Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
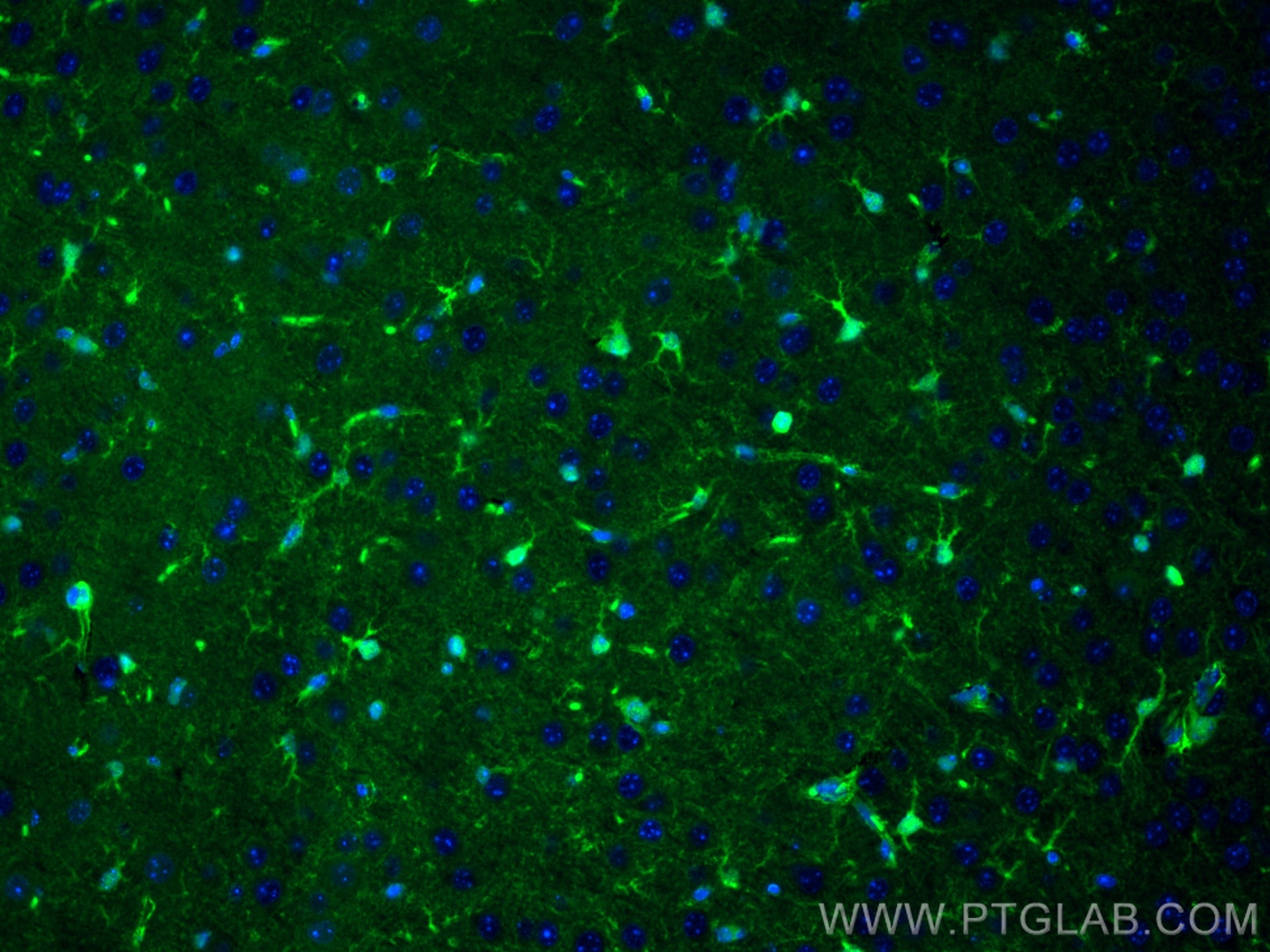
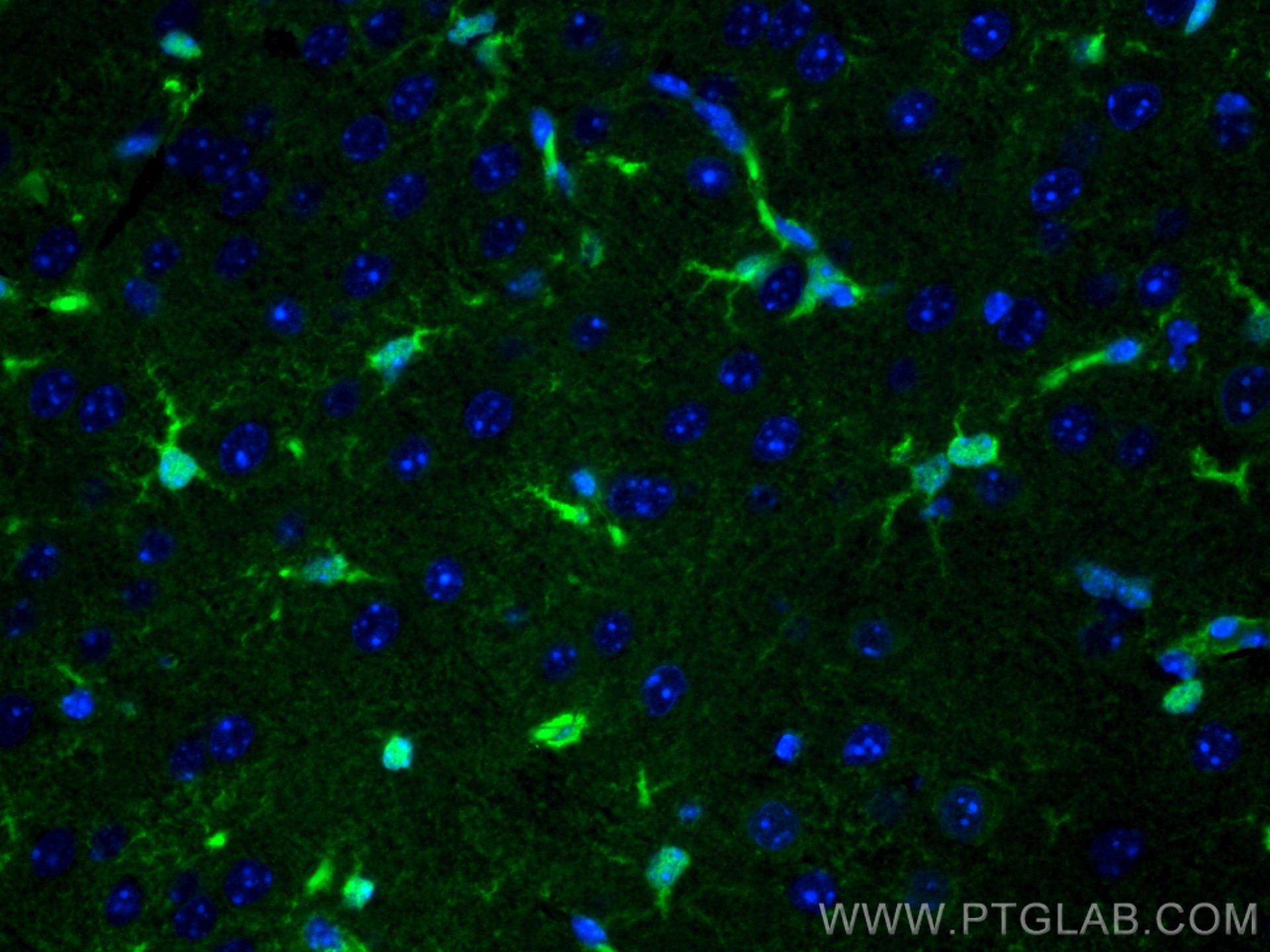
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse brain tissue |
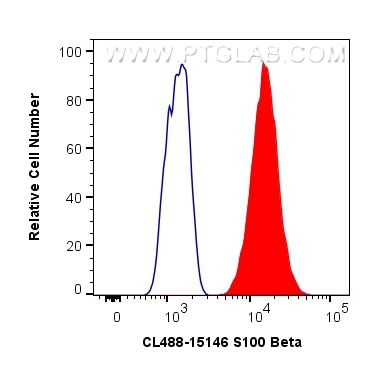
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | A375 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.80 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL488-15146 targets S100B in IF-P, FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag7440 Product name: Recombinant human S100B protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-92 aa of BC001766 Sequence: MSELEKAMVALIDVFHQYSGREGDKHKLKKSELKELINNELSHFLEEIKEQEVVDKVMETLDNDGDGECDFQEFMAFVAMVTTACHEFFEHE 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | S100 calcium binding protein B |
| Calculated molecular weight | 11 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 11 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC001766 |
| Gene Symbol | S100 Beta |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6285 |
| RRID | AB_2934410 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| 激发激光 | Blue laser (488 nm) |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P04271 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
S100B belongs to the EF-band calcium binding proteins and is found primarily in astrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS). S100B has a variety of functions, including calcium homeostasis, cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and survival, as well as neurite outgrowth and regeneration.
1. What is the molecular weight of S100B?
S100B protein is composed of non-covalently linked homodimers of 11 kDa size.
2. What is the subcellular localization of S100B?
S100B localizes to the nucleus and cytoplasm, associating with intracellular membranes, the centrosomes, microtubules, and type III intermediate filaments (PMID: 19110011). Additionally, it can be released from astrocytes into the extracellular space and can enter the bloodstream.
3. What is the expression pattern of S100B?
S100B is predominantly expressed in astrocytes and maturing oligodendrocytes but is also present in other cell types such as kidney epithelial cells, neural progenitor cells, pituicytes, ependymocytes, chondrocytes, adipocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, certain lymphocyte subpopulations, skeletal myofibers, myoblasts, and muscle satellite cells (PMID: 19110011). S100B is a commonly used marker of Schwann cells and reactive astrocytes in ICC, IHC, and WB applications.
4. What is the diagnostic use of S100B in the clinic?
S100B is naturally secreted by astrocytes into the extracellular space and low amounts of S100B can pass through the brain-blood barrier and enter the bloodstream. Elevated levels of S100B in the serum are observed in patients with traumatic head injuries, as well as in patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases (PMID: 30144068). This increase in S100B levels is attributed to the elevated secretion of S100B protein from astrocytes as part of the physiological response to the injury, as well as to the physical damage of astrocytes and increased blood-brain barrier permeability.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for CL Plus 488 S100B antibody CL488-15146 | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 S100B antibody CL488-15146 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |