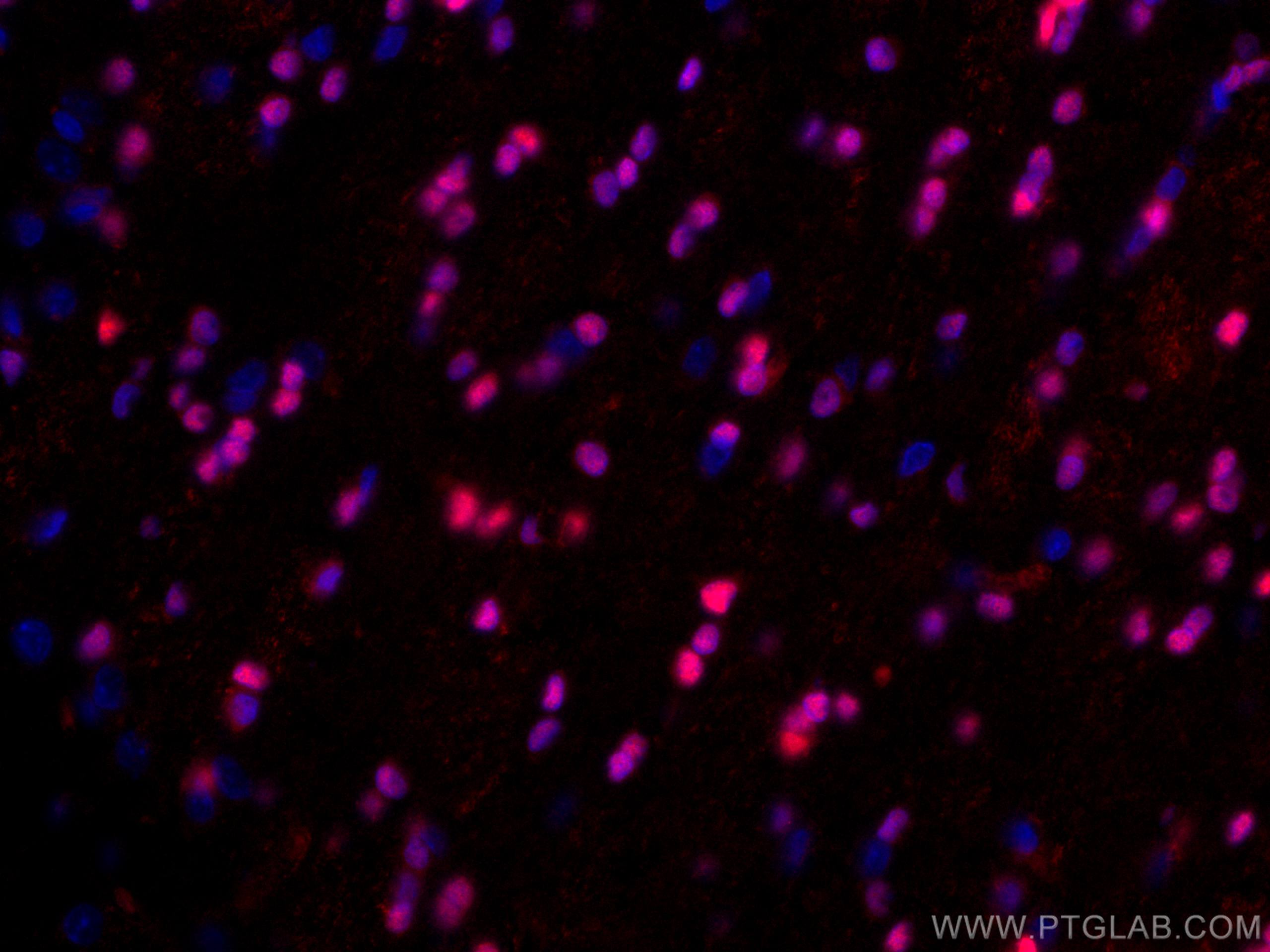
| Positive IF-P detected in | rat brain tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
CL594-13999 targets OLIG2 in IF-P applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag5089 Product name: Recombinant human OLIG2 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-323 aa of BC047511 Sequence: MDSDASLVSSRPSSPEPDDLFLPARSKGSSGSAFTGGTVSSSTPSDCPPELSAELRGAMGSAGAHPGDKLGGSGFKSSSSSTSSSTSSAAASSTKKDKKQMTEPELQQLRLKINSRERKRMHDLNIAMDGLREVMPYAHGPSVRKLSKITTLLLARNYILMLTNSLEEMKRLVSEIYGGHHAGFHPSACGGLAHSAPLPAATAHPAAAAHAAHHPAVHHPILPPAAAAAAAAAAAAAVSSASLPGSGLPSVGSIRPPHGLLKSPSAAAAAPLGGGGGGSGASGGFQHWGGMPCPCSMCQVPPPHHHVSAMGAGSLPRLTSDAK 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | oligodendrocyte lineage transcription factor 2 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 32 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 32 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC047511 |
| Gene Symbol | OLIG2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10215 |
| RRID | AB_2919802 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| 激发激光 | Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm) |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q13516 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
What is the specificity of Olig2?
Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 (OLIG2) is expressed by cells found in the central nervous system (CNS) called oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), which form the myelin sheaths wrapping the axons of neurons in the brain and spinal cord. OPCs differentiate into oligodendrocytes that form the myelin, providing metabolic support and saltatory conduction. OLIG2 is expressed broadly throughout their development to OPCs. This protein can be used to identify many cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage. It is found mostly in the nucleoplasm but also in the cytoplasm.
What is the function of OLIG2?
The basic helix-loop-helix structure of OLIG2 allows it to function as a transcription factor, determining cell fate in the development of neural tissue, where it is located at the pMN domain in the embryonic spinal cord. Expression of OLIG2 causes neural precursors to develop into oligodendrocytes or into motor neurons and expression is then maintained postnatally. OLIG2 co-operates with other factors to cause this differentiation from precursors, although overexpression alone can cause differentiation to the oligodendrocyte lineage.1 The continued expression of OLIG2 in OPCs indicates an ongoing role in the maintenance of their stemness.
What is the involvement of OLIG2 in disease?
The expression of OLIG2 in glioblastoma, the most common type of malignant brain tumor in adults, is well characterized, where the pathological function is an extension of the normal function. Stem-like cells that propagate the tumor growth have been shown to be OLIG2-expressing, and are one of the key transcription factors involved in the re-programming of differentiated cells of the tumor to stem-like cells.2 OLIG2 has also been associated with demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS), as OPCs have been shown to be involved in the process of remyelination.3
1. Liu, Z. et al. Induction of oligodendrocyte differentiation by Olig2 and Sox10: Evidence for reciprocal interactions and dosage-dependent mechanisms. Dev. Biol. 302, 683-693 (2007).
2. Wegener, A. et al. Gain of Olig2 function in oligodendrocyte progenitors promotes remyelination. Brain 138, 120-35 (2015).
3. Ettle, B., Schlachetzki, J. C. M. & Winkler, J. Oligodendroglia and Myelin in Neurodegenerative Diseases: More Than Just Bystanders? Mol. Neurobiol. 53, 3046-3062 (2016).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL594 OLIG2 antibody CL594-13999 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |