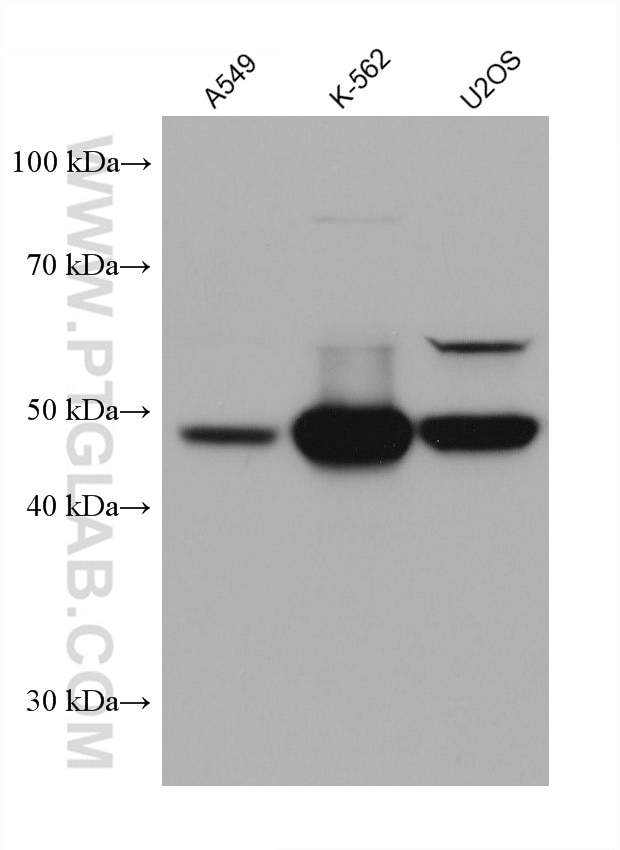
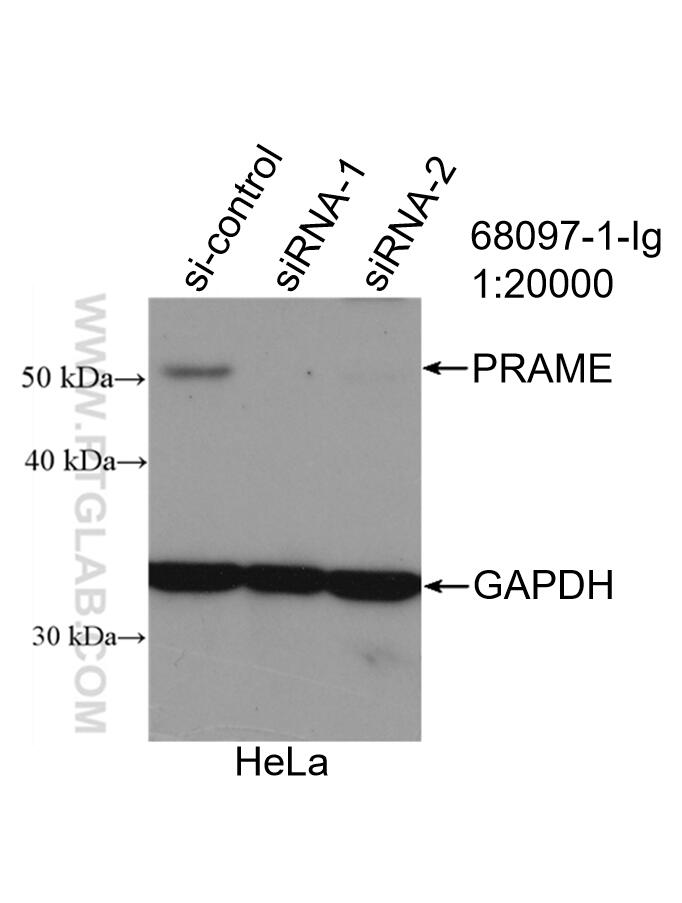
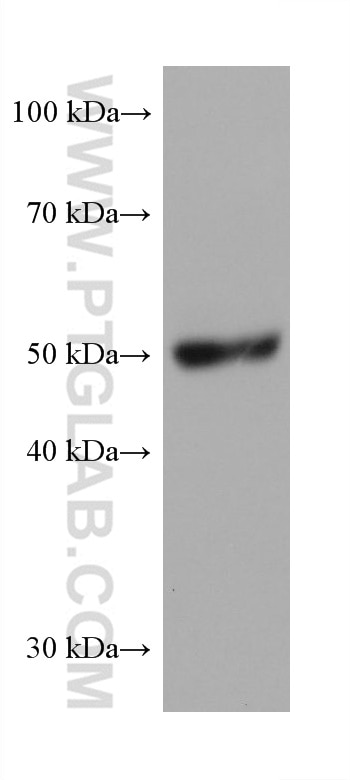
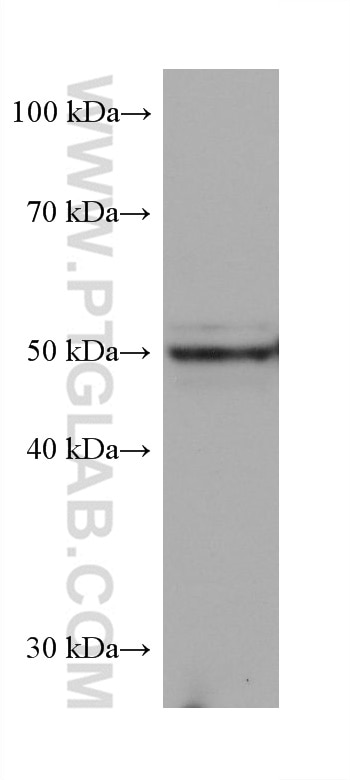
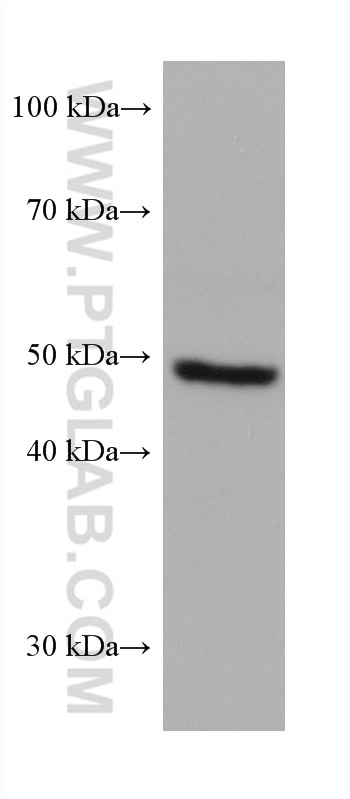
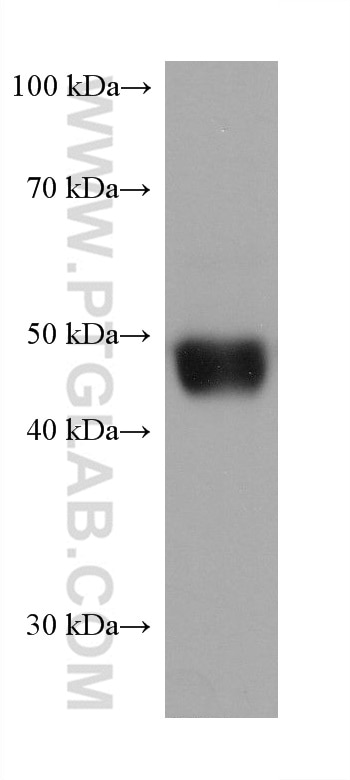
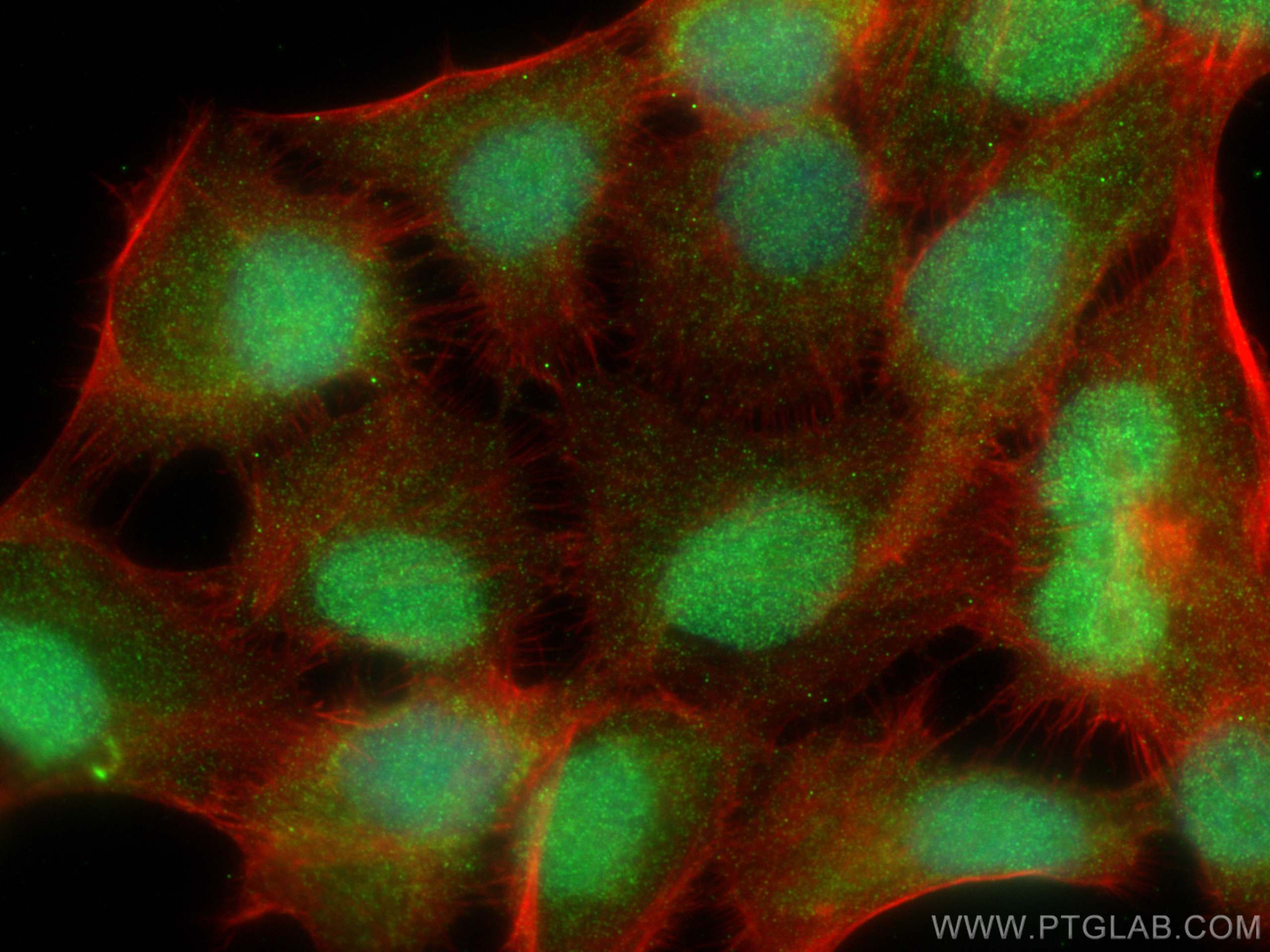
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
68097-1-PBS targets PRAME in WB, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | PRAME fusion protein Ag1906 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma |
| Calculated molecular weight | 509 aa, 58 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 50 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC014074 |
| Gene Symbol | PRAME |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 23532 |
| RRID | AB_2918834 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P78395 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
The PRAME (preferentially expressed antigen of melanoma) gene was previously shown to be overexpressed in ovarian/primary peritoneal serous carcinoma compared with malignant mesothelioma using gene expression arrays. It is considered a melanocyte differentiation antigen which is overexpressed in both solid and hematologic tumors. In normal tissue, a very low level of PRAME expression is found in normal testis, adrenals, ovary and endometrium. A high level of PRAME expression has been reported for several solid tumors, including ovarian cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer and melanomas, medulloblastoma, sarcomas, head and neck cancers, neuroblastoma, renal cancer, and Wilms'tumor. As a nuclear transcriptional repressor protein, PRAME binds to retinoic acid receptor a, thereby inhibiting retinoic acid induced differentiation, growth arrest, and apoptosis.