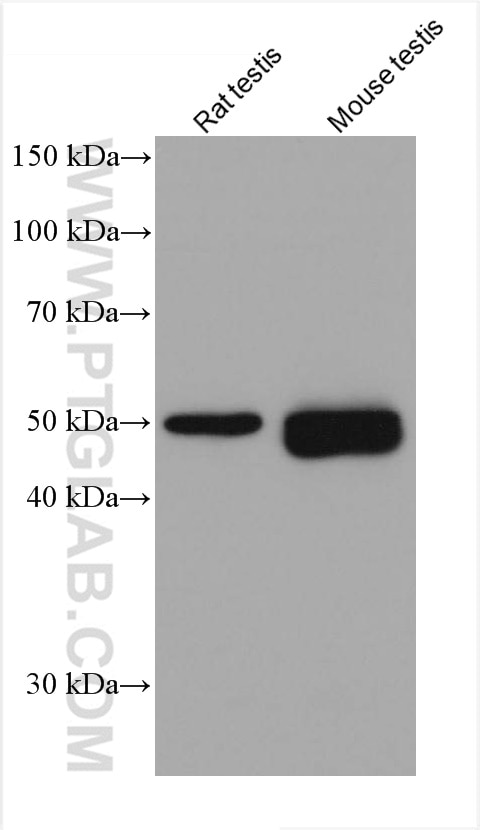
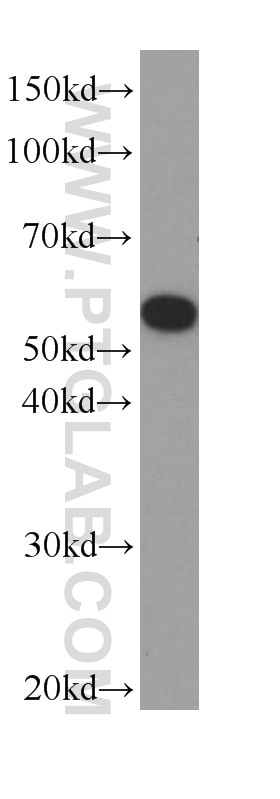
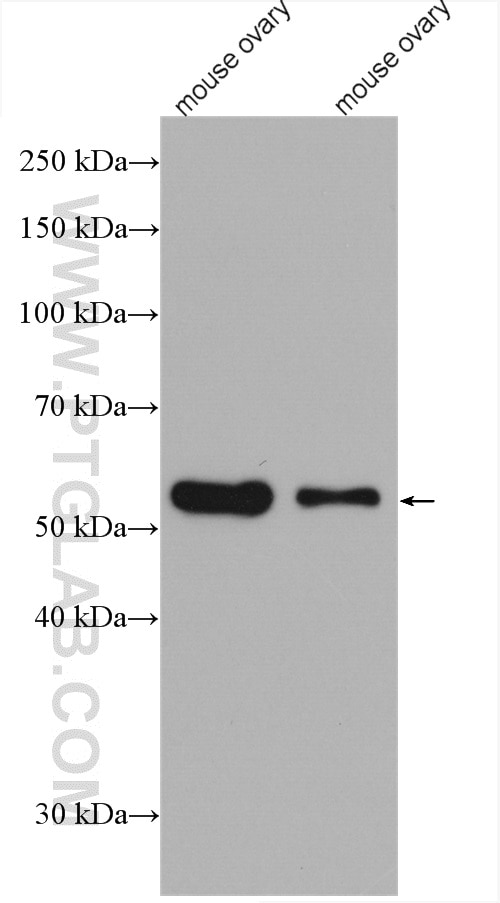
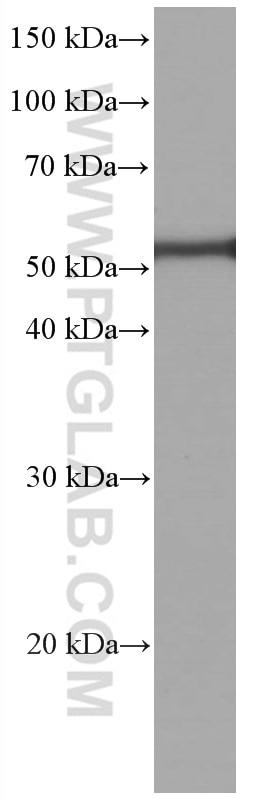
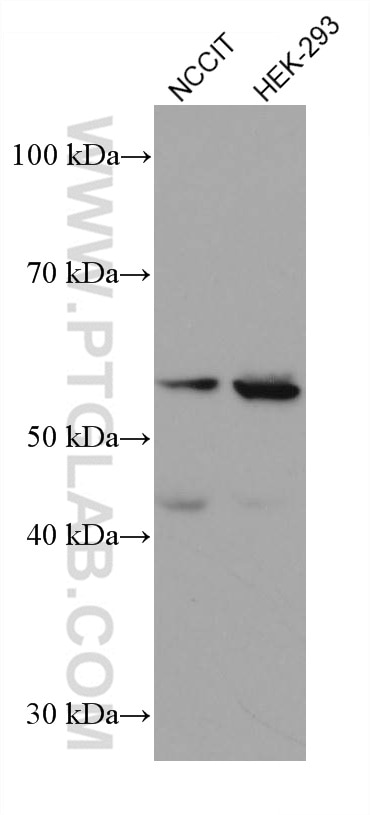
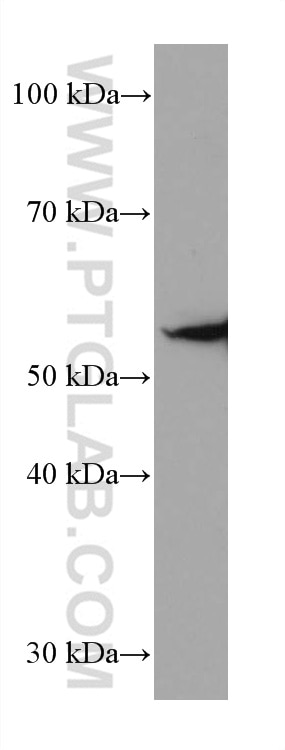
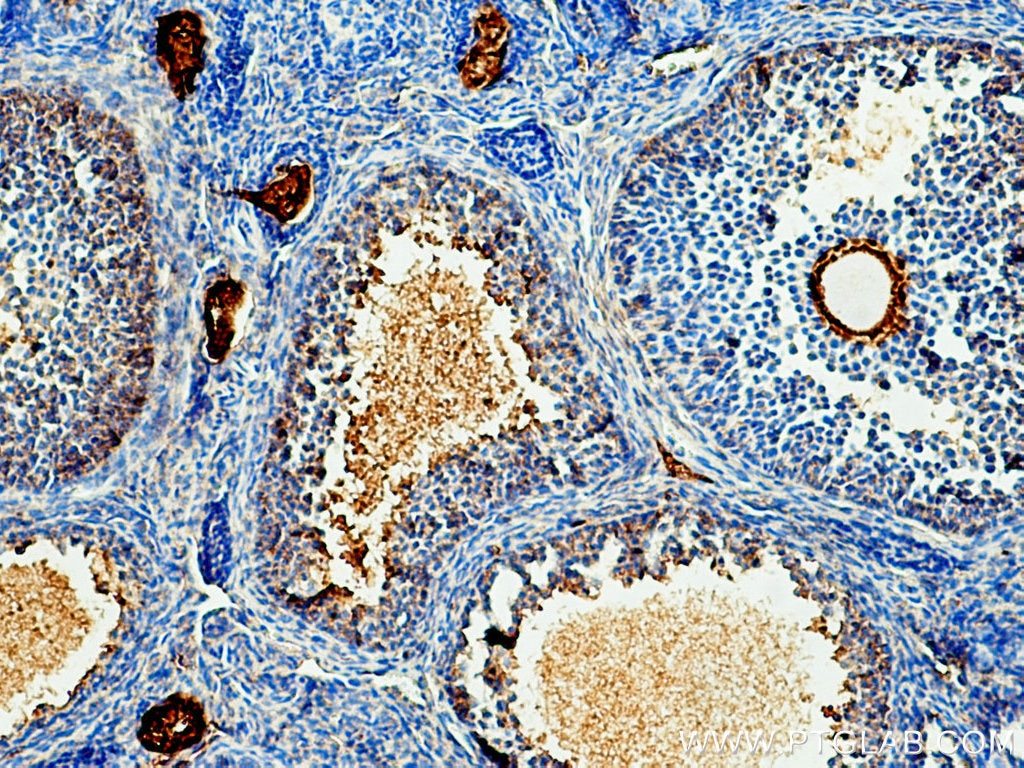
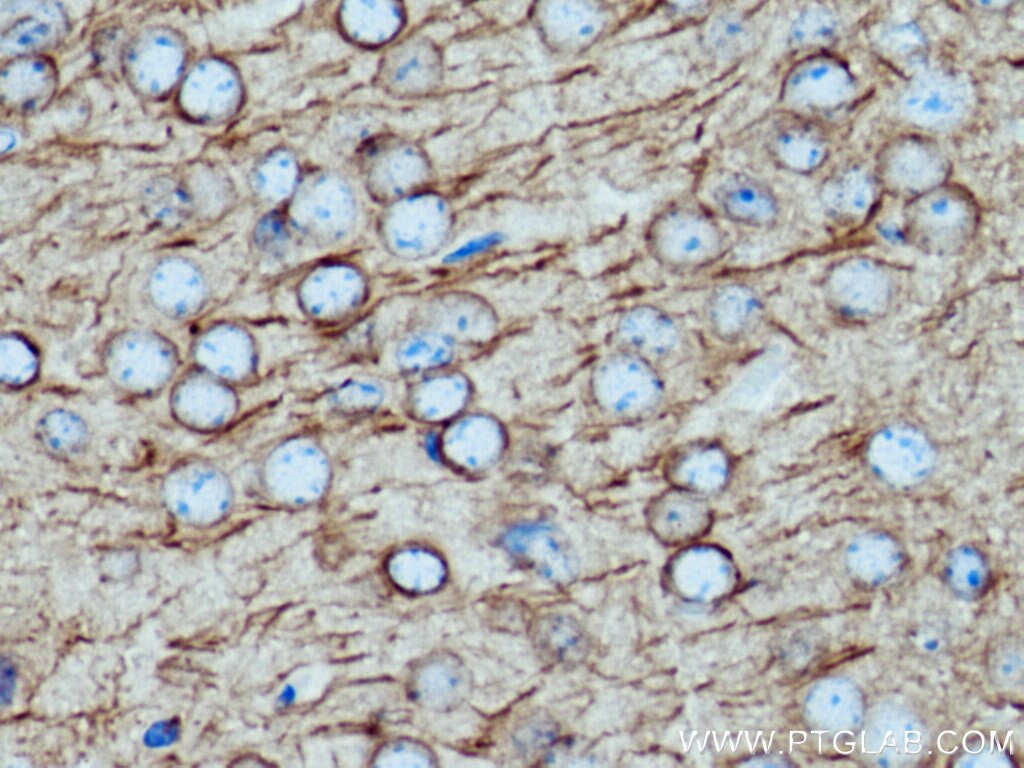
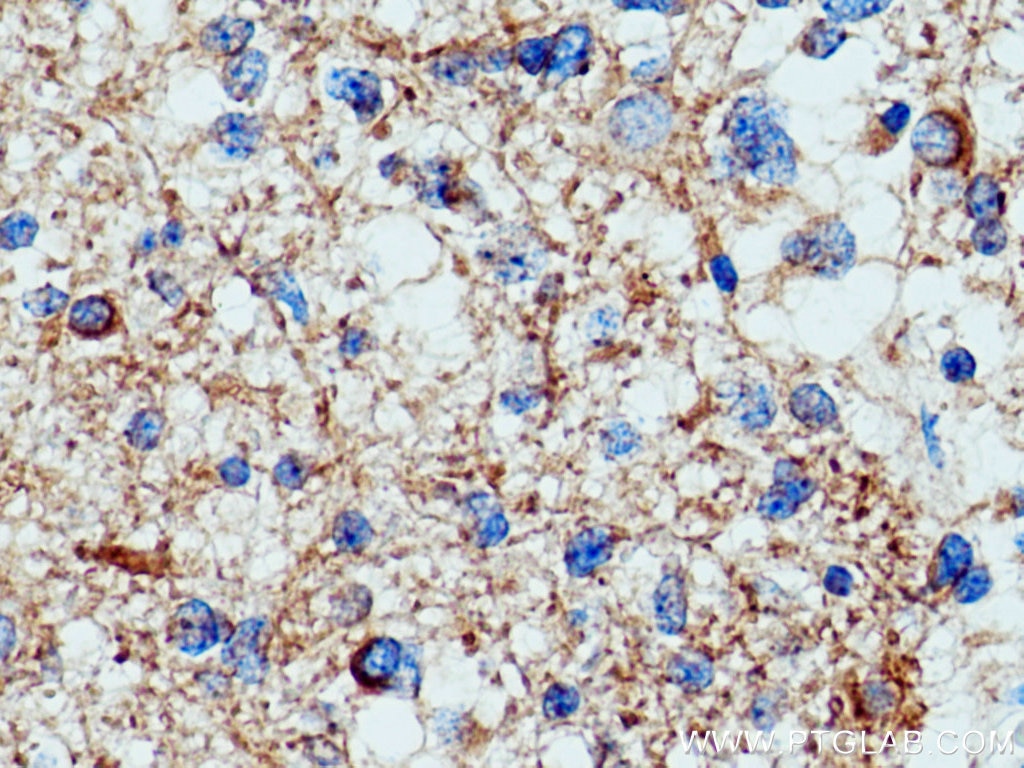
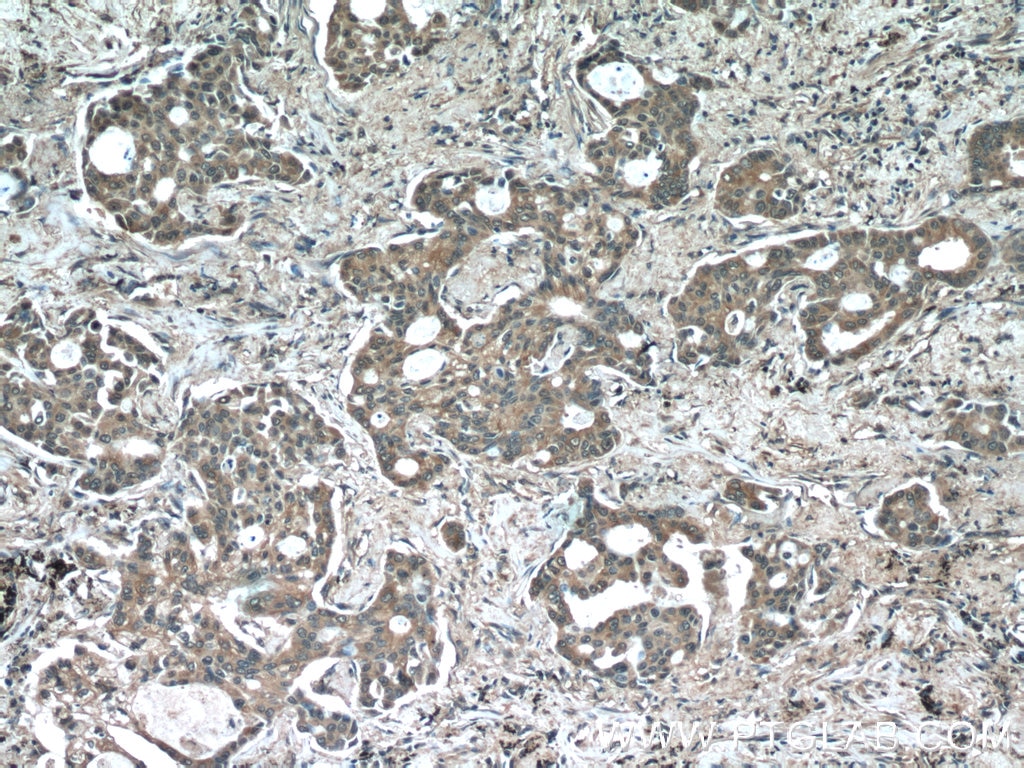
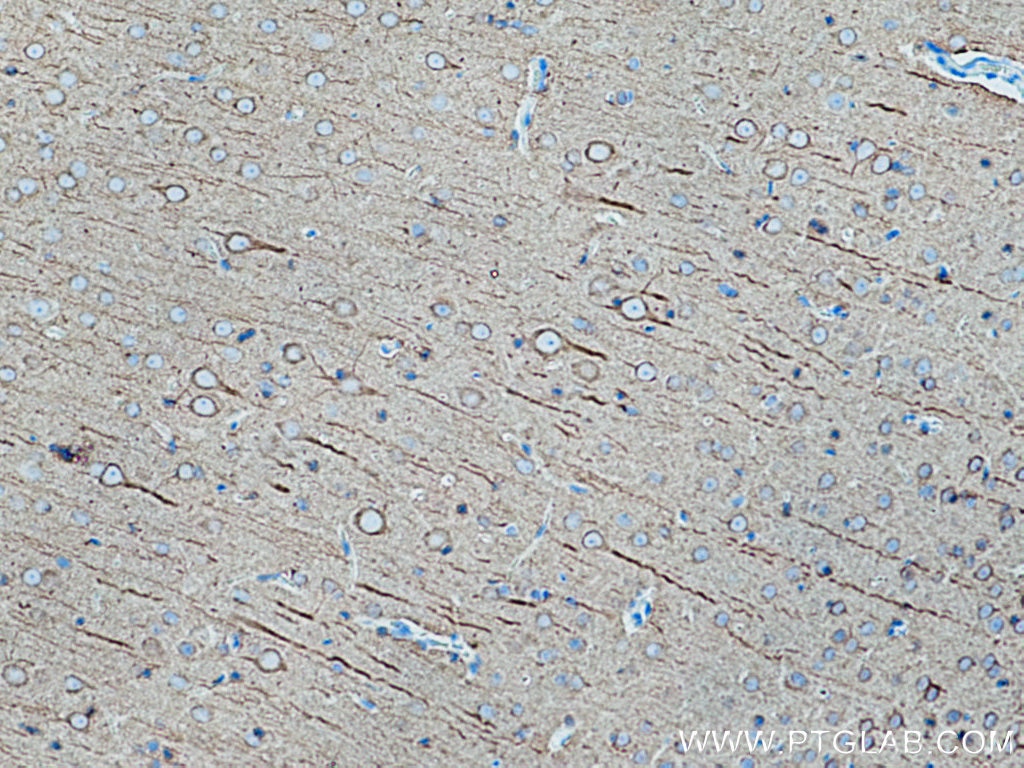
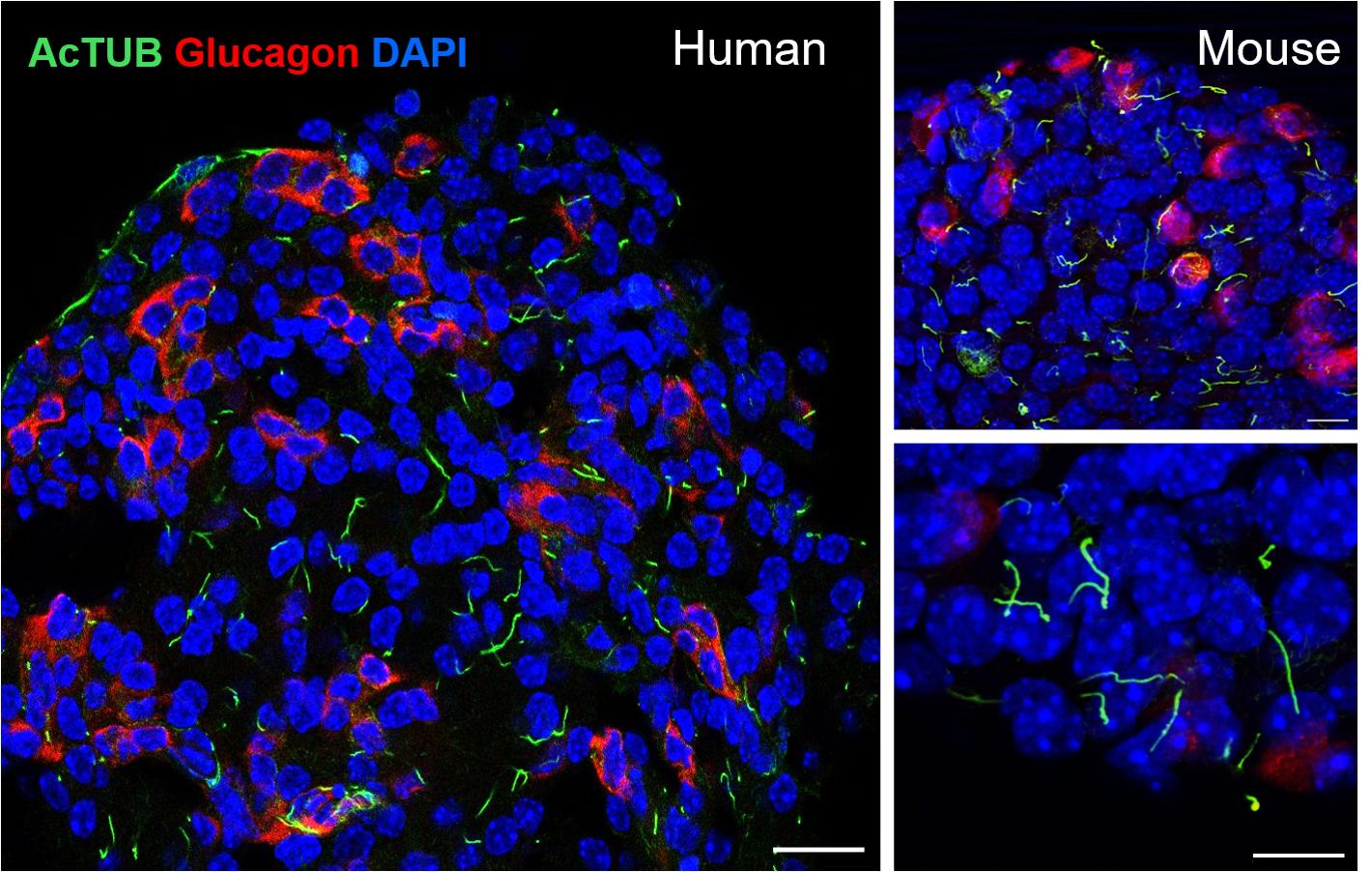
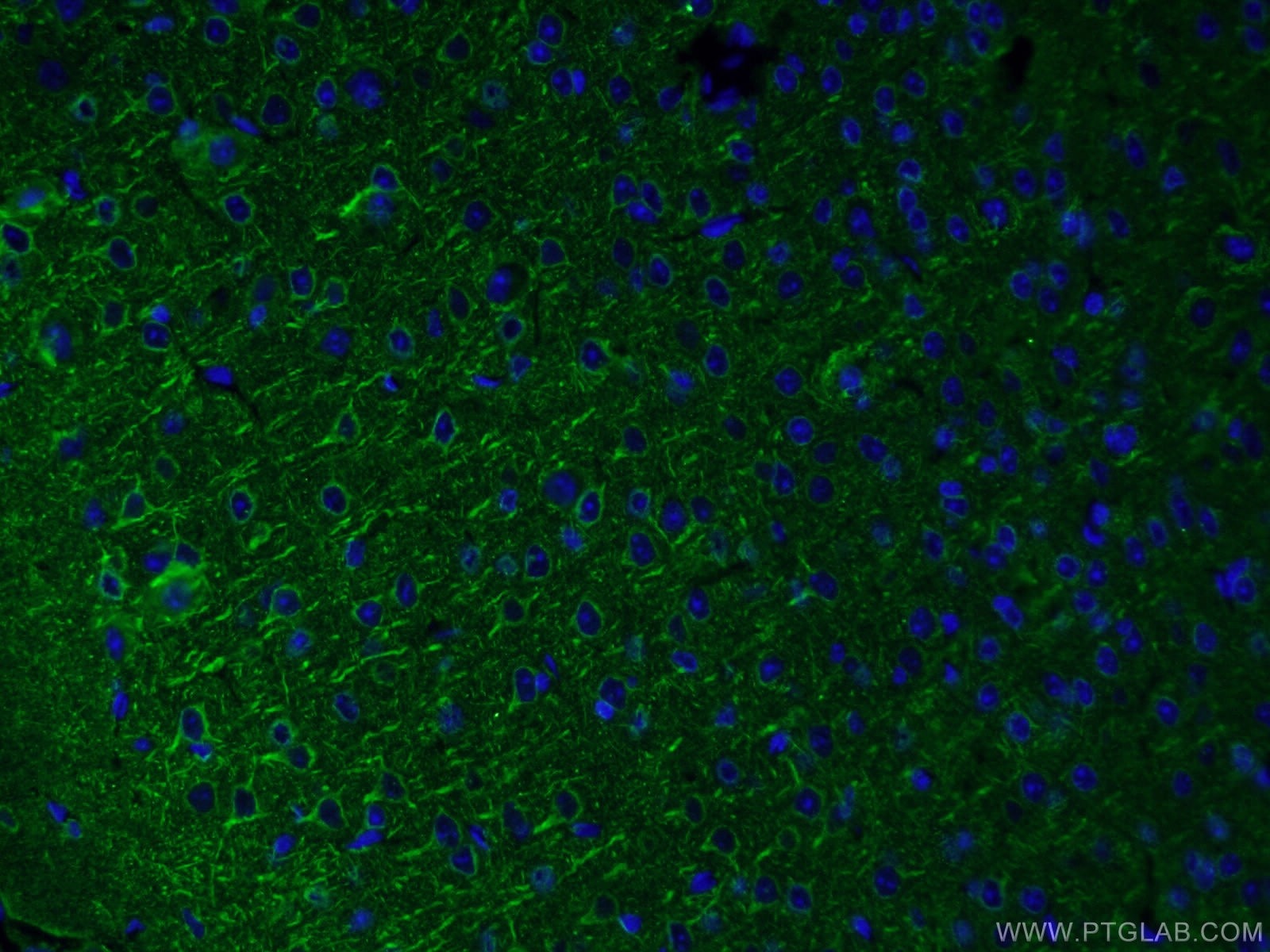
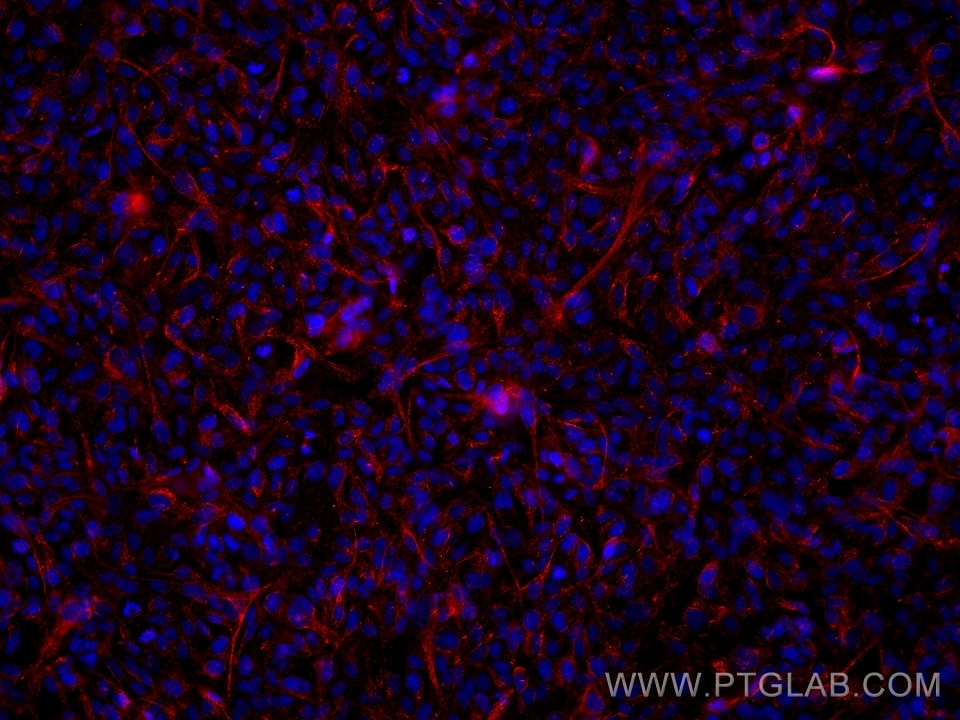
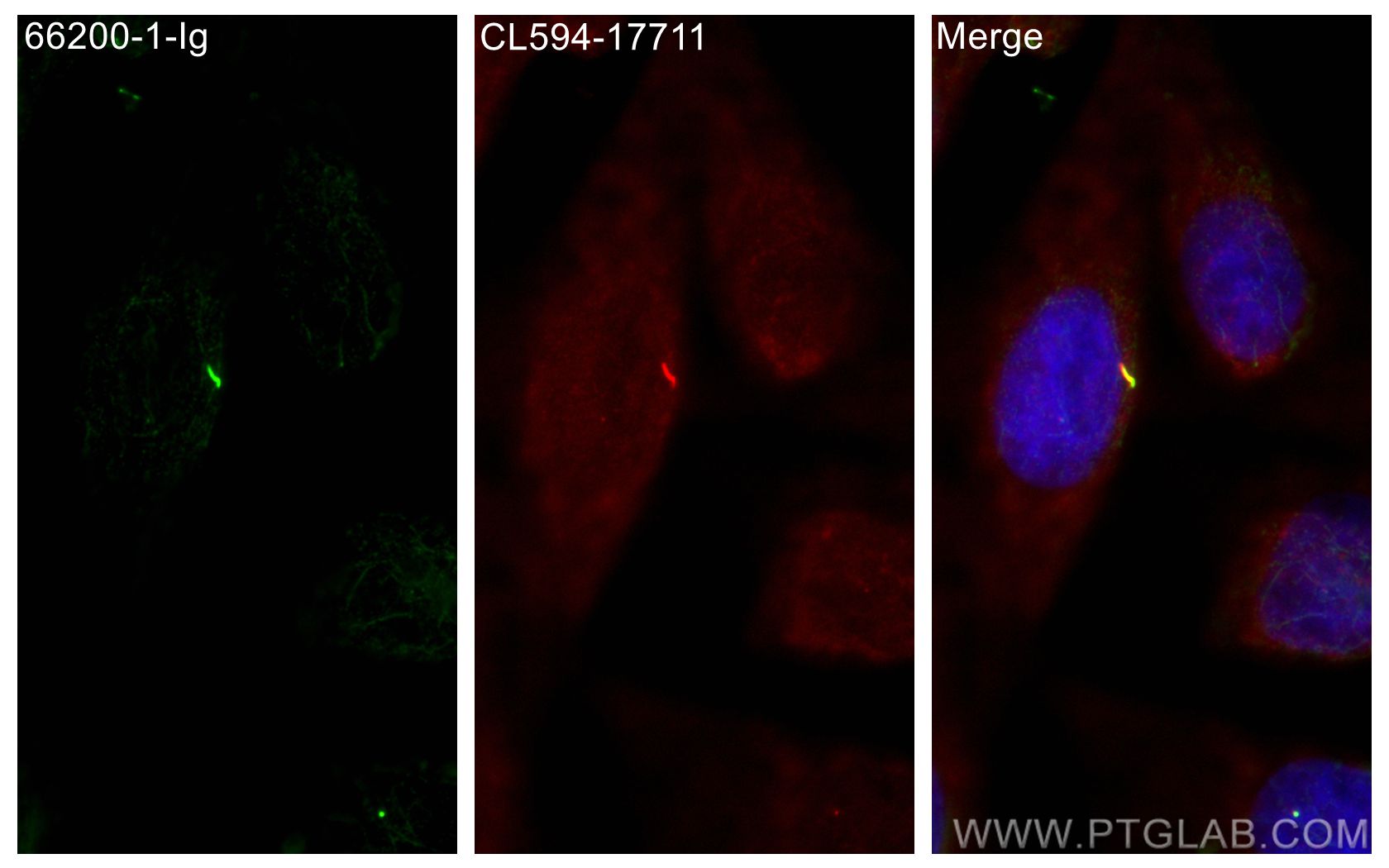
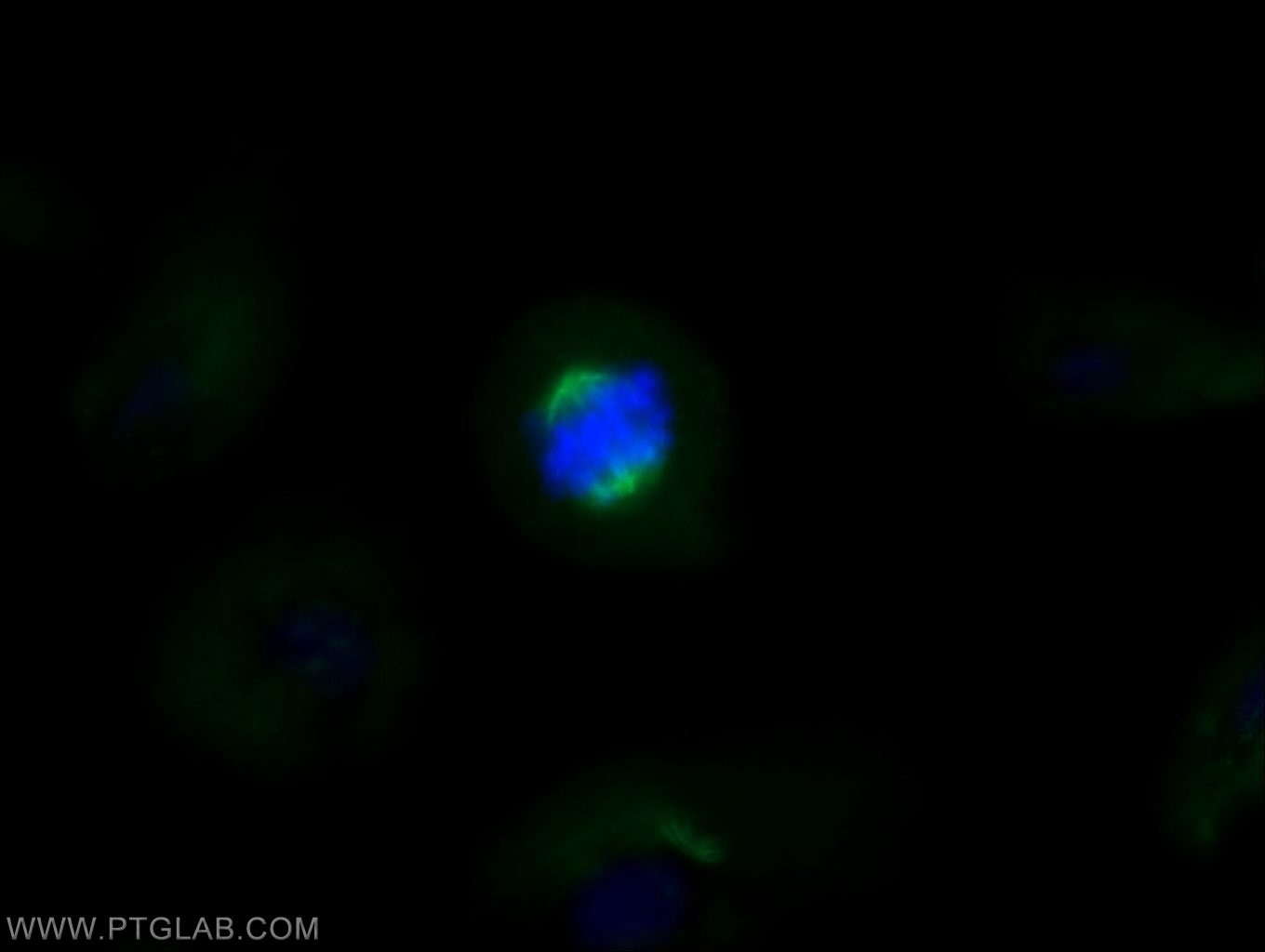
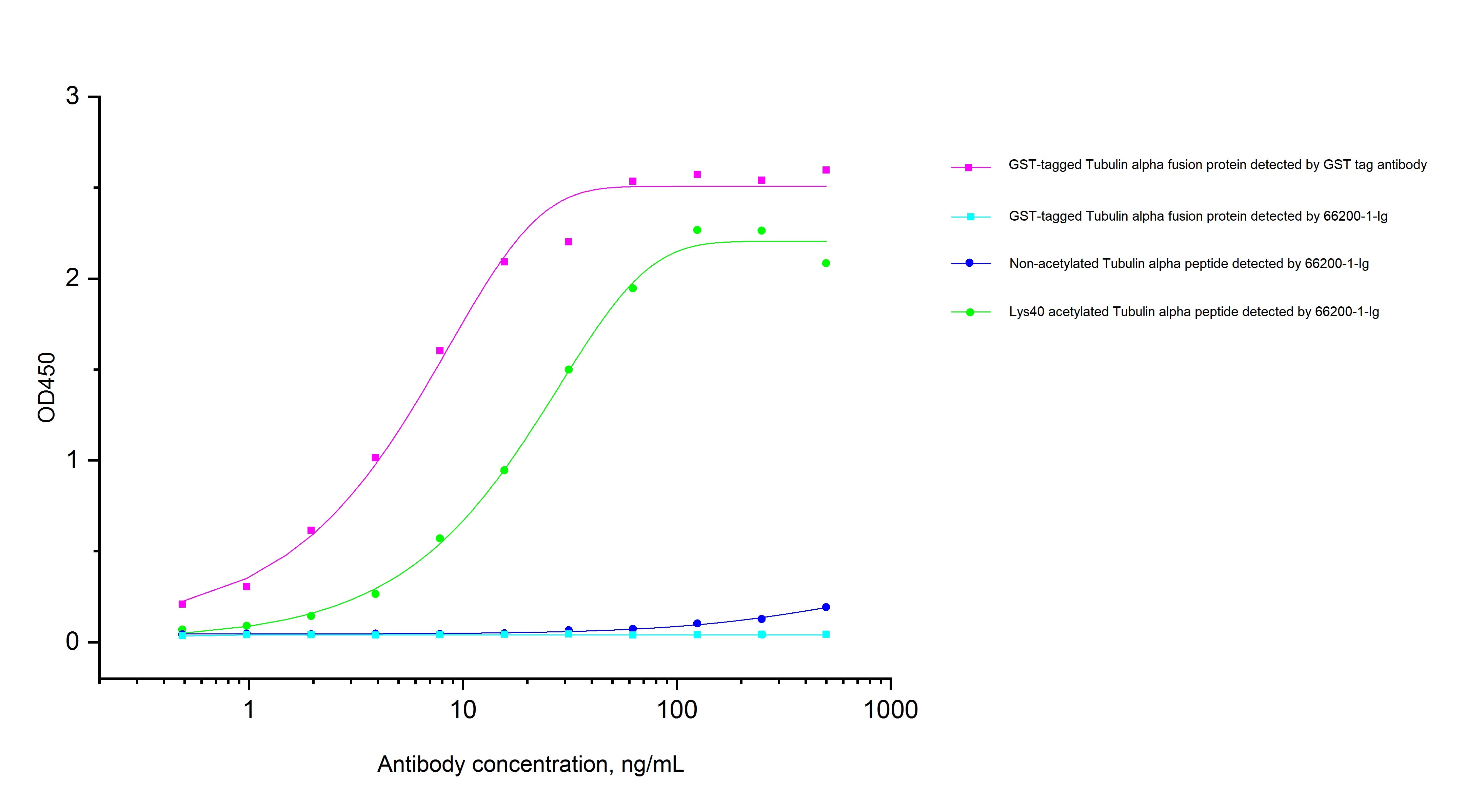
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66200-1-PBS targets Acetyl-Tubulin (Lys40) in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, pig, canine samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, canine |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | tubulin, alpha 1a |
| Calculated molecular weight | 52 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_006009 |
| Gene Symbol | Alpha Tubulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7846 |
| RRID | AB_2722562 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q71U36 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
What is the molecular weight of acetyl-α-tubulin?
The molecular weight of acetylated tubulin is 52 kD.
Where does the acetylation of Lys 40 occur?
This acetylation occurs inside the microtubule lumen by the α-tubulin acetyltransferase 1 (αTAT1) (PMID: 29207274).
How can acetylation be reversed?
Acetylation of Lys 40 can be reversed by deacetylase 6 (HDAC6), which is mostly cytoplasmic that also deacetylates Hsp90, and sirtuin 2 (SIRT2), which also mainly cytoplasmic and uses NAD as a coenzyme. Unlike HDAC6, SIRT uses both polymerized and soluble tubulin as substrates. Deacetylases are believed to be more active on soluble tubulin, while acetylases function preferentially on stable polymers (PMIDs: 29207274, 30079247, 19185337).
What is the function of acetylation?
Acetylation is a conserved post-translational modification of alpha tubulin at Lys 40 during tubulin assembly, and it correlates to increased microtubule stability and intracellular transport (PMIDs: 29207274, 30079247, 20940043).
Is acetylation of α-tubulin strictly associated with stable microtubules?
Not necessarily, as acetylation can have other effects on microtubule subpopulations (PMID 20940043).
Is ac-tubulin found only in cilia?
Acetylated-α-tubulin is located in cytoplasmic tubulin as well as in cilia; therefore, it is not strictly region-specific (PMID: 30079247).
What are the cellular effects of tubulin acetylation?
Microtubule acetylation seems to provide a critical role in neuronal development and function, and while its effect on cancer cells remains unclear, it has been shown that decreased acetylated α-tubulin impairs neuronal cell line migration. The post-translational modification may also help regulate organelle-independent signalling throughout the cell, supporting the notion of a microtubule network serving as a coordinator of cellular signaling (PMIDs: 29207274, 25503560, 20940043, 19185337).