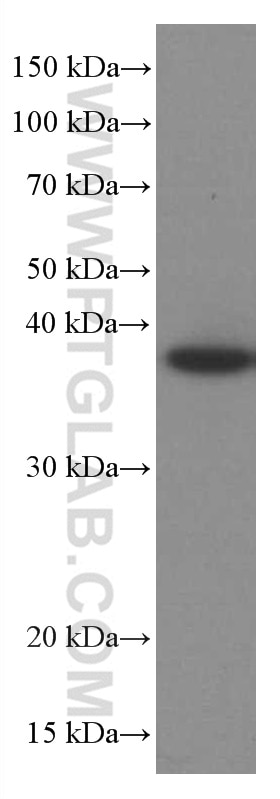
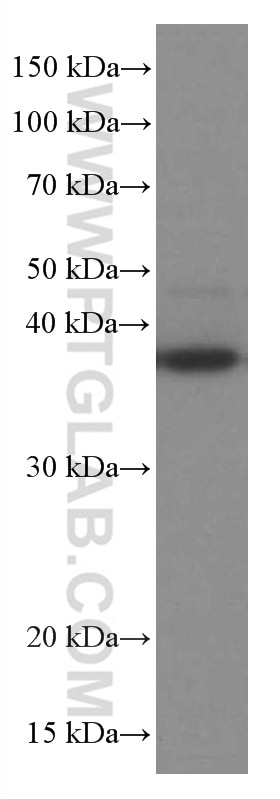
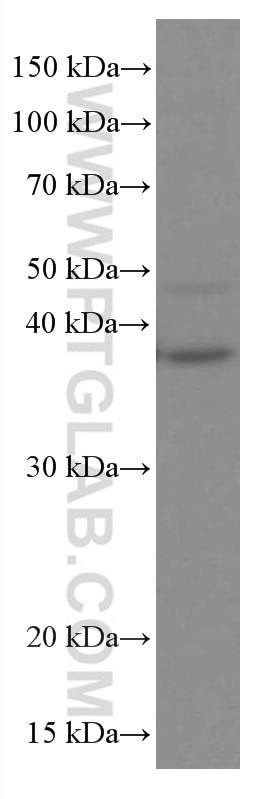
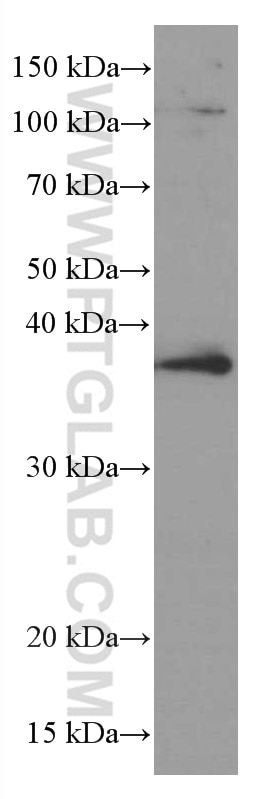
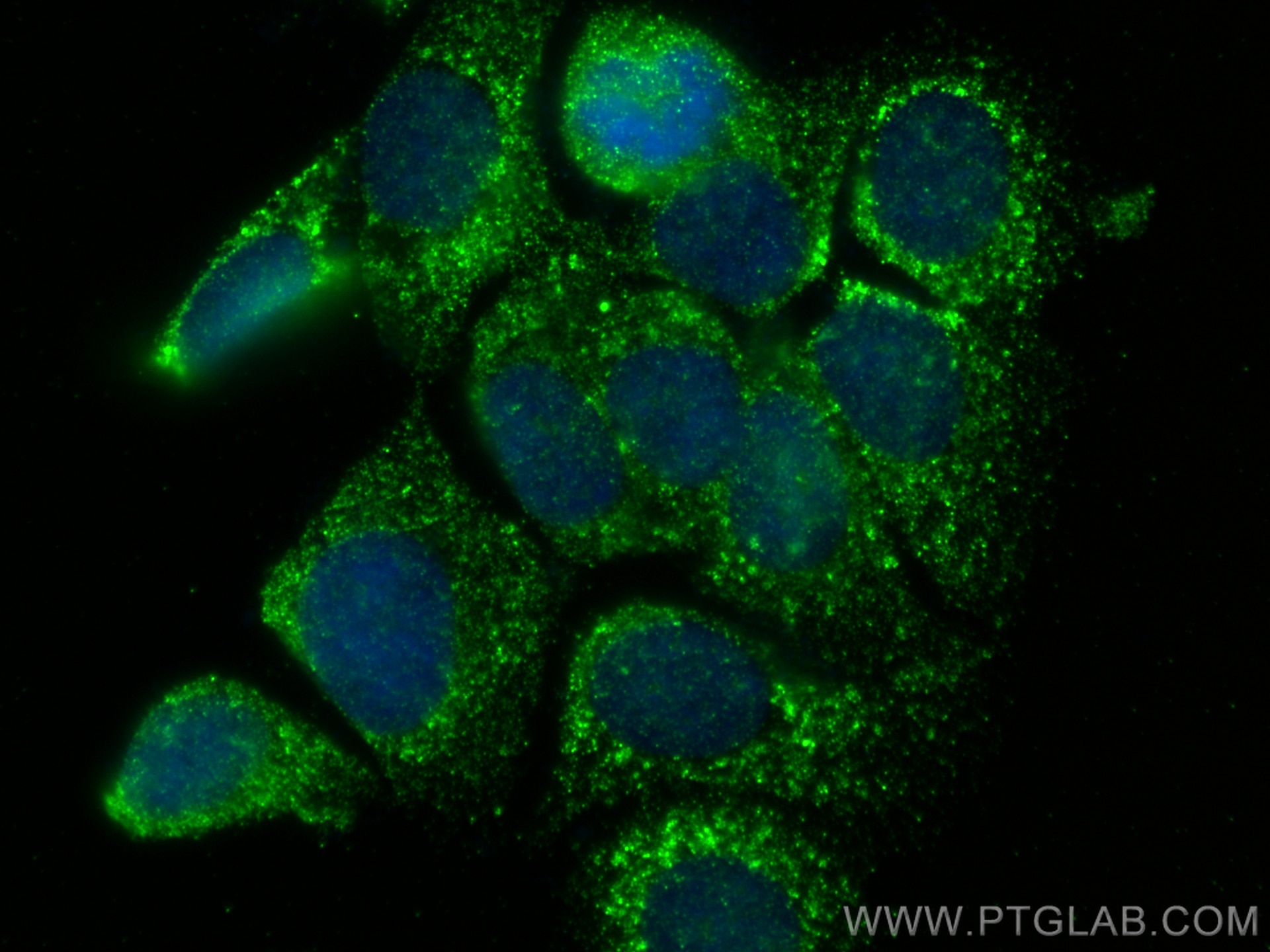
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
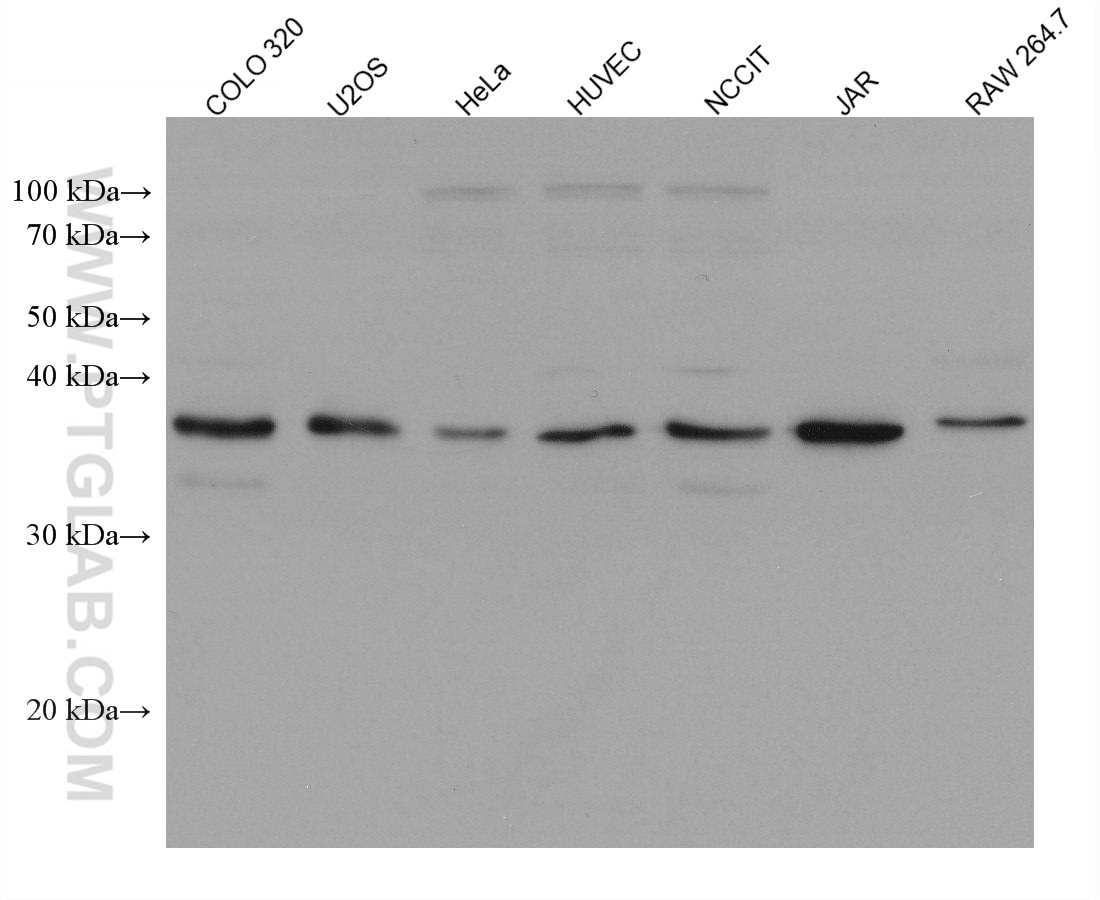
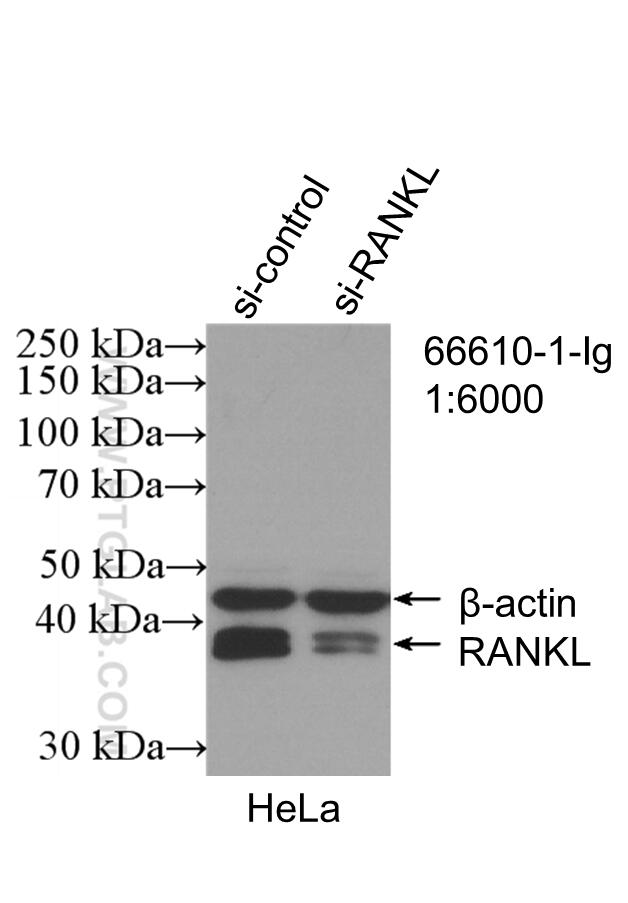
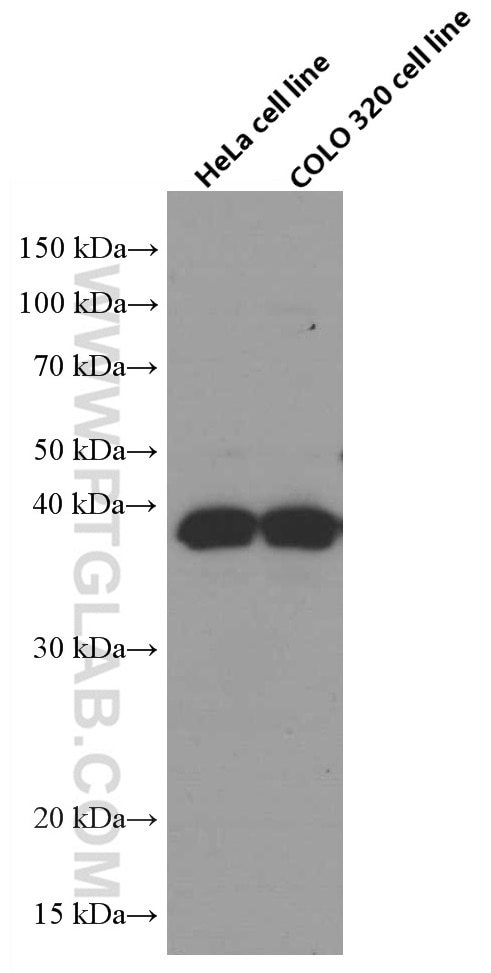
| Positive WB detected in | COLO 320 cells, HeLa cells, U2OS cells, HUVEC cells, NCCIT cells, human spleen tissue, DC2.4 cells, JAR cells, RAW 264.7 cells |
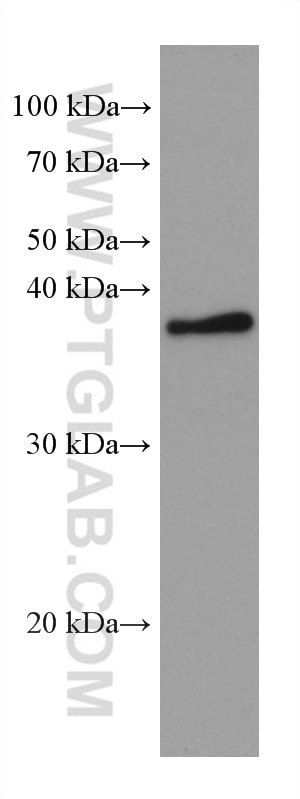
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | MCF-7 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:400-1:1600 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 8 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
Product Information
66610-1-Ig targets TNFSF11/RANKL in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | TNFSF11/RANKL fusion protein Ag19975 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 317 aa, 35 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 35-38 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC074890 |
| Gene Symbol | RANKL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8600 |
| RRID | AB_2881970 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O14788 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
TNFSF11 also known as RANKL, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. RANKL is a polypeptide of 217 amino acids that exerts its biological activity both in a transmembrane form of about 40-45 kDa and in soluble one of 31 kDa (PMID: 15308315). The membrane-bound RANKL (mRANKL) is cleaved into a sRANKL by the metalloprotease-disintegrin TNF-alpha convertase (TACE) or a related metalloprotease (MP). RANKL induces osteoclast formation through its receptor, RANK, which transduces signals by recruiting adaptor molecules, such as the TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family of proteins. RANKL was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. RANKL was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for TNFSF11/RANKL antibody 66610-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for TNFSF11/RANKL antibody 66610-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Cancer Gut microbiota deficiency ameliorates multiple myeloma and myeloma-related bone disease by Th17 cells in mice models | ||
Folia Histochem Cytobiol Platelet-rich plasma ameliorates cartilage degradation in rat models of osteoarthritis via the OPG/RANKL/RANK system | ||
Cell Death Dis RANK promotes colorectal cancer migration and invasion by activating the Ca2+-calcineurin/NFATC1-ACP5 axis. | ||
Open Life Sci Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice | ||
Adv Healthc Mater Structured Polymers Enable the Sustained Delivery of Glucocorticoids within the Intra-Articular Space | ||
J Periodontal Res Role of Piezo1 in modulating the RANKL/OPG ratio in mouse osteoblast cells exposed to Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide and mechanical stress |