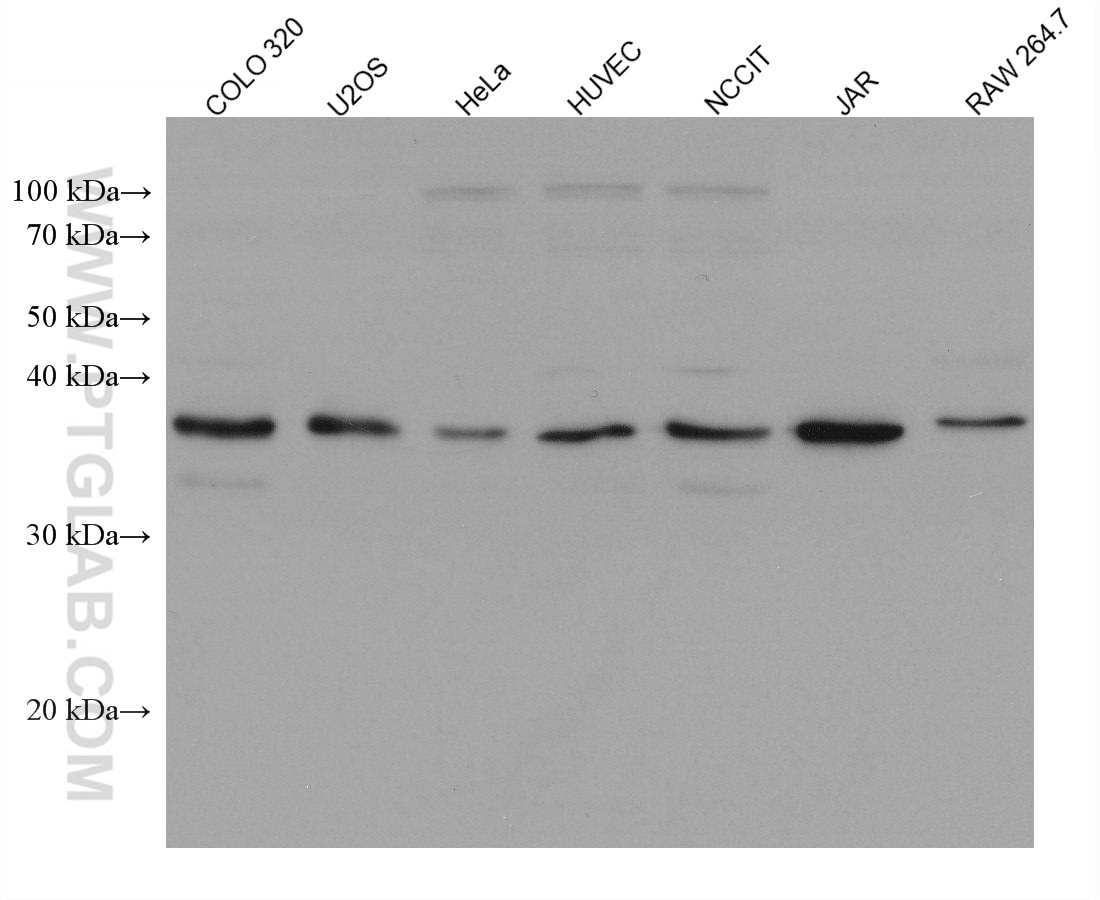
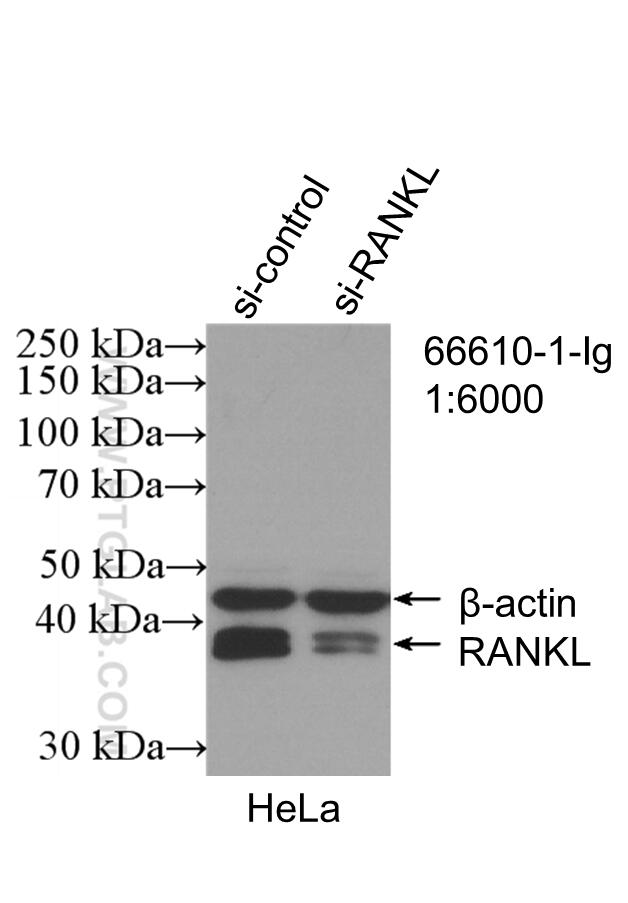
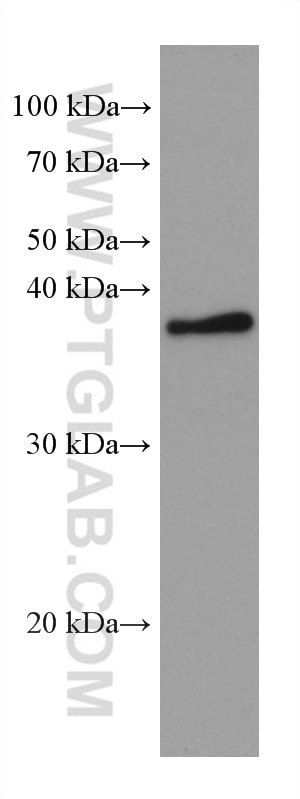
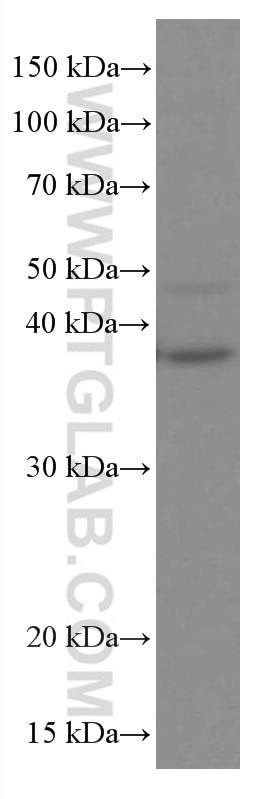
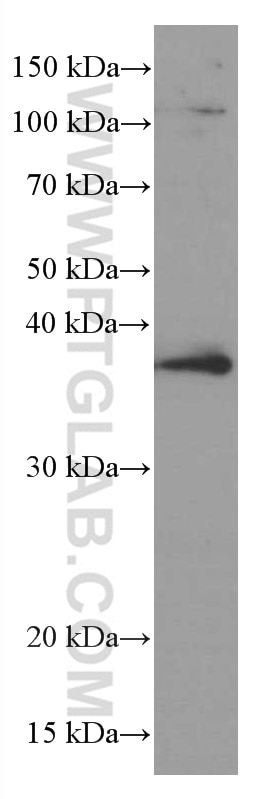
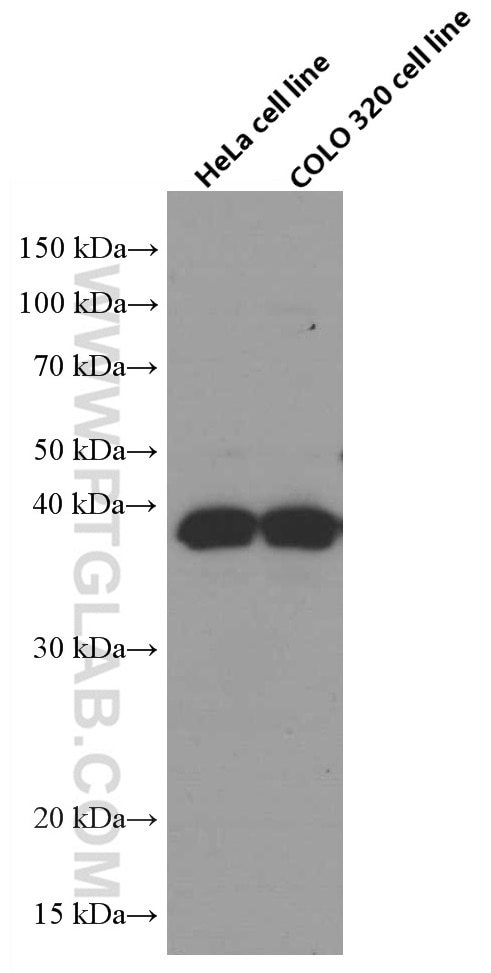
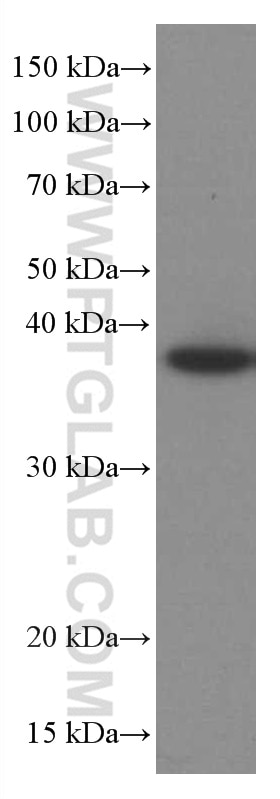
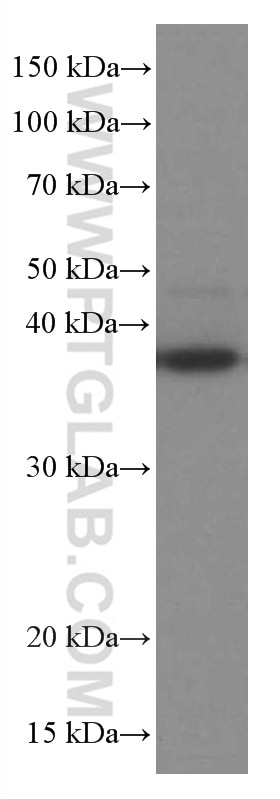
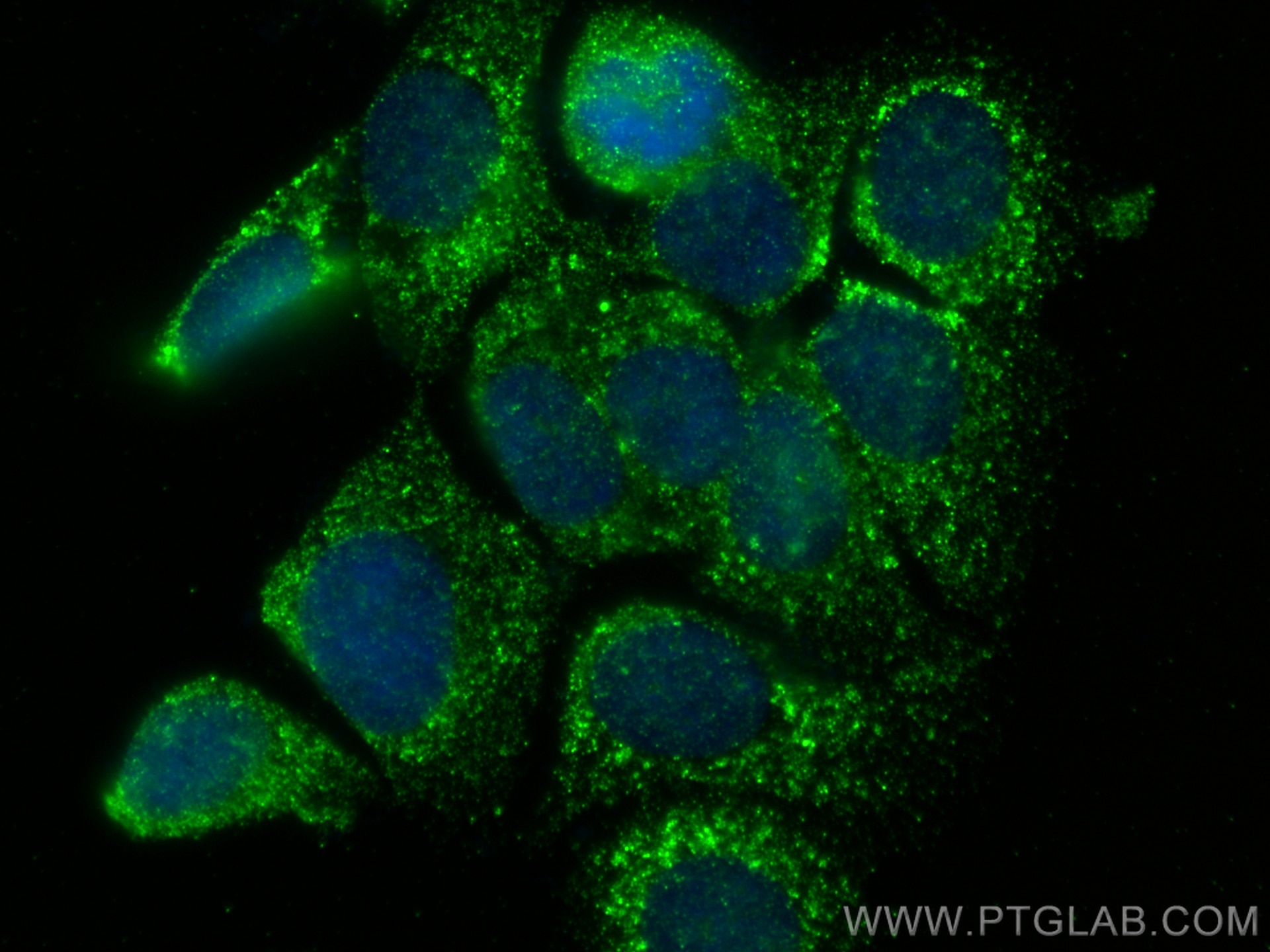
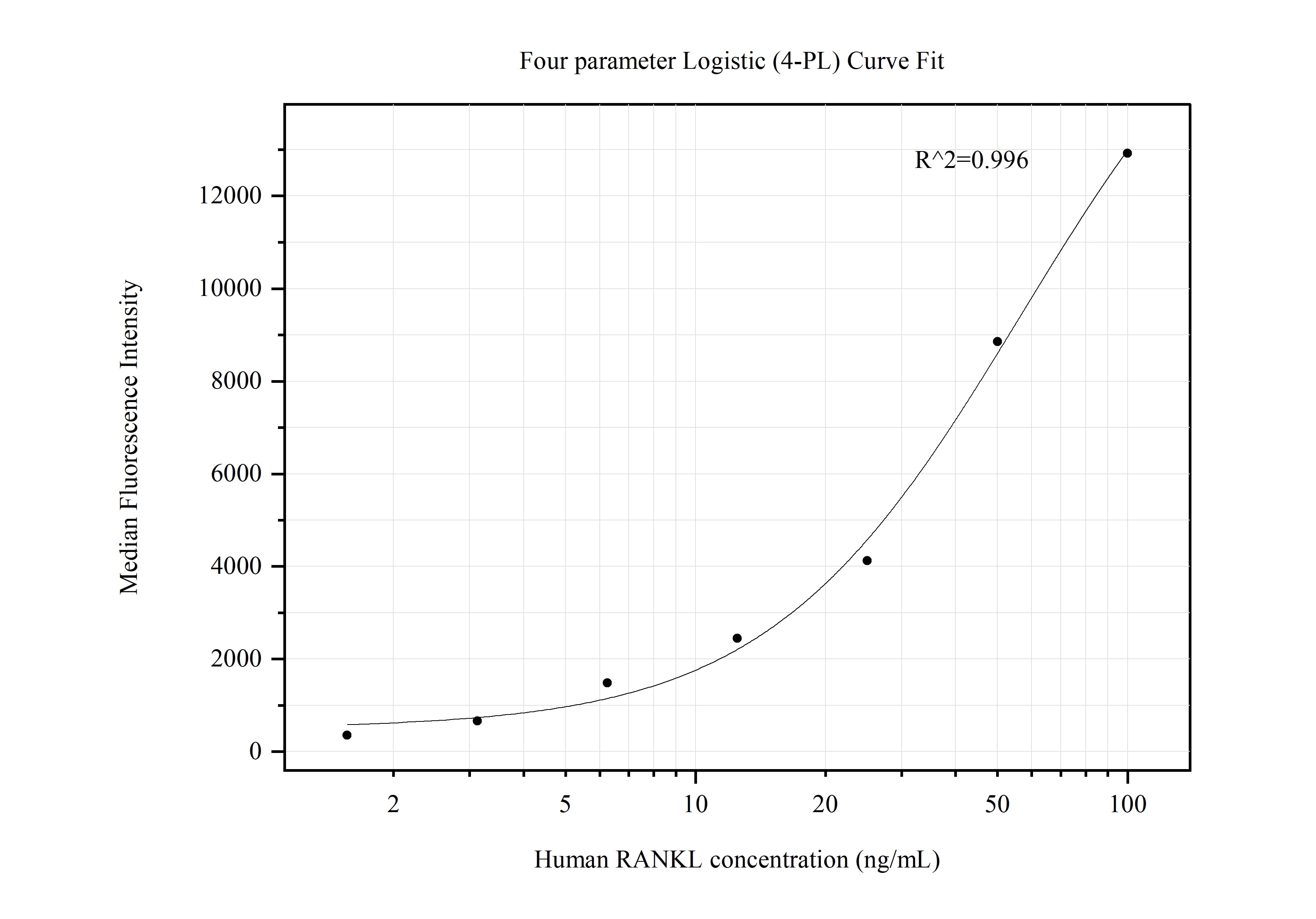
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66610-1-PBS targets TNFSF11/RANKL as part of a matched antibody pair:
MP50526-1: 66610-1-PBS capture and 66610-2-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | TNFSF11/RANKL fusion protein Ag19975 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 317 aa, 35 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 35-38 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC074890 |
| Gene Symbol | RANKL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8600 |
| RRID | AB_2881970 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O14788 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
TNFSF11 also known as RANKL, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. RANKL is a polypeptide of 217 amino acids that exerts its biological activity both in a transmembrane form of about 40-45 kDa and in soluble one of 31 kDa (PMID: 15308315). The membrane-bound RANKL (mRANKL) is cleaved into a sRANKL by the metalloprotease-disintegrin TNF-alpha convertase (TACE) or a related metalloprotease (MP). RANKL induces osteoclast formation through its receptor, RANK, which transduces signals by recruiting adaptor molecules, such as the TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family of proteins. RANKL was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. RANKL was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis.