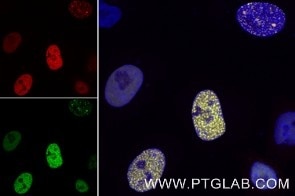
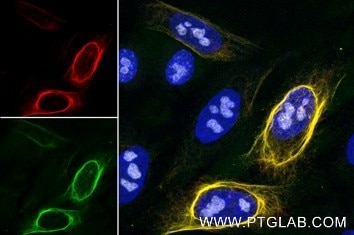
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
anti-RFP VHH/ Nanobody conjugated to fluorophore for IF, of mCherry and other red fluorescent protein-fusion proteins
| Description | The RFP-Booster stabilizes, enhances, and reactivates the signal of RFP-fusion proteins such as mCherry, mRFP, etc.. Due to its small size, the RFP-Booster enables higher image quality in epifluorescence, confocal, and super-resolution microscopy: • Considerably higher tissue penetration rates • Superior accessibility and labelling of epitopes in crowded cellular/organelle environments • Less than 2 nm epitope-label displacement minimizes linkage error • Monovalent VHHs do not cluster their epitopes • Validation: structure and function characterized • Consistent and reliable performance due to recombinant production |
| Applications | IF, (FC, WB) |
| Host | Alpaca |
| Specificity/Target | mCherry, mPlum, mRFP, mRFPruby, mKate2 For the complete list, please click here: Fluorescent protein specificity table antibodies |
| Conjugate | Alexa Fluor® 488 |
| Form | Liquid |
| Suggested Dilution | / |
| Type | Nanobody |
| Format | Alpaca single domain antibody, Nanobody or VHH; monovalent |
| Class | Recombinant |
| DOL | 2 fluorophores per Nanobody |
| RRID | / |
| Affinity (KD) | / |
| Excitation/ Emission | Excitation max: 490 nm, Emission max: 525 nm |
| Storage Buffer | 10 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 500 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, Preservative: 0.09% Sodium azide |
| Storage Condition | Shipped at ambient temperature. Store at -20°C. Protect from light. |
| Size | 10 μL; 50 μL |
| Note | This product is for research use only, not for diagnostic or therapeutic use |
Documentation
| SDS |
|---|
| rb2AF488_SDS_RFP-Booster Alexa Fluor® 488 (EN) |
| Datasheet |
|---|
| RFP-Booster Alexa Fluor® 488 Datasheet |
| RFP-TRAP Specificity |
|---|
| Fluorescent protein specificity table Nano-Booster |
| Brochure |
|---|
| Chromotek nanobodies brochure (PDF) |
Publications
| Application | Title |
|---|---|
Aging Cell Senescent Endothelial Cells in Cerebral Microcirculation Are Key Drivers of Age-Related Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption, Microvascular Rarefaction, and Neurovascular Coupling Impairment in Mice |